Abstract
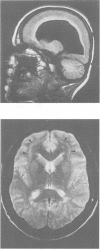
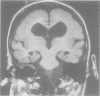
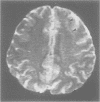
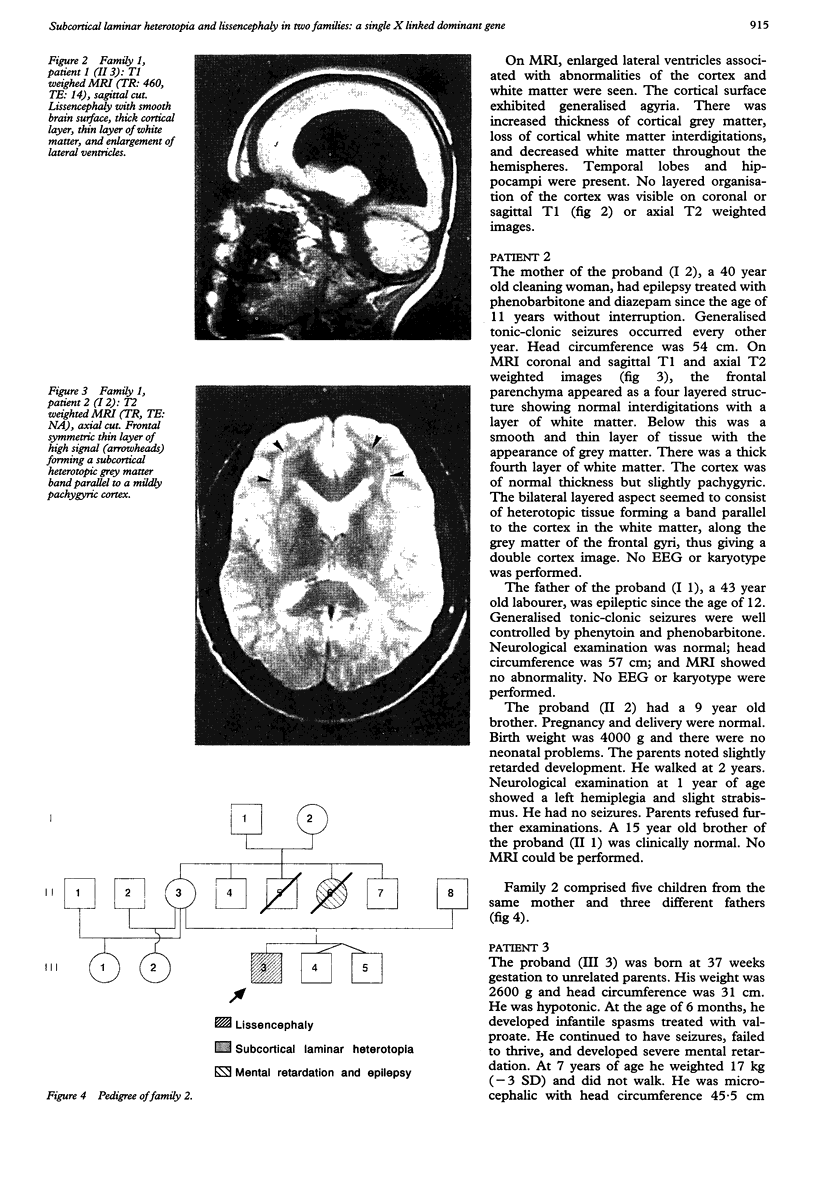
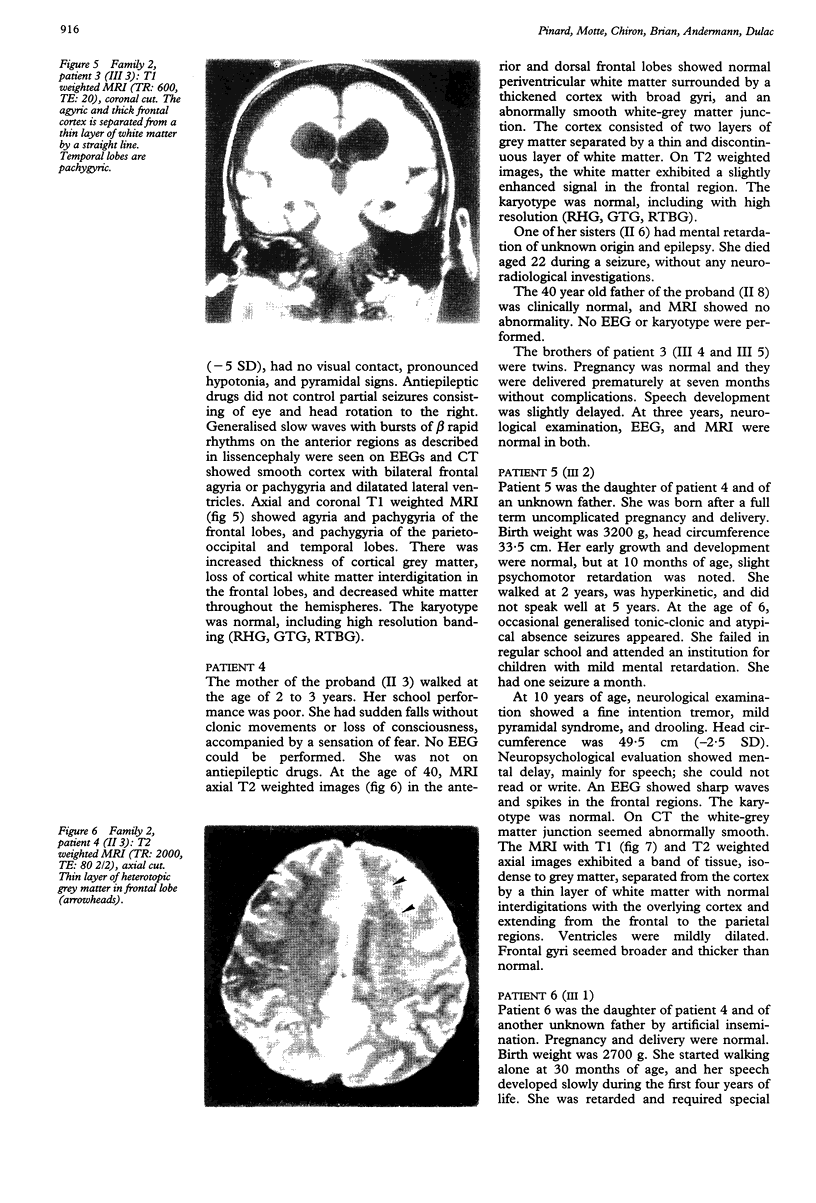
Neuronal migration disorders can now be recognised by MRI. This paper reports two families in which the mothers had subcortical laminar heterotopia and four of their children had either similar heterotopia (two girls) or severe pachygyria or lissencephaly (two boys). Laminar heterotopia was more evident on MRI T2 weighted images. The patients had mild to severe epilepsy and mental retardation depending on the extent of cortical abnormalities. In these families, subcortical laminar heterotopia, pachygyria, and lissencephaly seem to share the same X linked or autosomal dominant gene. No chromosomal abnormalities, especially of chromosome 17, could be identified. For appropriate genetic counselling of the family of a child with lissencephaly or subcortical laminar heterotopia, MRI should be performed in parents or siblings with mental retardation or epilepsy.
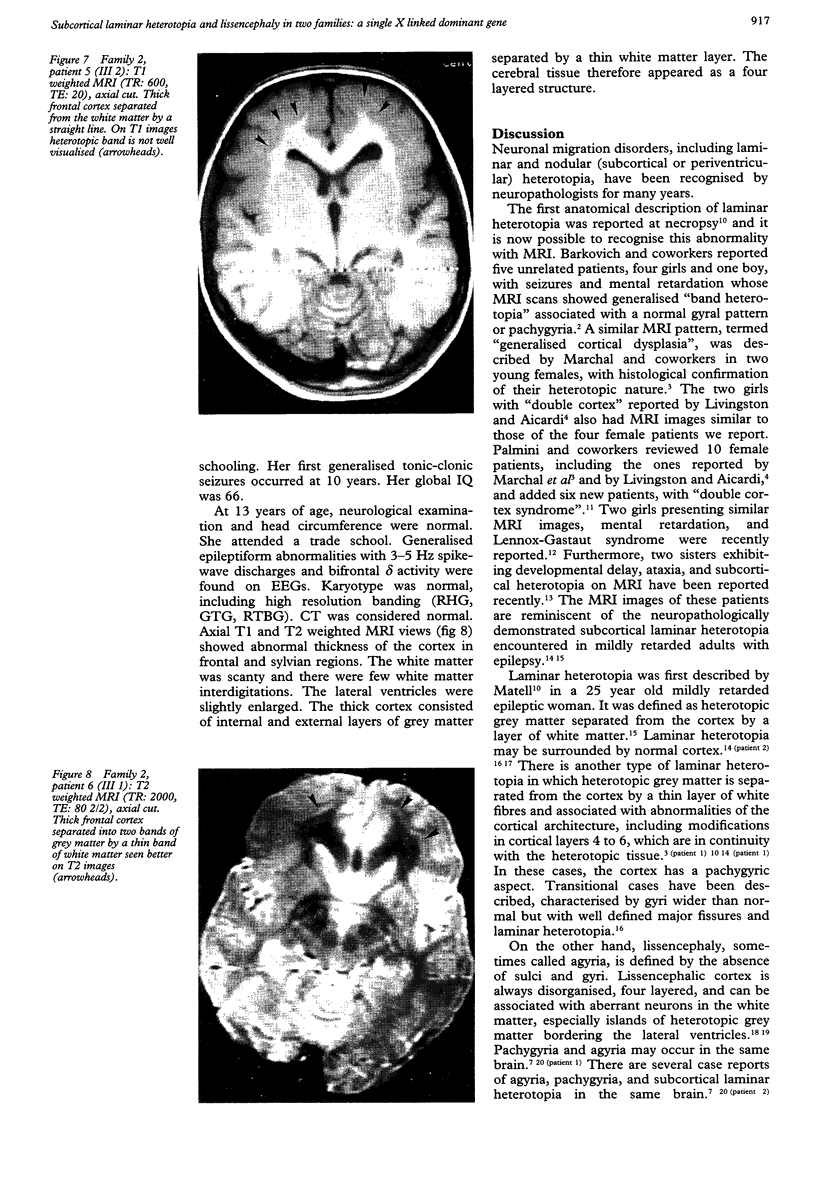
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERCA-SERRANO R., REZNIK M. TURRIC'EPHALIE H'R'EDITAIRE, MICROC'EPHALIE FAMILIALE AVEC LISSENC'EPHALIE; RAPPORT DE CE SYNDROME MALFORMATIF AVEC LES DYSRAPHIES C'ER'EBRO-M'EDULLAIRES. J Neurol Sci. 1964 Nov-Dec;1(6):555–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(64)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aicardi J., Chevrie J. J., Rousselie F. Le syndrome spasmes en flexion agénesie calleuse, anomalies chorio-rétiniennes. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1969;26(10):1103–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNETT C. H., DENT C. E., HARPER C., WARLAND B. J. VITAMIN D-RESISTANT RICKETS. ANALYSIS OF TWENTY-FOUR PEDIGREES WITH HEREDITARY AND SPORADIC CASES. Am J Med. 1964 Feb;36:222–232. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich A. J., Jackson D. E., Jr, Boyer R. S. Band heterotopias: a newly recognized neuronal migration anomaly. Radiology. 1989 May;171(2):455–458. doi: 10.1148/radiology.171.2.2468173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROME L. Pachygyria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(2):335–352. doi: 10.1002/path.1700710208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOEGE T. C., THULINE H. C., PRIEST J. H., NORBY D. E., BRYANT J. S. STUDIES OF A FAMILY WITH THE ORAL-FACIAL-DIGITAL SYNDROME. N Engl J Med. 1964 Nov 19;271:1073–1078. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196411192712101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daube J. R., Chou S. M. Lissencephaly: two cases. Neurology. 