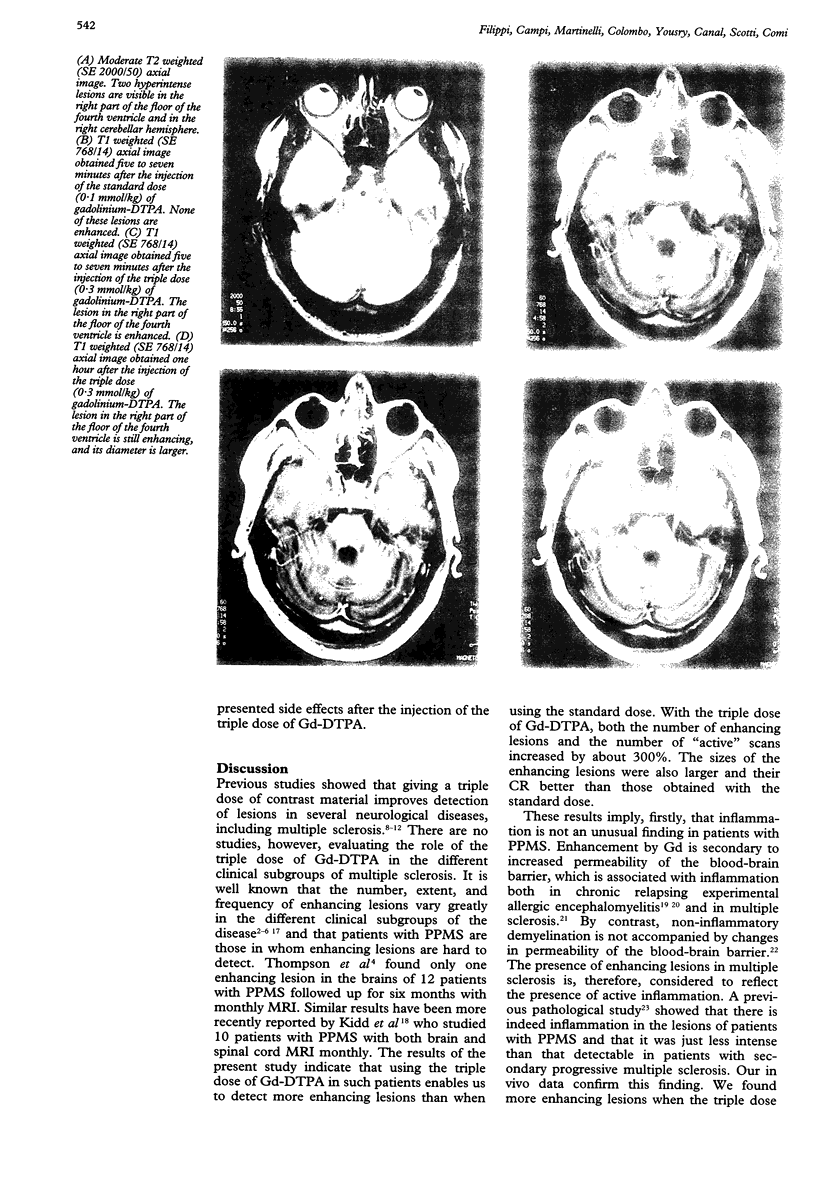
Abstract
This study was performed to evaluate whether a triple dose of gadolinium-DTPA (Gd-DTPA) increases the sensitivity of brain MRI for detecting enhancing lesions in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS). T1 weighted brain MRI was obtained for 10 patients with PPMS in two sessions. In the first session, one scan was obtained five to seven minutes after the injection of 0.1 mmol/kg Gd-DTPA (standard dose). In the second session, six to 24 hours later, one scan before and two scans five to seven minutes and one hour after the injection of 0.3 mmol/kg Gd-DTPA (triple dose) were obtained. Four enhancing lesions were detected in two patients when the standard dose of Gd-DTPA was used. The numbers of enhancing lesions increased to 13 and the numbers of patients with such lesions to five when the triple dose of Gd-DTPA was used and to 14 and six in the one hour delayed scans. The mean contrast ratio for enhancing lesions detected with the triple dose of Gd-DTPA was higher than those for lesions present in both the standard dose (P < 0.0009) and the one hour delayed scans (P = 0.04). These data indicate that with a triple dose of Gd-DTPA many more enhancing lesions can be detected in patients with PPMS. This is important both for planning clinical trials and for detecting the presence of inflammation in vivo in the lesions of such patients.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awad I. A., Johnson P. C., Spetzler R. F., Hodak J. A. Incidental subcortical lesions identified on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. II. Postmortem pathological correlations. Stroke. 1986 Nov-Dec;17(6):1090–1097. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.6.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi M., Campi A., Mammi S., Martinelli V., Locatelli T., Scotti G., Amadio S., Canal N., Comi G. Brain magnetic resonance imaging and multimodal evoked potentials in benign and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995 Jan;58(1):31–37. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.58.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard G., Weisberg L. A. MRI periventricular lesions in adults. Neurology. 1986 Jul;36(7):998–1001. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.7.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Sweeney M. G., Miller D. H., Mumford C. J., Kellar-Wood H., Menard D., McDonald W. I., Compston D. A. Occurrence of a multiple sclerosis-like illness in women who have a Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy mitochondrial DNA mutation. Brain. 1992 Aug;115(Pt 4):979–989. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.4.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. O., Frank J. A., Patronas N., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. Serial gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging scans in patients with early, relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: implications for clinical trials and natural history. Ann Neurol. 1991 May;29(5):548–555. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haustein J., Laniado M., Niendorf H. P., Louton T., Beck W., Planitzer J., Schöffel M., Reiser M., Kaiser W., Schörner W. Triple-dose versus standard-dose gadopentetate dimeglumine: a randomized study in 199 patients. Radiology. 1993 Mar;186(3):855–860. doi: 10.1148/radiology.186.3.8430199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. P., Mackenzie F., Tofts P., du Boulay E. P., McDonald W. I. Patterns of blood-brain barrier breakdown in inflammatory demyelination. Brain. 1991 Apr;114(Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.2.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. P., Munro P. M., MacKenzie F., Kesselring J., Tofts P. S., du Boulay E. P., Landon D. N., McDonald W. I. Duration and selectivity of blood-brain barrier breakdown in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis studied by gadolinium-DTPA and protein markers. Brain. 1990 Apr;113(Pt 2):365–378. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D., Taubenberger J. K., Cannella B., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S., McFarland H. F. Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging findings and lesion development in chronic, active multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1993 Nov;34(5):661–669. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermode A. G., Tofts P. S., Thompson A. J., MacManus D. G., Rudge P., Kendall B. E., Kingsley D. P., Moseley I. F., du Boulay E. P., McDonald W. I. Heterogeneity of blood-brain barrier changes in multiple sclerosis: an MRI study with gadolinium-DTPA enhancement. Neurology. 1990 Feb;40(2):229–235. