Abstract
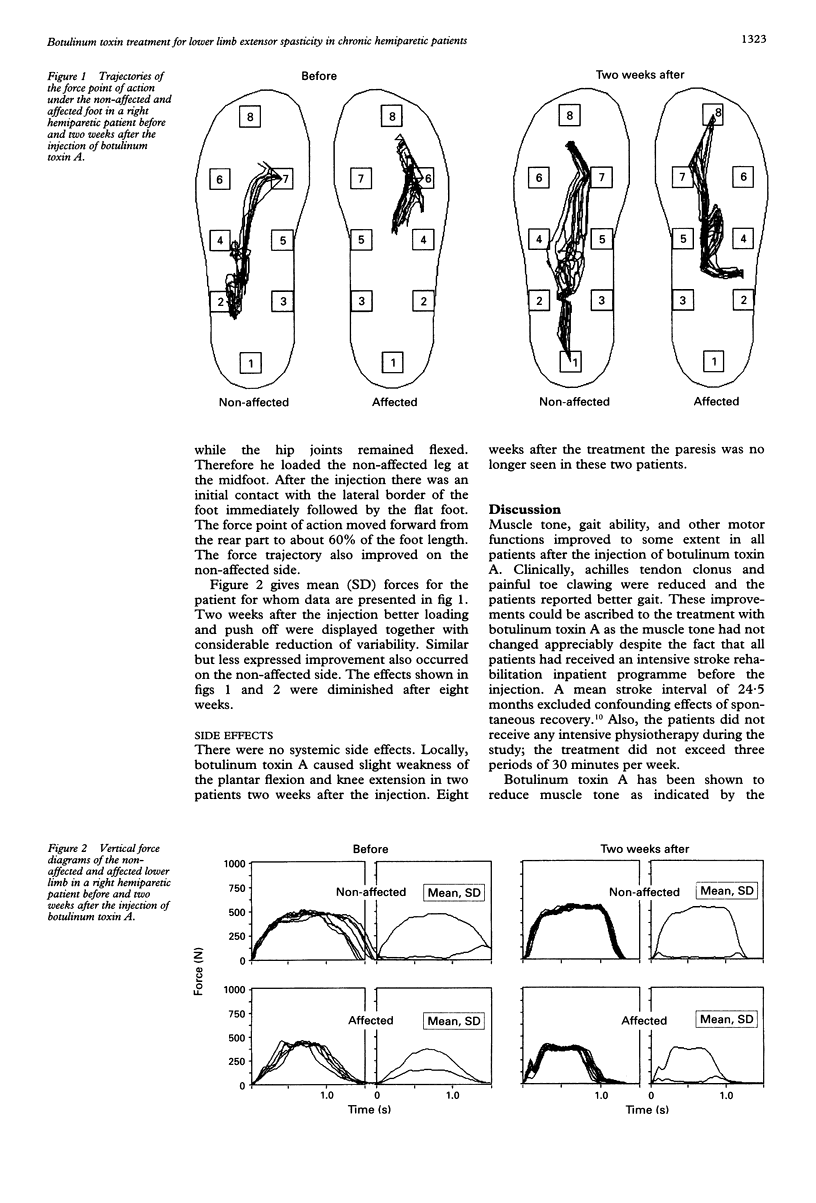
Twelve chronic hemiparetic outpatients with pronounced lower limb extensor spasticity were injected with 400 units of botulinum toxin A, EMG guided into the soleus, tibialis posterior, and both heads of the gastrocnemius muscles. Botulinum toxin A caused a definite reduction of plantar flexor spasticity, in 10 patients two weeks after the injection, as assessed by the Ashworth scale. Four of the patients were able to achieve active dorsiflexion of their affected ankle. Gait analysis including the measurement of vertical ground reaction forces showed a statistically significant (p < 0.01) improvement in velocity, stride length, stance symmetry, and the length of the force point of action under the affected foot. Qualitative improvements on the force diagrams indicated a better loading, advancement of the body, and push off of the affected limb in seven patients. Eight weeks after the injection the effects waned.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artieda J., Quesada P., Obeso J. A. Reciprocal inhibition between forearm muscles in spastic hemiplegia. Neurology. 1991 Feb;41(2 ):286–289. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.2_part_1.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon R. W., Smith M. B. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther. 1987 Feb;67(2):206–207. doi: 10.1093/ptj/67.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen F. M., Wade D. T., Bradshaw C. M. Mobility after stroke: reliability of measures of impairment and disability. Int Disabil Stud. 1990 Jan-Mar;12(1):6–9. doi: 10.3109/03790799009166594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das T. K., Park D. M. Botulinum toxin in treating spasticity. Br J Clin Pract. 1989 Nov;43(11):401–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dengler R., Neyer U., Wohlfarth K., Bettig U., Janzik H. H. Local botulinum toxin in the treatment of spastic drop foot. J Neurol. 1992 Aug;239(7):375–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00812153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermens H. J., deWaal C. A., Buurke J., Zilvold G. A new gait analysis system for clinical use in a rehabilitation center. Orthopedics. 1986 Dec;9(12):1669–1675. doi: 10.3928/0147-7447-19861201-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutsson E., Richards C. Different types of disturbed motor control in gait of hemiparetic patients. Brain. 1979 Jun;102(2):405–430. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.2.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln N., Leadbitter D. Assessment of motor function in stroke patients. Physiotherapy. 1979 Feb;65(2):48–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry J., Waters R. L., Perrin T. Electromyographic analysis of equinovarus following stroke. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978 Mar-Apr;(131):47–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiavi R., Bugle H. J., Limbird T. Electromyographic gait assessment, Part 2: Preliminary assessment of hemiparetic synergy patterns. J Rehabil Res Dev. 1987 Spring;24(2):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilbeck C. E., Wade D. T., Hewer R. L., Wood V. A. Recovery after stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Jan;46(1):5–8. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow B. J., Tsui J. K., Bhatt M. H., Varelas M., Hashimoto S. A., Calne D. B. Treatment of spasticity with botulinum toxin: a double-blind study. Ann Neurol. 1990 Oct;28(4):512–515. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thilmann A. F., Fellows S. J., Garms E. The mechanism of spastic muscle hypertonus. Variation in reflex gain over the time course of spasticity. Brain. 1991 Feb;114(Pt 1A):233–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa N., Tanaka R., Ito Z. Reciprocal Ia inhibition in spastic hemiplegia of man. Brain. 1976 Sep;99(3):555–574. doi: 10.1093/brain/99.3.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