1966 Feb;16(2):179–191. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.2_part_1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis J., Bower B. D. The Aicardi syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1972 Jun;14(3):382–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb02604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns W. B. Developmental aspects of lissencephaly and the lissencephaly syndromes. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1987;23(1):225–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns W. B., Gilbert E. F., Opitz J. M. Further comments on the lissencephaly syndromes. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Sep;22(1):197–211. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320220119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns W. B., Stratton R. F., Greenberg F. Syndromes with lissencephaly. I: Miller-Dieker and Norman-Roberts syndromes and isolated lissencephaly. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jul;18(3):509–526. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns W. B., Stratton R. F., Parke J. T., Greenberg F., Nussbaum R. L., Ledbetter D. H. Miller-Dieker syndrome: lissencephaly and monosomy 17p. J Pediatr. 1983 Apr;102(4):552–558. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenichel G. M., Phillips J. A. Familial aplasia of the cerebellar vermis. Possible X-linked dominant inheritance. Arch Neurol. 1989 May;46(5):582–583. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520410118036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg B., Aicardi J., Dias K., Ramos O. A progressive syndrome of autism, dementia, ataxia, and loss of purposeful hand use in girls: Rett's syndrome: report of 35 cases. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):471–479. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbord M. G., Boyd S., Hall-Craggs M. A., Kendall B., McShane M. A., Baraitser M. Ataxia, developmental delay and an extensive neuronal migration abnormality in 2 siblings. Neuropediatrics. 1990 Nov;21(4):218–221. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatten M. E. Riding the glial monorail: a common mechanism for glial-guided neuronal migration in different regions of the developing mammalian brain. Trends Neurosci. 