Abstract
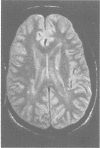
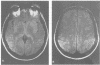
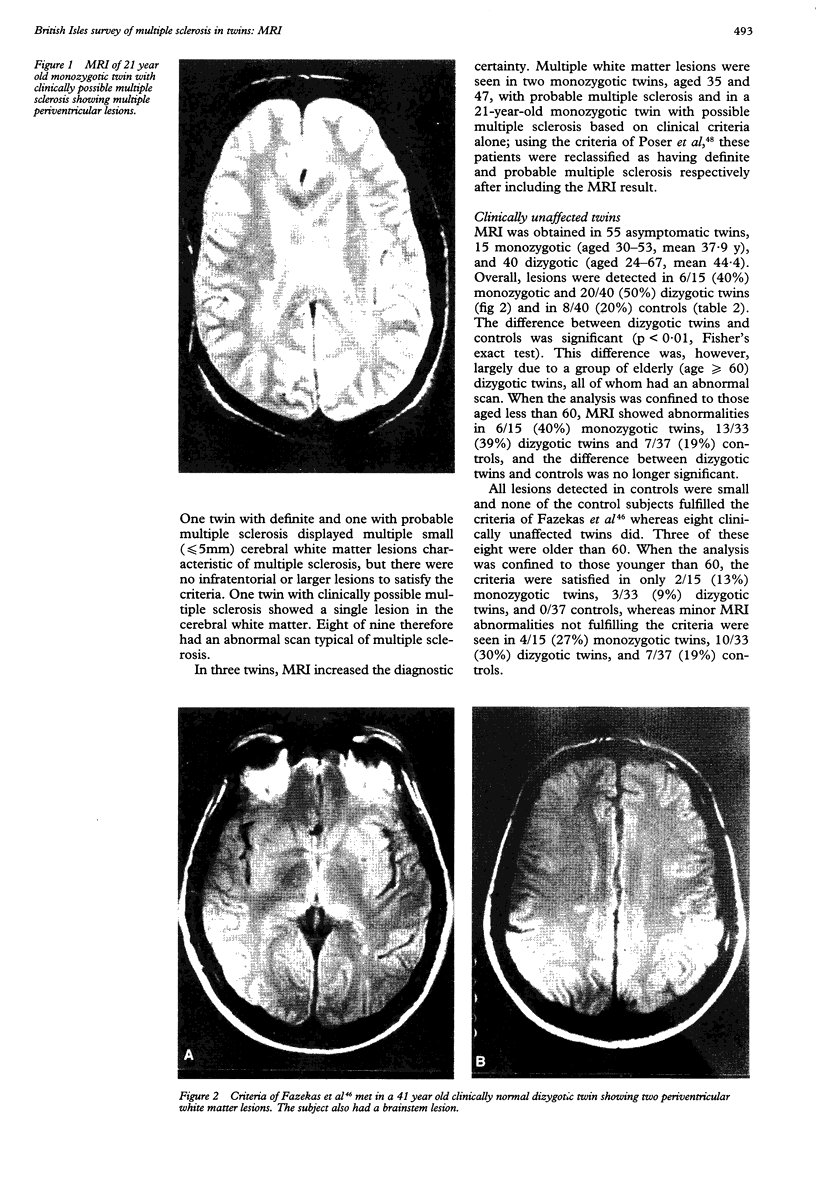
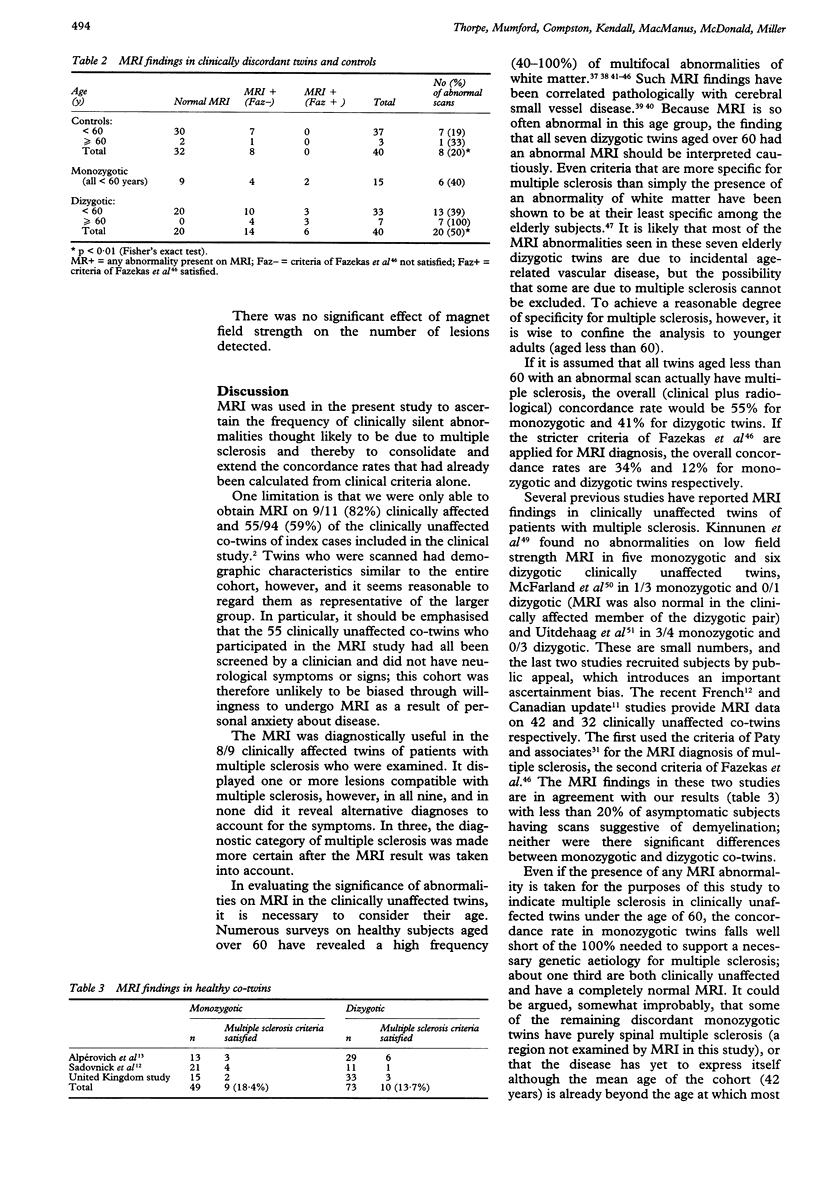
64/105 subjects who have a twin with multiple sclerosis included in a study of clinical concordance also underwent MRI of the brain. 8/23 monozygotic and 1/41 dizygotic co-twins from this subgroup were clinically concordant of whom 8/9 had MRI appearances typical of multiple sclerosis. Of the 48 clinically discordant twins aged less than 60, abnormalities on MRI were detected in 6/15 (40%) monozygotic and 13/33 (39%) dizygotic twins compared with 7/37 (19%) healthy age-matched controls. Abnormalities on MRI typical of multiple sclerosis (defined by the Fazekas criteria) were, however, present in only 2/15 (13%) monozygotic and 3/33 (9%) dizygotic twins and 0/37 controls. These results suggest that about 10% of monozygotic and dizygotic twins have "subclinical multiple sclerosis". It is likely that most of the MRI abnormalities seen in clinically discordant twins, however, represent incidental pathology.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awad I. A., Spetzler R. F., Hodak J. A., Awad C. A., Carey R. Incidental subcortical lesions identified on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. I. Correlation with age and cerebrovascular risk factors. Stroke. 1986 Nov-Dec;17(6):1084–1089. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.6.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobowick A. R., Kurtzke J. F., Brody J. A., Hrubec Z., Gillespie M. Twin study of multiple sclerosis: an epidemiologic inquiry. Neurology. 1978 Oct;28(10):978–987. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.10.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braffman B. H., Zimmerman R. A., Trojanowski J. Q., Gonatas N. K., Hickey W. F., Schlaepfer W. W. Brain MR: pathologic correlation with gross and histopathology. 1. Lacunar infarction and Virchow-Robin spaces. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Sep;151(3):551–558. doi: 10.2214/ajr.151.3.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brant-Zawadzki M., Fein G., Van Dyke C., Kiernan R., Davenport L., de Groot J. MR imaging of the aging brain: patchy white-matter lesions and dementia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1985 Sep-Oct;6(5):675–682. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundey S. Uses and limitations of twin studies. J Neurol. 1991 Oct;238(7):360–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00319852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier R. D., Eldridge R. Possible risk factors in multiple sclerosis as found in a national twin study. Arch Neurol. 1982 Mar;39(3):140–144. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510150010003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. R., Aminoff M. J., Brant-Zawadzki M. Evaluation of patients with multiple sclerosis by evoked potentials and magnetic resonance imaging: a comparative study. Ann Neurol. 1986 Nov;20(5):645–648. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Bulman D. E., Sadovnick A. D., Paty D. W., Warren S., Hader W., Murray T. J., Seland T. P., Duquette P., Grey T. A population-based study of multiple sclerosis in twins. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1638–1642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engell T. A clinical patho-anatomical study of clinically silent multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1989 May;79(5):428–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1989.tb03811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas F. Magnetic resonance signal abnormalities in asymptomatic individuals: their incidence and functional correlates. Eur Neurol. 