Abstract
Two selections of bread wheat, Triticum aestivum L., differing in their relative salt resistance, were grown in salinized solution culture, and relative growth rates, osmotic adjustment, ion accumulation, and photosynthesis were monitored to study the responses of the plants to salinity.
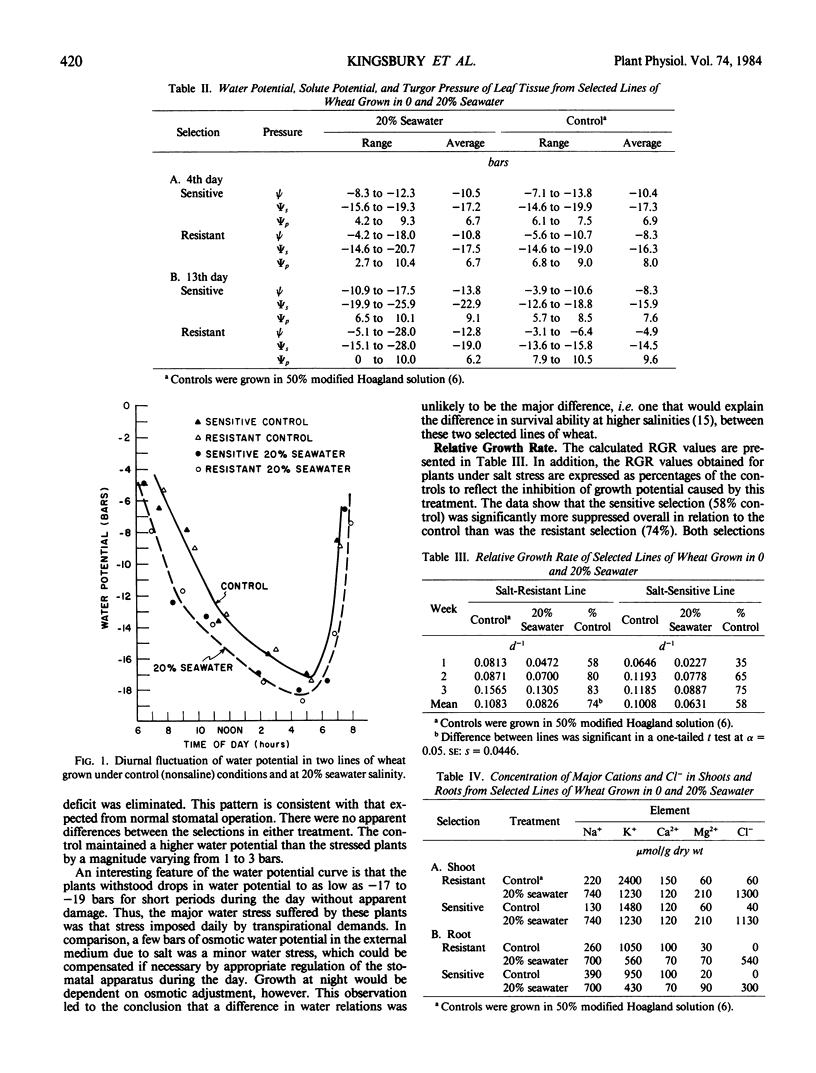
Differences in water relations were minimal and were only apparent for 3 days following salinization. The lines differed substantially in their relative growth rates and photosynthetic responses for several weeks following salinization, despite full osmotic adjustment. Concentrations of major cations and Cl− in the plant organs were remarkably similar in both lines, indicative of minimal differences in gross ion absorption and translocation.
The authors interpret these results to suggest that the major difference between these two lines of wheat was their response to specific ion effects, at the level of the organ, tissue, cell, and subcellular entities. Superior compartmentation of toxic ions by the more salt-tolerant line, presumably in the vacuole, might have enabled it to maintain its cytoplasmic metabolic apparatus in a stabler and more nearly normal state than the sensitive line was able to do; a measure of true cytoplasmic toleration of salt may also be a factor.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Epstein E., Norlyn J. D., Rush D. W., Kingsbury R. W., Kelley D. B., Cunningham G. A., Wrona A. F. Saline culture of crops: a genetic approach. Science. 1980 Oct 24;210(4468):399–404. doi: 10.1126/science.210.4468.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. The essential role of calcium in selective cation transport by plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1961 Jul;36(4):437–444. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholander P. F., Bradstreet E. D., Hemmingsen E. A., Hammel H. T. Sap Pressure in Vascular Plants: Negative hydrostatic pressure can be measured in plants. Science. 1965 Apr 16;148(3668):339–346. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3668.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twente J. W., Twente J. A. Regulation of hibernating periods by temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1044–1051. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


