Abstract
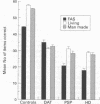
Ten patients with dementia of Alzheimer's type, 10 patients with progressive supranuclear palsy, and 10 patients with Huntington's disease were compared on two types of verbal fluency task--namely, initial letter fluency and category (semantic) fluency. The groups were carefully matched for overall level of dementia on the dementia rating scale, and were compared with 25 age matched normal controls. The controls found letter fluency more difficult than category fluency, and this relative pattern of performance was repeated in the progressive supranuclear palsy and Huntington's disease groups, although both groups were significantly impaired on both tasks. By contrast, patients with Alzheimer's disease performed just as poorly as the progressive supranuclear palsy and Huntington's disease groups on the category tasks, but were significantly less impaired at letter fluency, performing at near normal levels on this task. From these results, it is suggested that the performances of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy and Huntington's disease relate largely to initiation and retrieval problems secondary to disruption of frontostriatal circuits, whereas in Alzheimer's disease, the poorer performance on category fluency is due principally to the breakdown of semantic knowledge, which probably reflects temporal neocortical involvement.
Full text
PDF

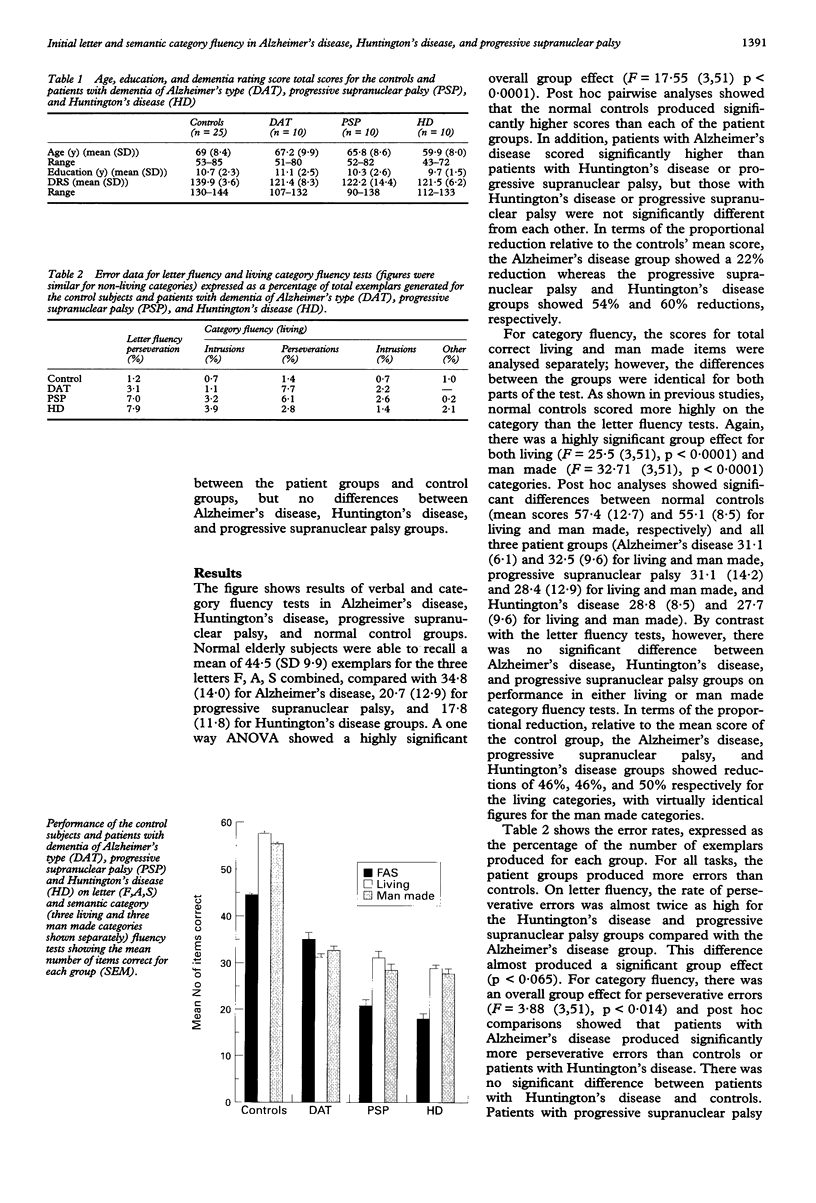



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. L., Feldman R. G., Willis A. L. The 'subcortical dementia' of progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Feb;37(2):121–130. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayles K. A., Tomoeda C. K. Confrontation naming impairment in dementia. Brain Lang. 1983 May;19(1):98–114. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(83)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters N., Granholm E., Salmon D. P., Grant I., Wolfe J. Episodic and semantic memory: a comparison of amnesic and demented patients. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1987 Oct;9(5):479–497. doi: 10.1080/01688638708410764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters N., Wolfe J., Granholm E., Martone M. An assessment of verbal recall, recognition and fluency abilities in patients with Huntington's disease. Cortex. 1986 Mar;22(1):11–32. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(86)80030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters N., Wolfe J., Martone M., Granholm E., Cermak L. S. Memory disorders associated with Huntington's disease: verbal recall, verbal recognition and procedural memory. Neuropsychologia. 1985;23(6):729–743. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(85)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chertkow H., Bub D. Semantic memory loss in dementia of Alzheimer's type. What do various measures measure? Brain. 1990 Apr;113(Pt 2):397–417. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.2.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damasio A. R., Damasio H., Tranel D., Brandt J. P. Neural regionalization of knowledge access: preliminary evidence. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:1039–1047. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffinet A. M., De Volder A. G., Gillain C., Rectem D., Bol A., Michel C., Cogneau M., Labar D., Laterre C. Positron tomography demonstrates frontal lobe hypometabolism in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol. 1989 Feb;25(2):131–139. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. R., Gurd J. M. Remote memory and lexical retrieval in a case of frontal Pick's disease. Arch Neurol. 1994 Aug;51(8):821–827. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1994.00540200101023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. R., Patterson K., Oxbury S., Funnell E. Semantic dementia. Progressive fluent aphasia with temporal lobe atrophy. Brain. 1992 Dec;115(Pt 6):1783–1806. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.6.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. R., Salmon D. P., Butters N. Differential impairment of semantic and episodic memory in Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases: a controlled prospective study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Dec;53(12):1089–1095. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.12.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. R., Salmon D. P., Butters N. Semantic memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease: failure of access or degraded knowledge? Neuropsychologia. 