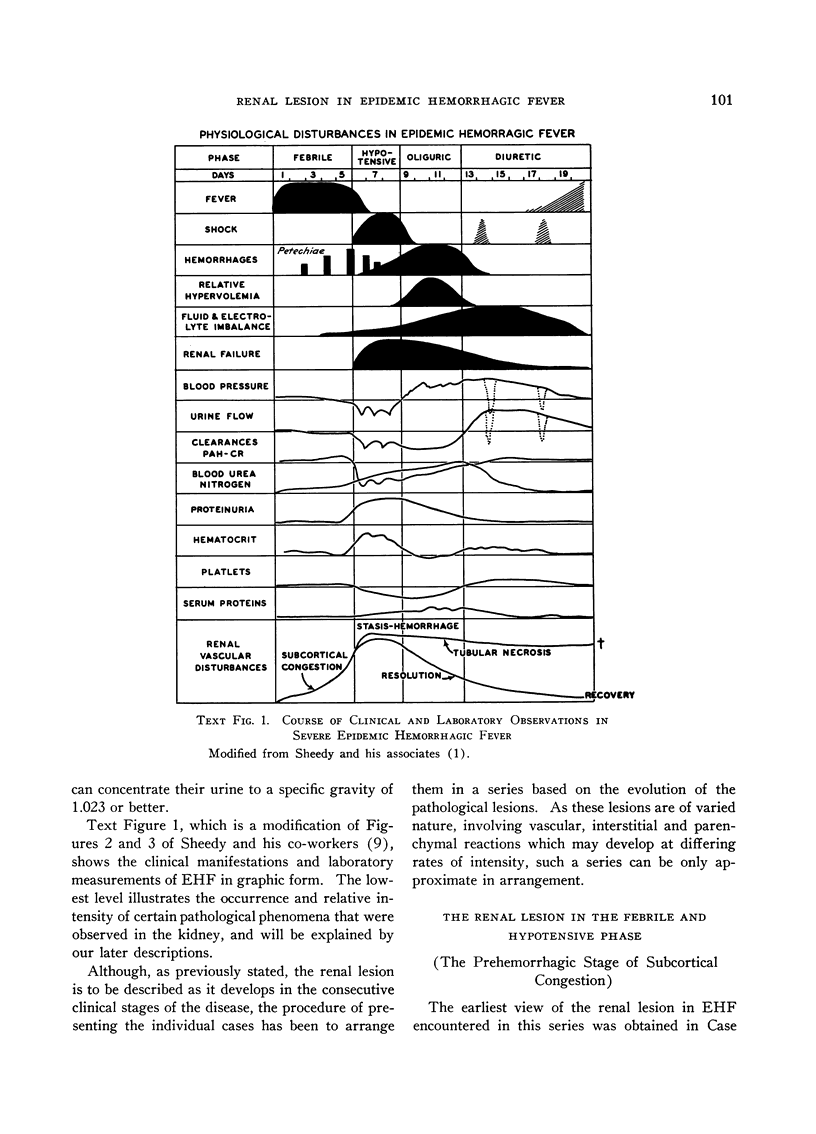
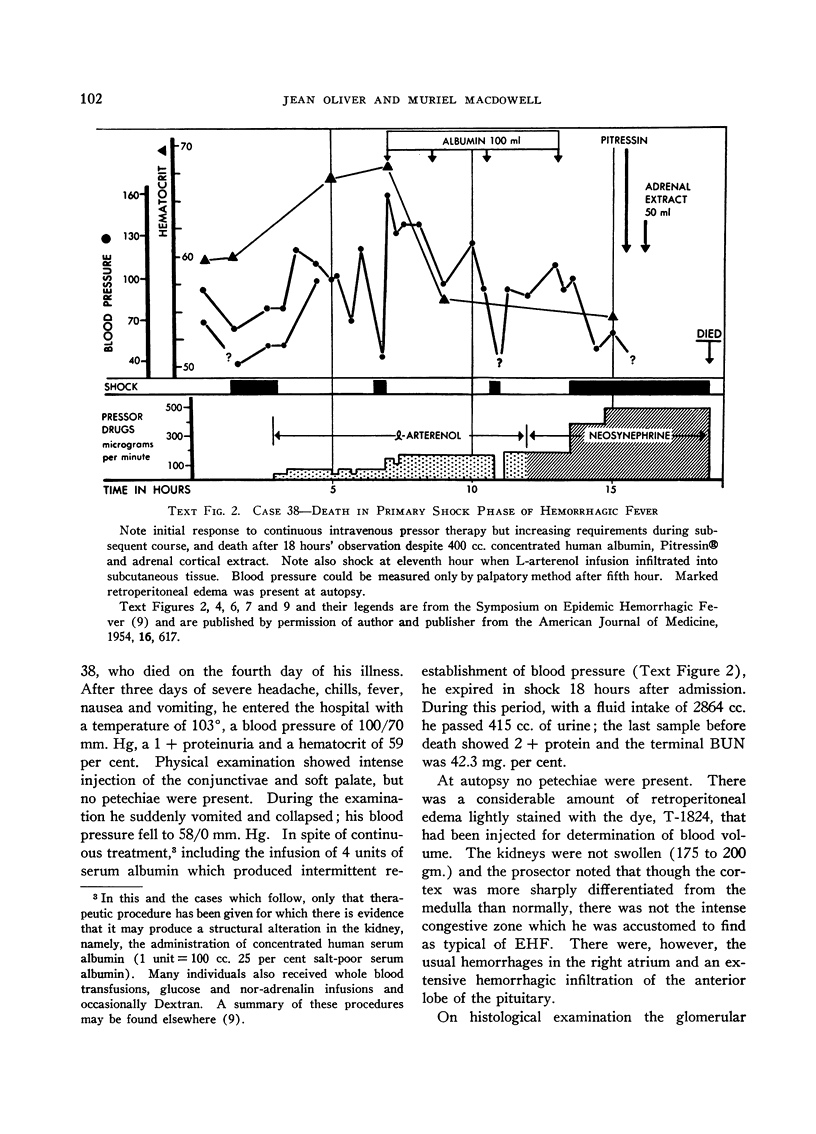
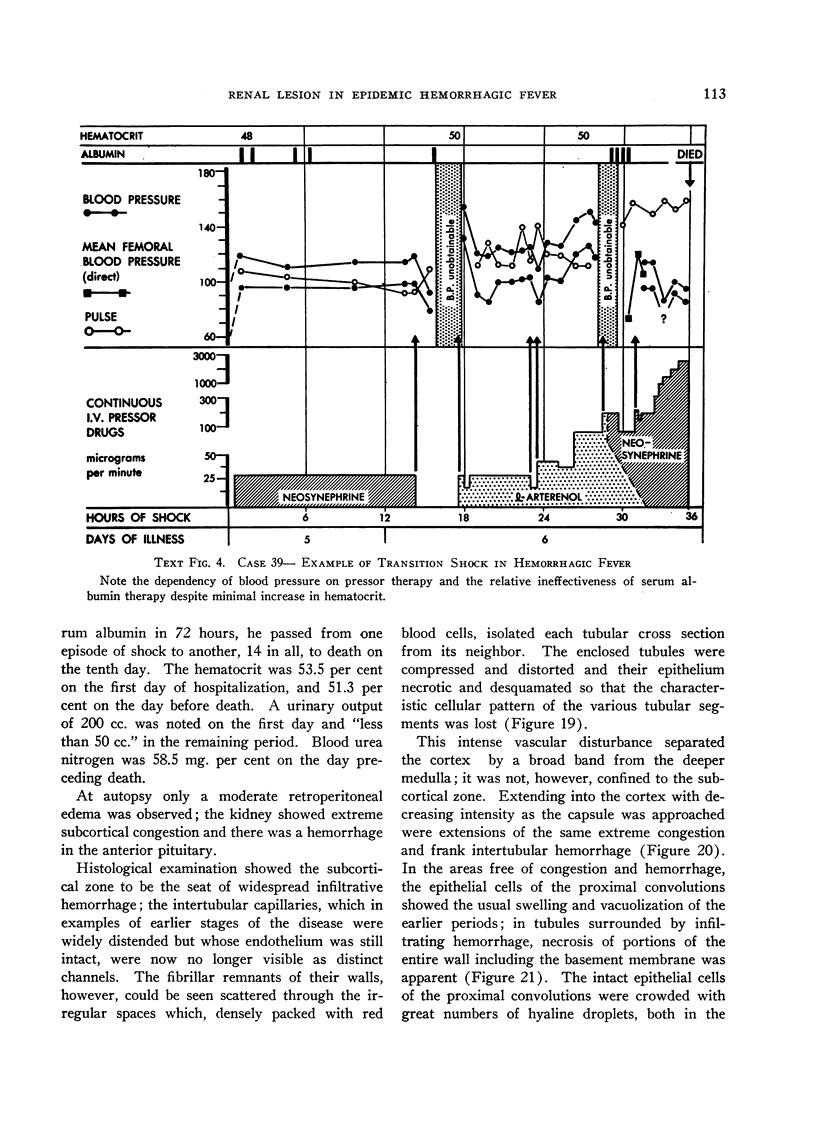
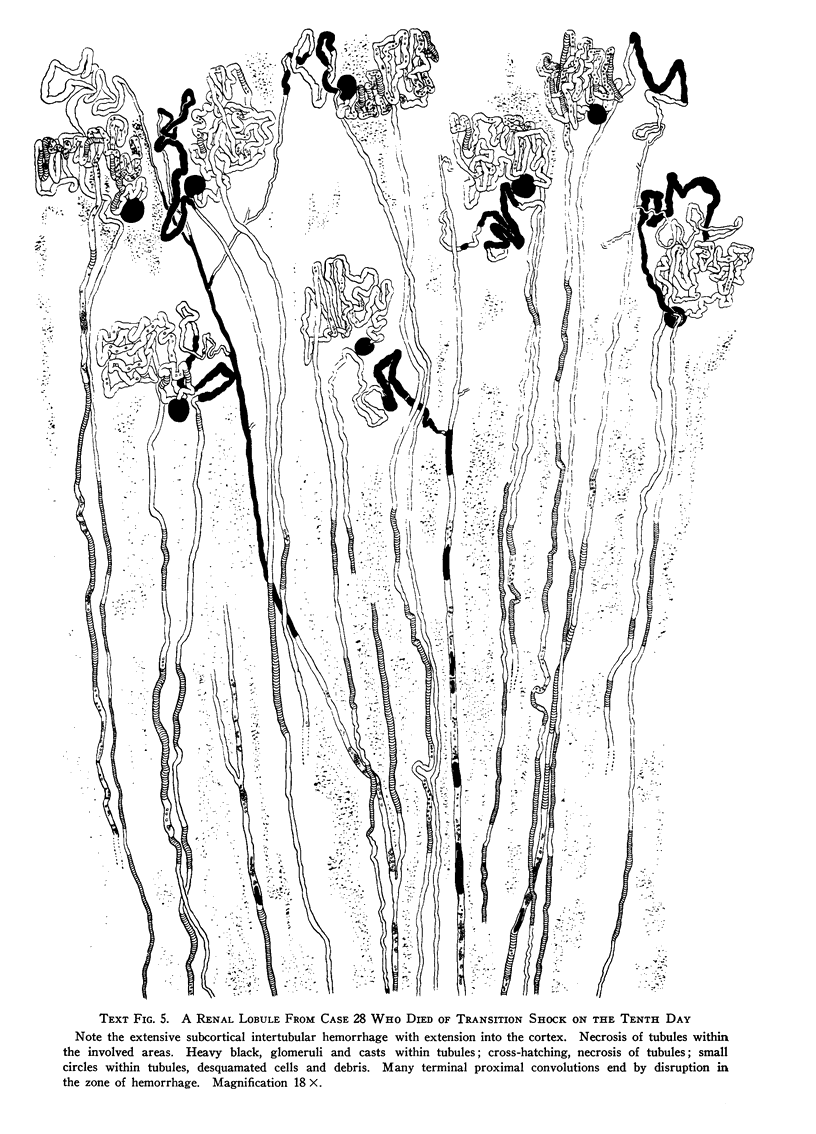
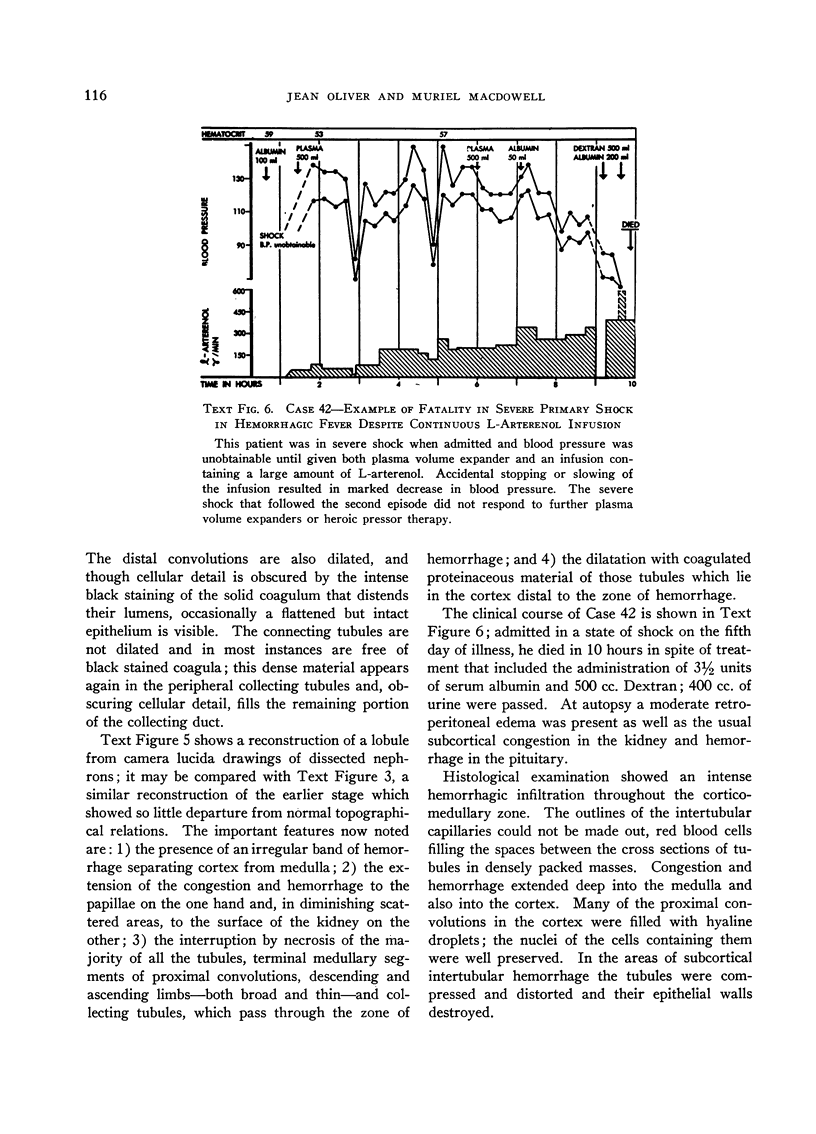
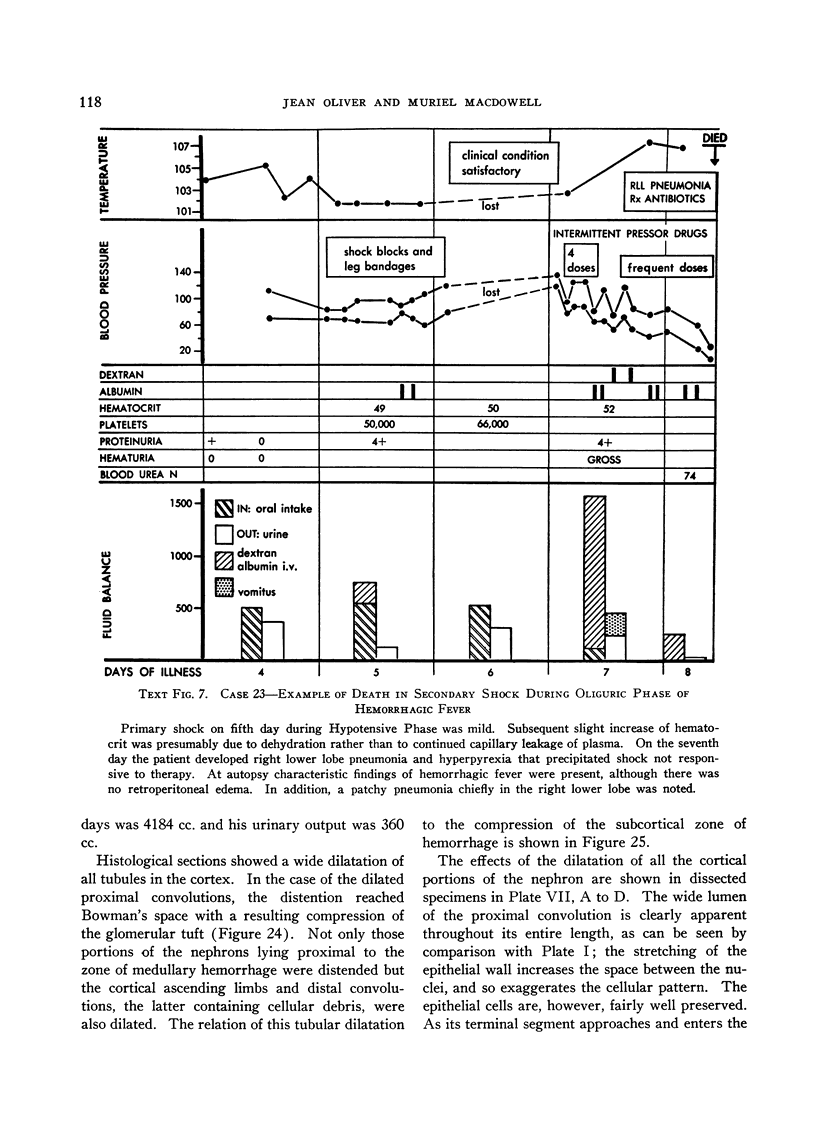
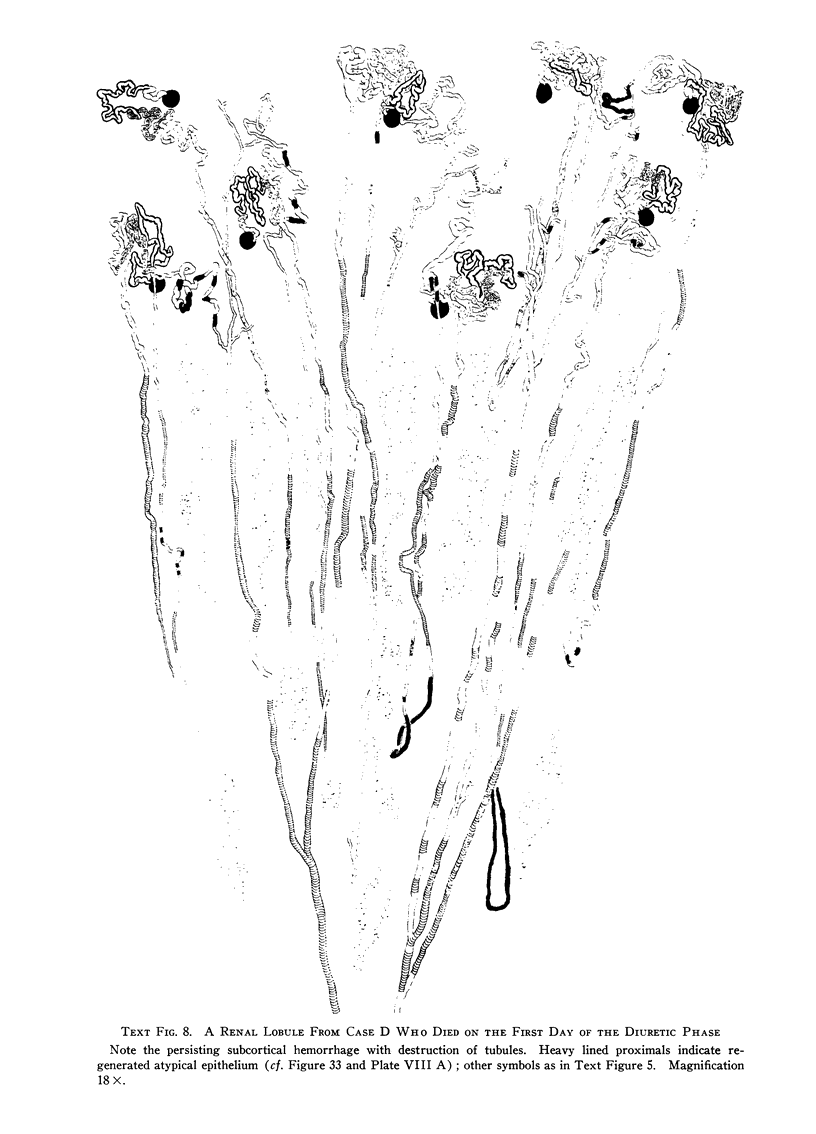
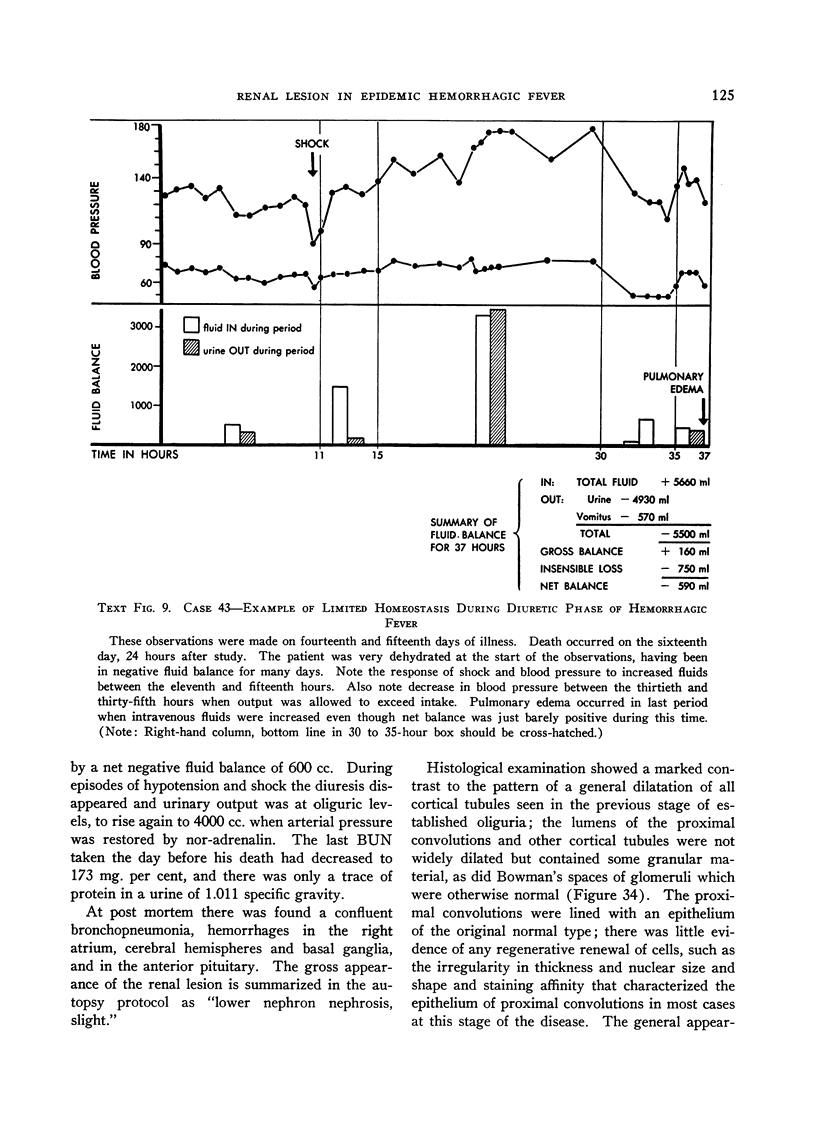
Full text
PDF
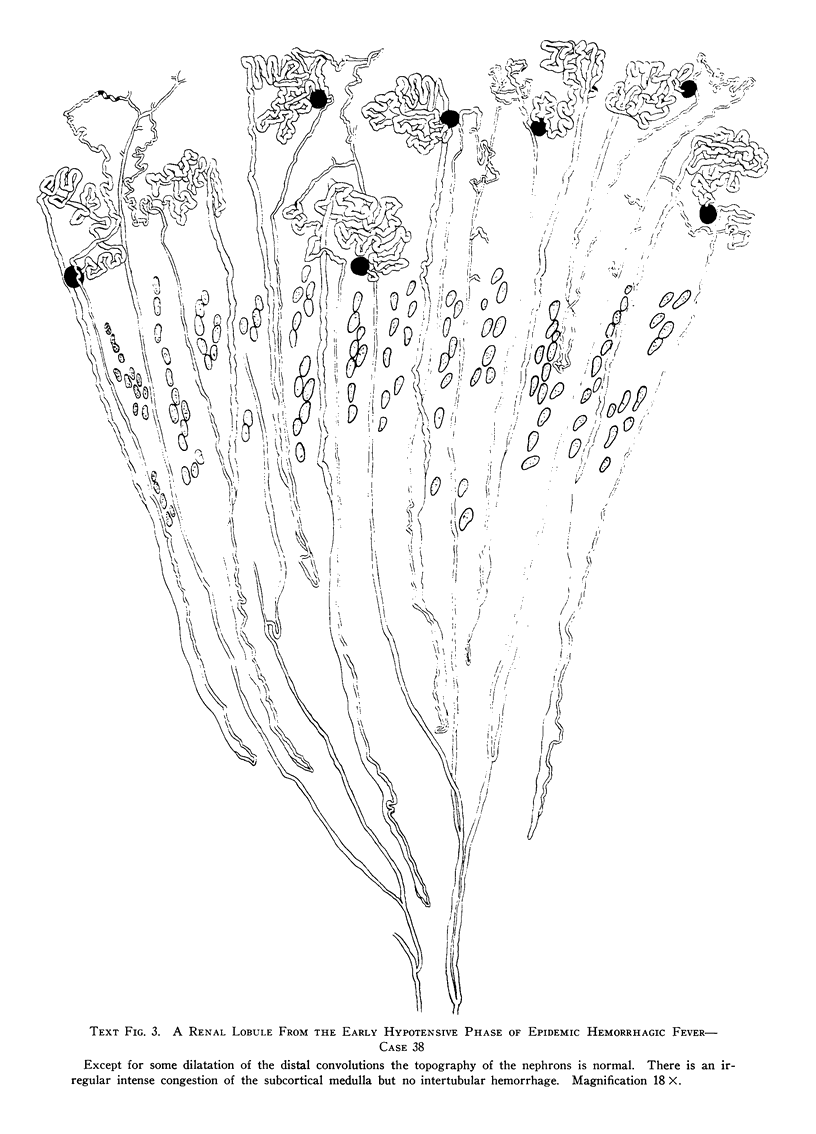


























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRIE H. J., KLEBANOFF S. J., CATES G. W. Direct medullary arterioles and arteriovenous anastomoses in the arcuate sponges of the kidney. Lancet. 