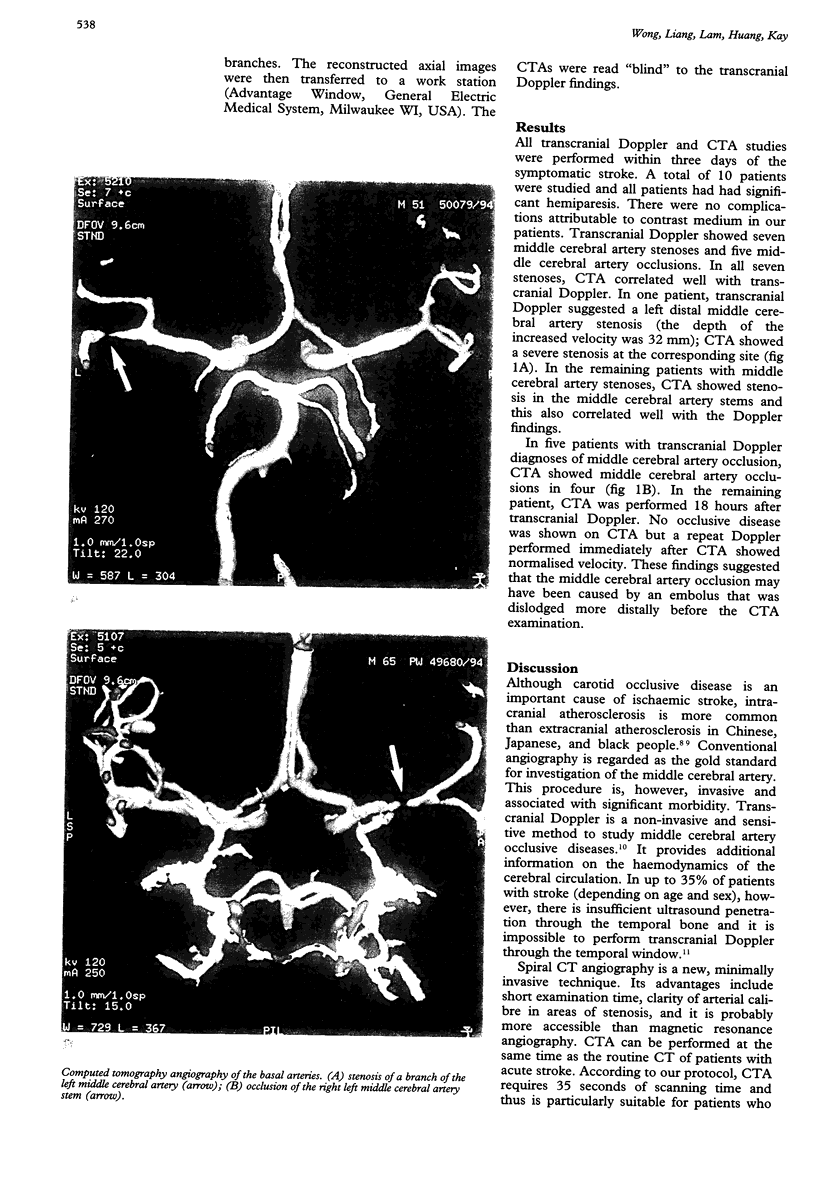
Abstract
There has been no report on the use of spiral computed tomography angiography (CTA) in the investigation of intracranial cerebral artery stenosis. A prospective pilot study was conducted to investigate the feasibility of CTA in the diagnosis of intracranial occlusive disease and its correlation with transcranial Doppler. With transcranial Doppler, 10 patients with acute ischaemic stroke with middle cerebral artery stenosis or occlusion were identified. There were seven middle cerebral artery stenoses and five middle cerebral artery occlusions. The CTA confirmed all diagnoses by transcranial Doppler except in one patient with middle cerebral artery occlusion in whom the embolus had probably propagated. The results showed that CTA is feasible and potentially useful in the diagnosis of middle cerebral artery occlusive disease. Further studies are required to assess its validity, sensitivity, and specificity in the diagnosis of middle cerebral artery occlusive disease.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caplan L. R., Gorelick P. B., Hier D. B. Race, sex and occlusive cerebrovascular disease: a review. Stroke. 1986 Jul-Aug;17(4):648–655. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.4.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming M. J., Morrow I. M. Carotid artery stenosis: a prospective comparison of CT angiography and conventional angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994 Sep;163(3):517–523. doi: 10.2214/ajr.163.3.8079836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaps M., Damian M. S., Teschendorf U., Dorndorf W. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound findings in middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke. 1990 Apr;21(4):532–537. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.4.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaps M., Teschendorf U., Dorndorf W. Haemodynamic studies in early stroke. J Neurol. 1992 Mar;239(3):138–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00833913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner M. J., Zanette E. M., Bastianello S., Mancini G., Sacchetti M. L., Carolei A., Bozzao L. Transcranial Doppler in acute hemispheric brain infarction. Neurology. 1991 Jan;41(1):109–113. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung S. Y., Ng T. H., Yuen S. T., Lauder I. J., Ho F. C. Pattern of cerebral atherosclerosis in Hong Kong Chinese. Severity in intracranial and extracranial vessels. Stroke. 1993 Jun;24(6):779–786. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.6.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. B. Neuroradiological applications of spiral CT. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1994 Apr;15(2):139–147. doi: 10.1016/s0887-2171(05)80096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. B., Tice H. M., Hooten S. M., Hsu L., Stieg P. E. Evaluation of cerebral aneurysms with helical CT: correlation with conventional angiography and MR angiography. Radiology. 1994 Sep;192(3):717–722. doi: 10.1148/radiology.192.3.8058939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velaj R., Drayer B., Albright R., Fram E. Comparative neurotoxicity of angiographic contrast media. Neurology. 1985 Sep;35(9):1290–1298. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.9.1290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanette E. M., Fieschi C., Bozzao L., Roberti C., Toni D., Argentino C., Lenzi G. L. Comparison of cerebral angiography and transcranial Doppler sonography in acute stroke. Stroke. 1989 Jul;20(7):899–903. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.7.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]