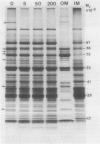
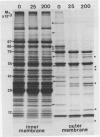
Abstract
Several proteases, i.e., pronase, a mixture of trypsin and chymotrypsin, and thermolysin were screened as potential surface probes of isolated intact pea (Pisum sativum var Laxton's Progress No. 9) chloroplasts. Of these, only thermolysin met the criteria of a suitable probe. Thermolysin destroyed outer envelope polypeptides, but did not affect inner envelope polypeptides, envelope permeability properties or such chloroplast activities as metabolite transport and O2 evolution.
Full text
PDF
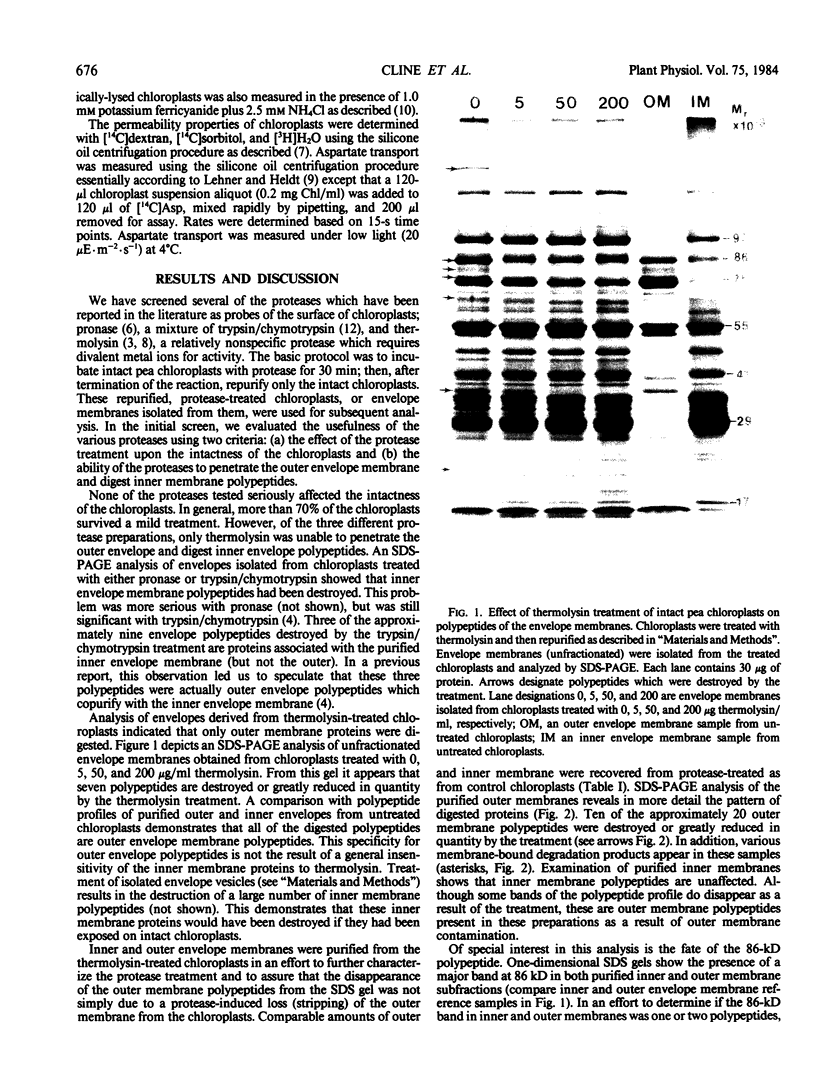
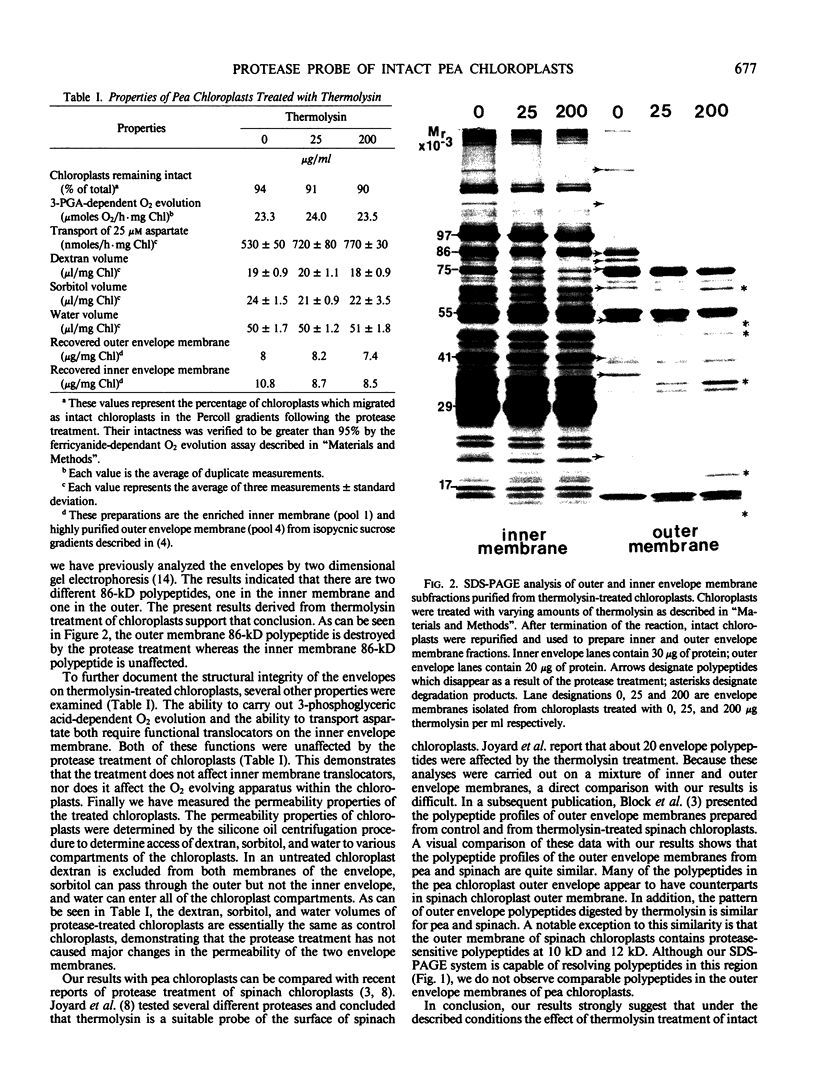

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. A., Dorne A. J., Joyard J., Douce R. Preparation and characterization of membrane fractions enriched in outer and inner envelope membranes from spinach chloroplasts. I. Electrophoretic and immunochemical analyses. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13273–13280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Andrews J., Mersey B., Newcomb E. H., Keegstra K. Separation and characterization of inner and outer envelope membranes of pea chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3595–3599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish L., Franceschi V. R., Stocking C. R. Effects of pronase on isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1979 Dec;64(6):1012–1014. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.6.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyard J., Billecocq A., Bartlett S. G., Block M. A., Chua N. H., Douce R. Localization of polypeptides to the cytosolic side of the outer envelope membrane of spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10000–10006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner K., Heldt H. W. Dicarboxylate transport across the inner membrane of the chloroplast envelope. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 13;501(3):531–544. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Cline K., Keegstra K. Analysis of pea chloroplast inner and outer envelope membrane proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and their comparison with stromal proteins. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):569–575. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]