1950 Jan 7;1(6593):23–23. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(50)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOCK M. A., WAKIM K. G., MANN F. C. Certain features of the vascular beds of the corticomedullary and medullary regions of the kidney. AMA Arch Pathol. 1952 May;53(5):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROEB H. F., McDOWELL M. E. Renal function in epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Am J Med. 1954 May;16(5):671–676. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES R. B., SHEEDY J. A., EKMAN C. N., FROEB H. F., CONLEY C. C., STOCKARD J. L., CUGELL D. W., VESTER J. W., KIYASU R. K., ENTWISLE G. The sequelae of epidemic hemorrhagic fever; with a note on causes of death. Am J Med. 1954 May;16(5):629–638. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULLINGHORST R. L., STEER A. Pathology of epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Ann Intern Med. 1953 Jan;38(1):77–101. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-38-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE K. G. The late prognosis in acute tubular necrosis; an interim follow-up report on 14 patients. Lancet. 1952 May 31;1(6718):1086–1088. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)90744-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUKES R. J. The pathology of thirty-nine fatal cases of epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Am J Med. 1954 May;16(5):639–650. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER C. F. Epidemic hemorrhagic fever of the Far East or endemic hemorrhagic nephroso-nephritis; morphology and pathogenesis. Lab Invest. 1952;1(3):291–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER C. F. European outbreaks of the Far-Eastern (Korean) type of epidemic hemorrhagic fever (EHF). Mil Med. 1955 Dec;117(6):502–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER J. Correlations of structure and function and mechanisms of recovery in acute tubular necrosis. Am J Med. 1953 Oct;15(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER J., STRAUS W., KRETCHMER N., LEE Y. C., DICKERMAN H. W., CHEROT F. The histochemical characteristics of absorption droplets in the nephron. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 Jul;3(4):277–283. doi: 10.1177/3.4.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER J. The spectrum of structural change in acute renal failure. Mil Med. 1955 Sep;117(3):229–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEER A. Pathology of hemorrhagic fever: a comparison of the findings; 1951 and 1952. Am J Pathol. 1955 Mar-Apr;31(2):201–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYNER J. C., MARKELS R. A. Continuous renal clearance studies in epidemic hemorrhagic fever. U S Armed Forces Med J. 1955 Jun;6(6):807–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL A. Selective renal vasospasm and ischemic renal necrosis produced experimentally with staphylococcal toxin: observations on the pathogenesis of bilateral cortical necrosis. Am J Pathol. 1955 Mar-Apr;31(2):233–259. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