1989;29(3):164–168. doi: 10.1159/000116401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas F., Niederkorn K., Schmidt R., Offenbacher H., Horner S., Bertha G., Lechner H. White matter signal abnormalities in normal individuals: correlation with carotid ultrasonography, cerebral blood flow measurements, and cerebrovascular risk factors. Stroke. 1988 Oct;19(10):1285–1288. doi: 10.1161/01.str.19.10.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas F., Offenbacher H., Fuchs S., Schmidt R., Niederkorn K., Horner S., Lechner H. Criteria for an increased specificity of MRI interpretation in elderly subjects with suspected multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1988 Dec;38(12):1822–1825. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.12.1822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferbert A., Busse D., Thron A. Microinfarction in classic migraine? A study with magnetic resonance imaging findings. Stroke. 1991 Aug;22(8):1010–1014. doi: 10.1161/01.str.22.8.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fog T., Hyllested K., Andersen S. R. A case of benign multiple sclerosis, with autopsy. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1972;51:369–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. E., de Leon M. J., Kalnin A., Rosner L., Goodgold A., Chase N. Leukoencephalopathy in normal and pathologic aging: 2. MRI of brain lucencies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1986 Jul-Aug;7(4):567–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard G., Weisberg L. A. MRI periventricular lesions in adults. Neurology. 1986 Jul;36(7):998–1001. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.7.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. J., Sadler M. Unsuspected multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1983 Sep;40(9):533–536. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050080033003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt A. L., Orrison W. W., Yeo R. A., Haaland K. Y., Rhyne R. L., Garry P. J., Rosenberg G. A. Clinical significance of MRI white matter lesions in the elderly. Neurology. 1989 Nov;39(11):1470–1474. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.11.1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Kinkel P. R., Kinkel W. R. Silent brain lesions in patients with isolated idiopathic optic neuritis. A clinical and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol. 1986 May;43(5):452–455. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520050032017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen E., Juntunen J., Ketonen L., Koskimies S., Konttinen Y. T., Salmi T., Koskenvuo M., Kaprio J. Genetic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. A co-twin study of a nationwide series. Arch Neurol. 1988 Oct;45(10):1108–1111. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520340062013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen E., Koskenvuo M., Kaprio J., Aho K. Multiple sclerosis in a nationwide series of twins. Neurology. 1987 Oct;37(10):1627–1629. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.10.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick J. B., Hayman L. A. White-matter lesions in MR imaging of clinically healthy brains of elderly subjects: possible pathologic basis. Radiology. 