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd D., Thompson A. J., Kendall B. E., Miller D. H., McDonald W. I. Benign form of multiple sclerosis: MRI evidence for less frequent and less inflammatory disease activity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Sep;57(9):1070–1072. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.9.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkel W. R., Jacobs L., Polachini I., Bates V., Heffner R. R., Jr Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). Computed tomographic, nuclear magnetic resonance, and clinical correlations. Arch Neurol. 1985 Oct;42(10):951–959. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060090033010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1444–1452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H. Magnetic resonance in monitoring the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1994;36 (Suppl):S91–S94. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H., Ormerod I. E., Gibson A., du Boulay E. P., Rudge P., McDonald W. I. MR brain scanning in patients with vasculitis: differentiation from multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology. 1987;29(3):226–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00451758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paty D. W., Li D. K. Interferon beta-1b is effective in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. II. MRI analysis results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. UBC MS/MRI Study Group and the IFNB Multiple Sclerosis Study Group. Neurology. 1993 Apr;43(4):662–667. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.4.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revesz T., Kidd D., Thompson A. J., Barnard R. O., McDonald W. I. A comparison of the pathology of primary and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1994 Aug;117(Pt 4):759–765. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.4.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge V. M., Kirsch J. E., Burke V. J., Price A. C., Nelson K. L., Thomas G. S., Dean B. L., Lee C. High-dose gadoteridol in MR imaging of intracranial neoplasms. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1992 Jan-Feb;2(1):9–18. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880020103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge V. M., Kirsch J. E., Thomas G. S. High-dose applications of gadolinium chelates in magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Dec;22(2):358–363. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910220241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears E. S., McCammon A., Bigelow R., Hayman L. A. Maximizing the harvest of contrast enhancing lesions in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1982 Aug;32(8):815–820. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.8.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E., Stone L. A., Albert P. S., Frank J. A., Martin R., Armstrong M., Maloni H., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. Clinical worsening in multiple sclerosis is associated with increased frequency and area of gadopentetate dimeglumine-enhancing magnetic resonance imaging lesions. Ann Neurol. 1993 May;33(5):480–489. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel S. M., Viñuela F., Fox A. J., Pelz D. M. CT of multiple sclerosis: reassessment of delayed scanning with high doses of contrast material. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985 Sep;145(3):497–500. doi: 10.2214/ajr.145.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. J., Kermode A. G., Wicks D., MacManus D. G., Kendall B. E., Kingsley D. P., McDonald W. I. Major differences in the dynamics of primary and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jan;29(1):53–62. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldemar G., Christiansen P., Larsson H. B., Høgh P., Laursen H., Lassen N. A., Paulson O. B. White matter magnetic resonance hyperintensities in dementia of the Alzheimer type: morphological and regional cerebral blood flow correlates. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Dec;57(12):1458–1465. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.12.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicks D. A., Tofts P. S., Miller D. H., du Boulay G. H., Feinstein A., Sacares R. P., Harvey I., Brenner R., McDonald W. I. Volume measurement of multiple sclerosis lesions with magnetic resonance images. A preliminary study. Neuroradiology. 1992;34(6):475–479. doi: 10.1007/BF00598953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolansky L. J., Bardini J. A., Cook S. D., Zimmer A. E., Sheffet A., Lee H. J. Triple-dose versus single-dose gadoteridol in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimaging. 1994 Jul;4(3):141–145. doi: 10.1111/jon199443141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]