1992 Apr;30(4):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(92)90104-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. R., Salmon D. P., Butters N. The nature of the naming deficit in Alzheimer's and Huntington's disease. Brain. 1991 Aug;114(Pt 4):1547–1558. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.4.1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Fedio P. Word production and comprehension in Alzheimer's disease: the breakdown of semantic knowledge. Brain Lang. 1983 May;19(1):124–141. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(83)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milberg W., Albert M. Cognitive differences between patients with progressive supranuclear palsy and Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1989 Oct;11(5):605–614. doi: 10.1080/01688638908400919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsch A. U., Bondi M. W., Butters N., Salmon D. P., Katzman R., Thal L. J. Comparisons of verbal fluency tasks in the detection of dementia of the Alzheimer type. Arch Neurol. 1992 Dec;49(12):1253–1258. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530360051017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss M. B., Albert M. S., Butters N., Payne M. Differential patterns of memory loss among patients with Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and alcoholic Korsakoff's syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1986 Mar;43(3):239–246. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520030031008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ober B. A., Koss E., Friedland R. P., Delis D. C. Processes of verbal memory failure in Alzheimer-type dementia. Brain Cogn. 1985 Jan;4(1):90–103. doi: 10.1016/0278-2626(85)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrini V., Nertempi P., Vaglia A., Revello M. G., Pinna V., Ferro-Milone F. Recovery from herpes simplex encephalitis: selective impairment of specific semantic categories with neuroradiological correlation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Oct;51(10):1284–1293. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.10.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillon B., Dubois B., Ploska A., Agid Y. Severity and specificity of cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's, Huntington's, and Parkinson's diseases and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology. 1991 May;41(5):634–643. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.5.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins T. W., James M., Owen A. M., Lange K. W., Lees A. J., Leigh P. N., Marsden C. D., Quinn N. P., Summers B. A. Cognitive deficits in progressive supranuclear palsy, Parkinson's disease, and multiple system atrophy in tests sensitive to frontal lobe dysfunction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Jan;57(1):79–88. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE J. C., RICHARDSON J. C., OLSZEWSKI J. PROGRESSIVE SUPRANUCLEAR PALSY. A HETEROGENEOUS DEGENERATION INVOLVING THE BRAIN STEM, BASAL GANGLIA AND CEREBELLUM WITH VERTICAL GAZE AND PSEUDOBULBAR PALSY, NUCHAL DYSTONIA AND DEMENTIA. Arch Neurol. 1964 Apr;10:333–359. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460160003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahakian B. J., Owen A. M. Computerized assessment in neuropsychiatry using CANTAB: discussion paper. J R Soc Med. 1992 Jul;85(7):399–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon D. P., Kwo-on-Yuen P. F., Heindel W. C., Butters N., Thal L. J. Differentiation of Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease with the Dementia Rating Scale. Arch Neurol. 1989 Nov;46(11):1204–1208. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520470060028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Butters N., White R., Lyon L., Granholm E. Priming semantic relations in patients with Huntington's disease. Brain Lang. 1988 Jan;33(1):27–40. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(88)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington E. K., Shallice T. Category specific semantic impairments. Brain. 1984 Sep;107(Pt 3):829–854. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.3.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Fersen L., Güntürkün O. Visual memory lateralization in pigeons. Neuropsychologia. 1990;28(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(90)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]