1990 May;13(5):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90044-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamuro K., Tenokuchi Y. Familial periventricular nodular heterotopia. Brain Dev. 1993 May-Jun;15(3):237–241. doi: 10.1016/0387-7604(93)90073-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann S., Kuchler S., Theveniau M., Vincendon G., Zanetta J. P. An endogenous lectin and one of its neuronal glycoprotein ligands are involved in contact guidance of neuron migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. H., Aicardi J. Unusual MRI appearance of diffuse subcortical heterotopia or "double cortex" in two children. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Jul;53(7):617–620. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.7.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. Q. LISSENCEPHALY IN 2 SIBLINGS. Neurology. 1963 Oct;13:841–850. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.10.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchal G., Andermann F., Tampieri D., Robitaille Y., Melanson D., Sinclair B., Olivier A., Silver K., Langevin P. Generalized cortical dysplasia manifested by diffusely thick cerebral cortex. Arch Neurol. 1989 Apr;46(4):430–434. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520400090025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill W. M., Jr, Atkin C. L., Bloomer H. A. Hereditary nephritis: a re-examination of its clinical and genetic features. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Feb;88(2):176–182. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-2-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmini A., Andermann F., Aicardi J., Dulac O., Chaves F., Ponsot G., Pinard J. M., Goutières F., Livingston J., Tampieri D. Diffuse cortical dysplasia, or the 'double cortex' syndrome: the clinical and epileptic spectrum in 10 patients. Neurology. 1991 Oct;41(10):1656–1662. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.10.1656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmini A., Andermann F., de Grissac H., Tampieri D., Robitaille Y., Langevin P., Desbiens R., Andermann E. Stages and patterns of centrifugal arrest of diffuse neuronal migration disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1993 Apr;35(4):331–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1993.tb11645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REZNIK M., ALBERCA-SERRANO R. FORME FAMILIALE D'HYPERT'ELORISME AVEC LISSENC'EPHALIE SE PR'ESENTANT CLINIQUEMENT SOUS FORME D'UNE ARRI'ERATION MENTALE AVEC EPILEPSIE ET PARAPL'EGIE SPASMODIQUE. J Neurol Sci. 1964 Jan-Feb;1(1):40–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(64)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REZNIK M., ALBERCA R. S. HYPERT'ELORISME ET LISSENC'EPHALIE. ETUDE D'UNE FORME FAMILIALE (FAMILLE MA...). (NOTE PR'ELIMINAIRE) Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1963 Nov;63:970–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner O., Carrozzo R., Shen Y., Wehnert M., Faustinella F., Dobyns W. B., Caskey C. T., Ledbetter D. H. Isolation of a Miller-Dieker lissencephaly gene containing G protein beta-subunit-like repeats. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):717–721. doi: 10.1038/364717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricci S., Cusmai R., Fariello G., Fusco L., Vigevano F. Double cortex. A neuronal migration anomaly as a possible cause of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1992 Jan;49(1):61–64. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530250065017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. E., Johnson J. P., Holycross B., Mandeville T. M., Sears T. S., Graul E. A., Carey J. C., Schroer R. J., Phelan M. C., Szollar J. Detection of submicroscopic deletions in band 17p13 in patients with the Miller-Dieker syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):597–604. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spano L. M., Opitz J. M. Bibliography on X-linked mental retardation, the fragile X, and related subjects V (1991). Am J Med Genet. 1991 Feb-Mar;38(2-3):173–185. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. M., Richman D. P., Caviness V. S., Jr Lissencephaly and Pachygyria: an architectonic and topographical analysis. Acta Neuropathol. 1975;31(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00696881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton R. F., Dobyns W. B., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. New chromosomal syndrome: Miller-Dieker syndrome and monosomy 17p13. Hum Genet. 1984;67(2):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00273000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEST W. D., HALLERVORDEN J. Migrationshemmung in Gross- und Kleinhirn. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1958;178(2):224–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rijk-van Andel J. F., Arts W. F., Barth P. G., Loonen M. C. Diagnostic features and clinical signs of 21 patients with lissencephaly type 1. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1990 Aug;32(8):707–717. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1990.tb08431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vanTuinen P., Dobyns W. B., Rich D. C., Summers K. M., Robinson T. J., Nakamura Y., Ledbetter D. H. Molecular detection of microscopic and submicroscopic deletions associated with Miller-Dieker syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):587–596. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]