Abstract
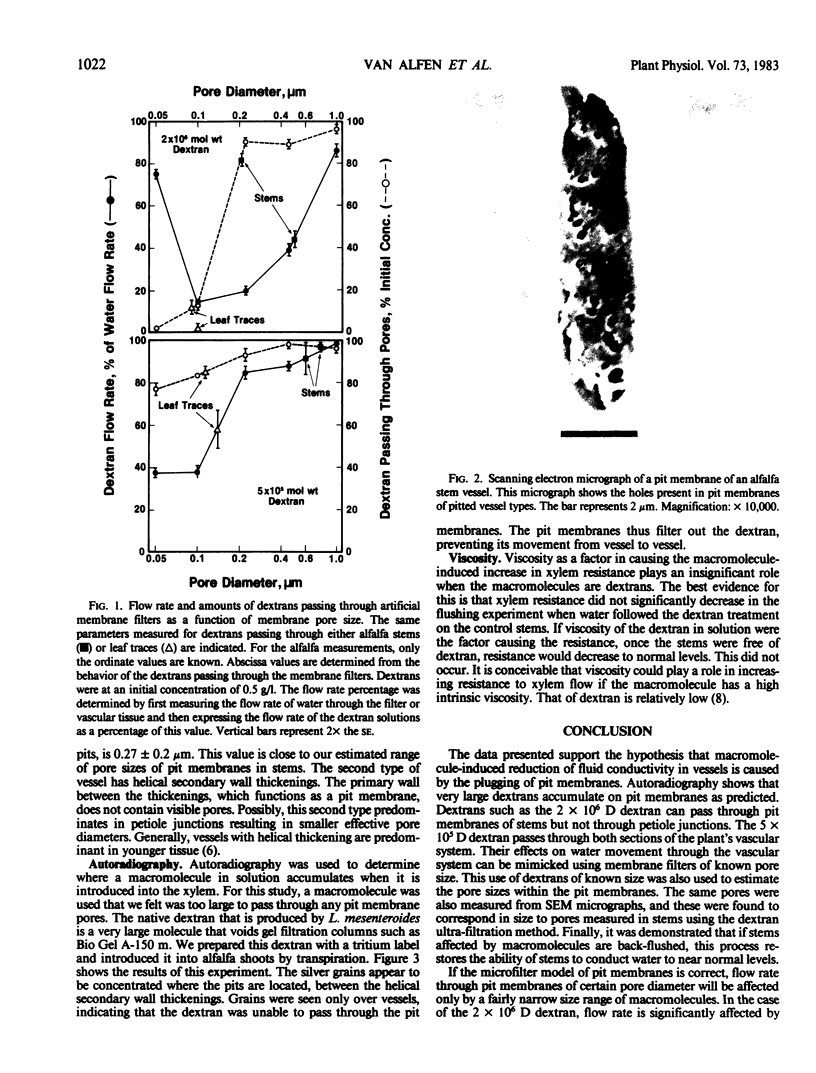
Macromolecules present in low concentrations in xylem fluid of Medicago sativa L. var DuPuits will increase the resistance to xylem liquid flow. This increase in resistance was found to be reversible by backflushing the xylem. Autoradiography showed that very large molecules do not pass through pit membrane pores. A comparison of pit membrane pore sizes to molecule sizes suggests that increased resistance to xylem flow is a result of plugging pit membrane pores. It was also found that pit membranes located in two parts of the plant differ in the apparent diameter of their pores and, thus, in their susceptibility to plugging by macromolecules. Macromolecules in xylem fluid may result from hostparasite interactions and may play a significant role in the outcome of the interaction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carpita N., Sabularse D., Montezinos D., Delmer D. P. Determination of the pore size of cell walls of living plant cells. Science. 1979 Sep 14;205(4411):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.205.4411.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokrovskaia T. G., Asinovskaia N. K., Mozhenok T. P., Nemchinskaia V. L. Sintez NAD+ v izolirovannykh iadrakh kletok pochek sobak posle vnutrivennogo vvedeniia amfoteritsina B. Tsitologiia. 1979 Aug;21(8):942–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Alfen N. K., Allard-Turner V. Susceptibility of plants to vascular disruption by macromolecules. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jun;63(6):1072–1075. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.6.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Alfen N. K., Turner N. C. Changes in Alfalfa Stem Conductance Induced by Corynebacterium insidiosum Toxin. Plant Physiol. 1975 Mar;55(3):559–561. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]