1987 Feb;162(2):509–511. doi: 10.1148/radiology.162.2.3797666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEHOCZKY T., HALASY-LEHOCZKY M. FORME "B'ENIGNE" DE LA SCL'EROSE EN PLAQUES. Presse Med. 1963 Nov 16;71:2294–2296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. G., Rose J. W., Smoker W., Petajan J. H. MRI in familial multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1990 Jun;40(6):900–903. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.6.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCALPINE D. The benign form of multiple sclerosis. A study based on 241 cases seen within three years of onset and followed up until the tenth year or more of the disease. Brain. 1961 Jun;84:186–203. doi: 10.1093/brain/84.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. P., Hirano A. Forms of benign multiple sclerosis. Report of two "clinically silent" cases discovered at autopsy. Arch Neurol. 1967 Dec;17(6):588–600. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470300030007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. P., Myrianthopoulos N. C. Multiple sclerosis in twins and their relatives. Arch Neurol. 1966 Nov;15(5):449–462. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470170003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H., Kendall B. E., Barter S., Johnson G., MacManus D. G., Logsdail S. J., Ormerod I. E., McDonald W. I. Magnetic resonance imaging in central nervous system sarcoidosis. Neurology. 1988 Mar;38(3):378–383. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.3.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H., McDonald W. I., Blumhardt L. D., du Boulay G. H., Halliday A. M., Johnson G., Kendall B. E., Kingsley D. P., MacManus D. G., Moseley I. F. Magnetic resonance imaging in isolated noncompressive spinal cord syndromes. Ann Neurol. 1987 Dec;22(6):714–723. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H., Ormerod I. E., Gibson A., du Boulay E. P., Rudge P., McDonald W. I. MR brain scanning in patients with vasculitis: differentiation from multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology. 1987;29(3):226–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00451758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morariu M., Klutzow W. F. Subclinical multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 1976 Jul 15;213(1):71–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00316341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Multiple sclerosis in 54 twinships: concordance rate is independent of zygosity. French Research Group on Multiple Sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1992 Dec;32(6):724–727. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford C. J., Wood N. W., Kellar-Wood H., Thorpe J. W., Miller D. H., Compston D. A. The British Isles survey of multiple sclerosis in twins. Neurology. 1994 Jan;44(1):11–15. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuwer M. R., Visscher B. R., Packwood J. W., Namerow N. S. Evoked potential testing in relatives of multiple sclerosis patients. Ann Neurol. 1985 Jul;18(1):30–34. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offenbacher H., Fazekas F., Schmidt R., Freidl W., Flooh E., Payer F., Lechner H. Assessment of MRI criteria for a diagnosis of MS. Neurology. 1993 May;43(5):905–909. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.5.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod I. E., Bronstein A., Rudge P., Johnson G., Macmanus D., Halliday A. M., Barratt H., Du Boulay E. P., Kendal B. E., Moseley I. F. Magnetic resonance imaging in clinically isolated lesions of the brain stem. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Jul;49(7):737–743. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.7.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod I. E., McDonald W. I., du Boulay G. H., Kendall B. E., Moseley I. F., Halliday A. M., Kakigi R., Kriss A., Peringer E. Disseminated lesions at presentation in patients with optic neuritis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Feb;49(2):124–127. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod I. E., Miller D. H., McDonald W. I., du Boulay E. P., Rudge P., Kendall B. E., Moseley I. F., Johnson G., Tofts P. S., Halliday A. M. The role of NMR imaging in the assessment of multiple sclerosis and isolated neurological lesions. A quantitative study. Brain. 1987 Dec;110(Pt 6):1579–1616. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.6.1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paty D. W., Oger J. J., Kastrukoff L. F., Hashimoto S. A., Hooge J. P., Eisen A. A., Eisen K. A., Purves S. J., Low M. D., Brandejs V. MRI in the diagnosis of MS: a prospective study with comparison of clinical evaluation, evoked potentials, oligoclonal banding, and CT. Neurology. 1988 Feb;38(2):180–185. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phadke J. G., Best P. V. Atypical and clinically silent multiple sclerosis: a report of 12 cases discovered unexpectedly at necropsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 May;46(5):414–420. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.5.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser C. M., Paty D. W., Scheinberg L., McDonald W. I., Davis F. A., Ebers G. C., Johnson K. P., Sibley W. A., Silberberg D. H., Tourtellotte W. W. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):227–231. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadovnick A. D., Armstrong H., Rice G. P., Bulman D., Hashimoto L., Paty D. W., Hashimoto S. A., Warren S., Hader W., Murray T. J. A population-based study of multiple sclerosis in twins: update. Ann Neurol. 1993 Mar;33(3):281–285. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tienari P. J., Salonen O., Wikström J., Valanne L., Palo J. Familial multiple sclerosis: MRI findings in clinically affected and unaffected siblings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Oct;55(10):883–886. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.10.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitdehaag B. M., Polman C. H., Valk J., Koetsier J. C., Lucas C. J. Magnetic resonance imaging studies in multiple sclerosis twins. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Dec;52(12):1417–1419. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.12.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A., Eldridge R., McFarland H., Houff S., Krebs H., McFarlin D. Multiple sclerosis in twins. Neurology. 1980 Nov;30(11):1139–1147. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.11.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. H., McFarlin D. E. Oligoclonal bands in CSF: twins with MS. Neurology. 1984 Jun;34(6):769–774. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.6.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yorifuji S., Takahashi M., Ogasahara S., Nakamura Y., Hazama T., Mitomo M., Tarui S. Focal luxury perfusion with an early-filling vein in relation to neurological symptoms evoked by heat. J Neurol. 1985;232(1):58–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00314044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]