Abstract
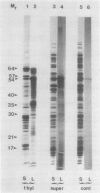
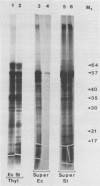
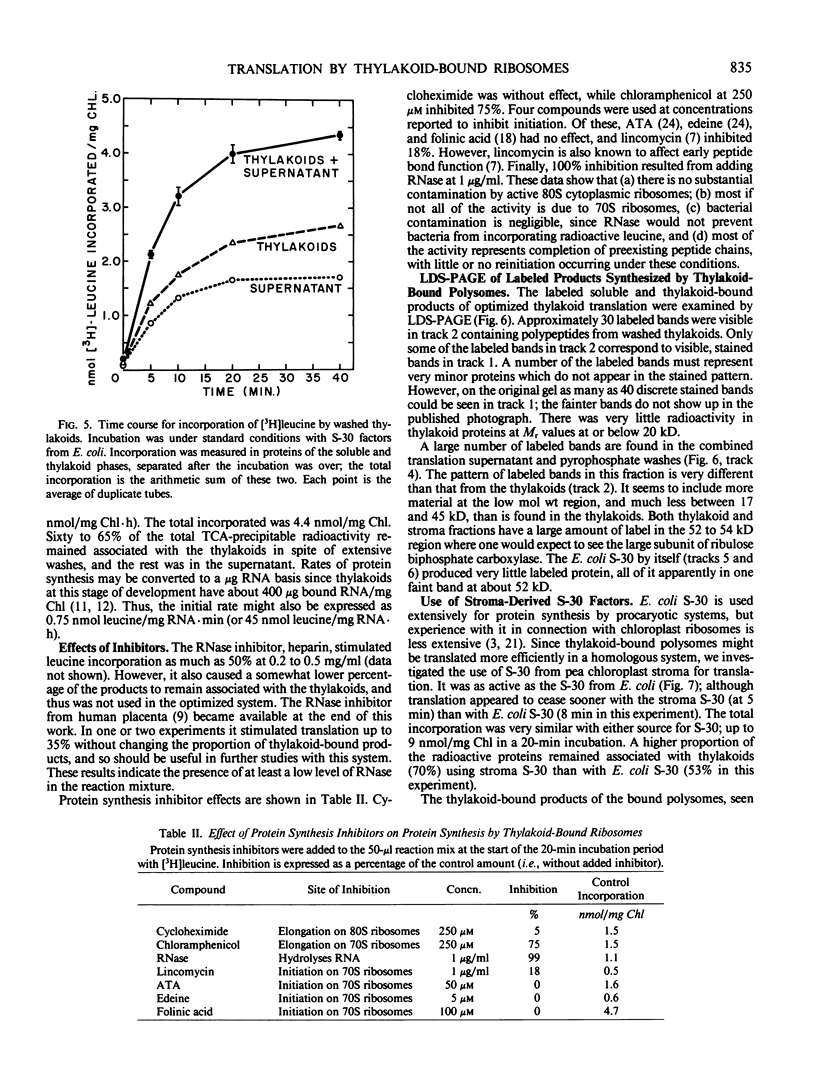
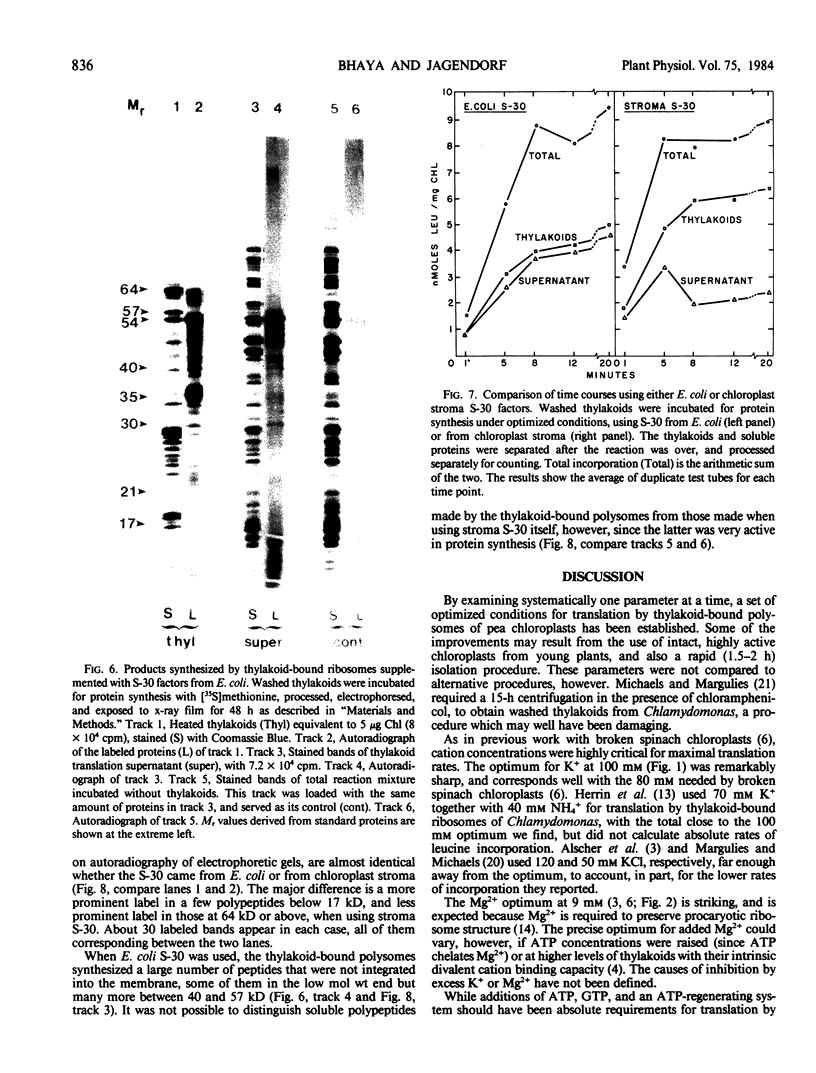
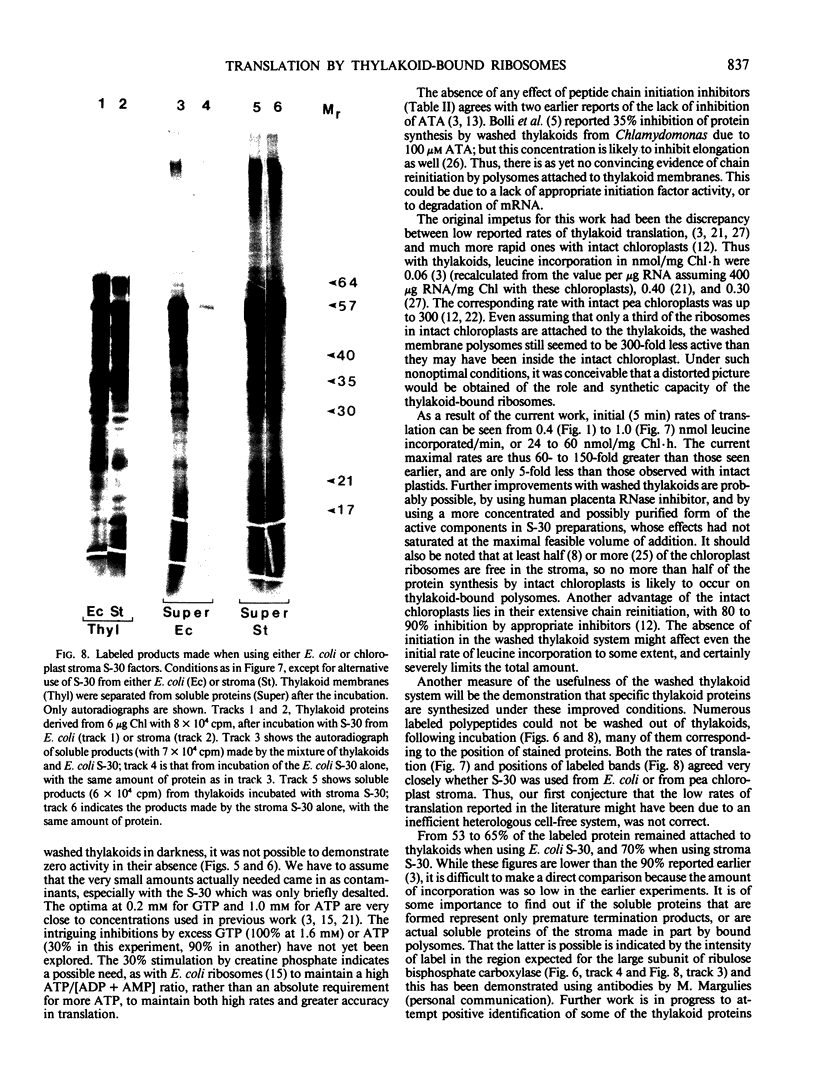
Polysomes bound to washed thylakoids from pea Pisum sativum cv Progress No. 9 chloroplasts are capable of protein synthesis when supplemented with amino acids, ATP and a regenerating system, GTP, and soluble factors required for translation. The extent of protein synthesis in previous reports, however, was quite low when compared to in organello translation. By systematic testing of parameters in the isolation of thylakoids and reaction mixture components we have been able to establish more optimal conditions. Incorporation of 2 to 10 nanomoles of leucine per milligram chlorophyll in a 20-minute reaction period is now possible, representing a 10- to 60-fold increase over amounts previously reported. Autoradiographs of solubilized, electrophoresed membranes show about 30 discrete labeled polypeptides which remain associated with the thylakoid membranes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham A. K., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Fidelity of protein synthesis in vitro is increased in the presence of spermidine. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alscher R., Patterson R., Jagendorf A. T. Activity of Thylakoid-bound Ribosomes in Pea Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):88–93. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli R., Mendiola-Morgenthaler L., Boschetti A. Isolation and characterization of polysomes from thylakoid membranes of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 27;653(2):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Spencer D., Whitfeld P. R. Protein synthesis in isolated spinach chloroplasts: comparison of light-driven and ATP-driven synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):106–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. J., Cundliffe E. Bacterial-protein synthesis. A novel system for studying antibiotic action in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 3;37(3):570–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Wildman S. G. "Free" and membrane-bound ribosomes, and nature of products formed by isolated tobacco chloroplasts incubated for protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 21;209(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90677-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler D. C., Tatar T. F., Lasater L. S. Effect of human placental ribonuclease inhibitor in cell-free ribosomal RNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 30;101(2):396–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish L. E., Jagendorf A. T. High rates of protein synthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):1107–1114. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish L. E., Jagendorf A. T. Light-induced increase in the number and activity of ribosomes bound to pea chloroplast thylakoids in vivo. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):814–824. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish L., Jagendorf A. T. A method for enzymic extraction and the measurement of chloroplast RNA. Plant Physiol. 1980 Apr;65(4):746–750. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.4.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Kakegawa T., Hirose S. Stabilization of 30 S ribosomal subunits of Bacillus subtilis W168 by spermidine and magnesium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 31;697(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelenc P. C., Kurland C. G. Nucleoside triphosphate regeneration decreases the frequency of translation errors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3174–3178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Translational control of protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:39–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini G., Bianchetti R. Initiation of protein synthesis in isolated mitochondria and chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 27;608(1):54–61. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M. M., Michaels A. Free and membrane-bound chloroplast polyribosomes Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 1;402(3):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels A., Margulies M. M. Amino acid incorporation into protein by ribosomes bound to chloroplast thylakoid membranes: formation of discrete products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 16;390(3):352–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao K. L., Jagendorf A. T. The ratio of free to membrane-bound chloroplast ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 14;324(4):518–532. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Burke J., Autz G., Jagendorf A. T. Bound Ribosomes of Pea Chloroplast Thylakoid Membranes: Location and Release in Vitro by High Salt, Puromycin, and RNase. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):940–949. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]