Abstract
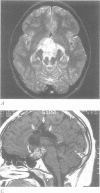
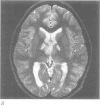
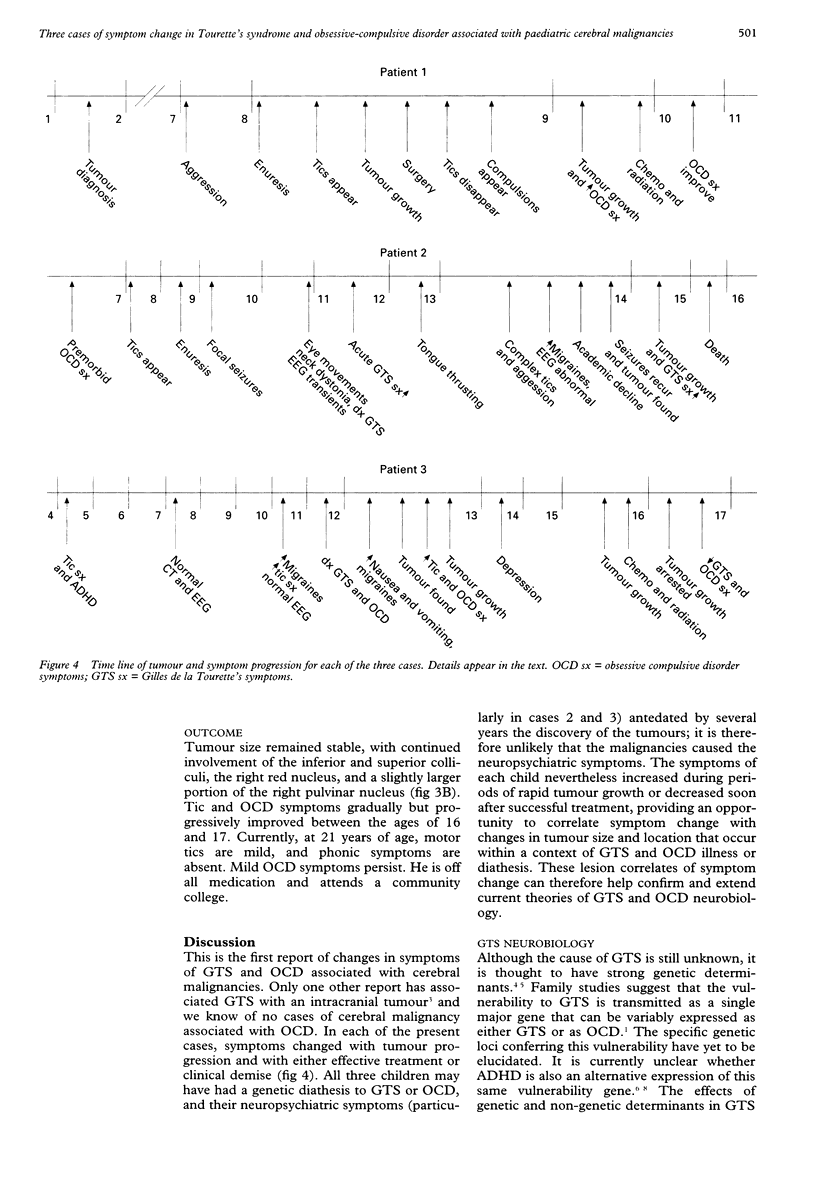
OBJECTIVE: To correlate behaviour manifestations with tumour location in three children who had Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome (GTS), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and primary cerebral malignancies. METHOD: Cases were ascertained from a chart review in a GTS and OCD specialty clinic. For each case the temporal progression of change in neuropsychiatric symptoms was qualitatively correlated with radiographic documentation of tumour progression. RESULTS: The change in symptom severities during tumour progression and treatment, together with prior neurobiological studies of GTS, suggest that the ventral striatum, corpus callosum, thalamus, and midbrain are potentially important neural substrates in the formation or modulation of tic symptoms. The limbic system, including the hypothalamus and cingulate, and the caudate nucleus, seem to be important in the neurobiology of OCD. All structures are neuroanatomically and functionally related to the corticostriato-thalamocortical circuitry that is thought to subserve symptom generation in both GTS and OCD. CONCLUSION: Although the malignancies were not likely to have caused the tic and OCD symptoms in these children, the locations of these intracranial lesions provide important clues in identifying brain regions that may contribute to the determination of tic and OCD severities.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander G. E., Crutcher M. D., DeLong M. R. Basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits: parallel substrates for motor, oculomotor, "prefrontal" and "limbic" functions. Prog Brain Res. 1990;85:119–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer L., Rauch S. L., Ballantine H. T., Jr, Martuza R., Cosgrove R., Cassem E., Giriunas I., Manzo P. A., Dimino C., Jenike M. A. Cingulotomy for intractable obsessive-compulsive disorder. Prospective long-term follow-up of 18 patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995 May;52(5):384–392. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950170058008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates J. F., Goldman-Rakic P. S. Prefrontal connections of medial motor areas in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Oct 8;336(2):211–228. doi: 10.1002/cne.903360205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter L. R., Jr, Schwartz J. M., Bergman K. S., Szuba M. P., Guze B. H., Mazziotta J. C., Alazraki A., Selin C. E., Ferng H. K., Munford P. Caudate glucose metabolic rate changes with both drug and behavior therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Sep;49(9):681–689. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820090009002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet K. A. Neurobiological dissection of Tourette syndrome: a neurochemical focus on a human neuroanatomical model. Adv Neurol. 1982;35:77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun A. R., Stoetter B., Randolph C., Hsiao J. K., Vladar K., Gernert J., Carson R. E., Herscovitch P., Chase T. N. The functional neuroanatomy of Tourette's syndrome: an FDG-PET study. I. Regional changes in cerebral glucose metabolism differentiating patients and controls. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1993 Dec;9(4):277–291. doi: 10.1038/npp.1993.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T. N., Geoffrey V., Gillespie M., Burrows G. H. Structural and functional studies of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1986;142(11):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E., Comings B. G. A controlled study of Tourette syndrome. I. Attention-deficit disorder, learning disorders, and school problems. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;41(5):701–741. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devinsky O. Neuroanatomy of Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. Possible midbrain involvement. Arch Neurol. 1983 Aug;40(8):508–514. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04210070048013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassler R., Dieckmann G. Traitement stéréotaxique des tics et cris inarticulés ou coprolaliques considérés comme phénomène d'obsession motrice au cours de la maladie de Gilles de la Tourette. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1970 Aug;123(2):89–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazrati L. N., Parent A. Contralateral pallidothalamic and pallidotegmental projections in primates: an anterograde and retrograde labeling study. Brain Res. 1991 Dec 20;567(2):212–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90798-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde T. M., Stacey M. E., Coppola R., Handel S. F., Rickler K. C., Weinberger D. R. Cerebral morphometric abnormalities in Tourette's syndrome: a quantitative MRI study of monozygotic twins. Neurology. 1995 Jun;45(6):1176–1182. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.6.1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel T. R. Toward a neuroanatomy of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Sep;49(9):739–744. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820090067011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korzen' A. V., Pushkov V. V., Kharitonov R. A., Shustin V. A. Stereotaksicheskaia talamotomiia v kompleksnom lechenii bolezni Zhilia de lia Turetta. Zh Nevropatol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 1991;91(3):100–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlan R., Kersun J., Ballantine H. T., Jr, Caine E. D. Neurosurgical treatment of severe obsessive-compulsive disorder associated with Tourette's syndrome. Mov Disord. 1990;5(2):152–155. doi: 10.1002/mds.870050211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakke J. P., Wilmink J. T. A case of Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome with midbrain involvement. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985 Dec;48(12):1293–1296. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.12.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckman J. F., Goodman W. K., North W. G., Chappell P. B., Price L. H., Pauls D. L., Anderson G. M., Riddle M. A., McSwiggan-Hardin M., McDougle C. J. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid levels of oxytocin in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Comparison with Tourette's syndrome and healthy controls. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Oct;51(10):782–792. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950100030003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckman J. F., Knorr A. M., Rasmusson A. M., Cohen D. J. Basal ganglia research and Tourette's syndromes. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Mar;14(3):94–94. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckman J. F., Peterson B. S. The pathogenesis of Tourette's syndrome: epigenetic factors active in early CNS development. Biol Psychiatry. 1993 Oct 1;34(7):425–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(93)90232-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckman J. F., de Lotbinière A. J., Marek K., Gracco C., Scahill L., Cohen D. J. Severe disturbances in speech, swallowing, and gait following stereotactic infrathalamic lesions in Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome. Neurology. 1993 May;43(5):890–894. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEAN P. D., DELGADO J. M. R. Electrical and chemical stimulation of frontotemporal portion of limbic system in the waking animal. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1953 Feb;5(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(53)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire P. K., Bates J. F., Goldman-Rakic P. S. Interhemispheric integration: II. Symmetry and convergence of the corticostriatal projections of the left and the right principal sulcus (PS) and the left and the right supplementary motor area (SMA) of the rhesus monkey. Cereb Cortex. 1991 Sep-Oct;1(5):408–417. doi: 10.1093/cercor/1.5.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A., Hazrati L. N. Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. I. The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1995 Jan;20(1):91–127. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(94)00007-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Hurst C. R., Kruger S. D., Leckman J. F., Kidd K. K., Cohen D. J. Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome and attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity. Evidence against a genetic relationship. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1986 Dec;43(12):1177–1179. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1986.01800120063012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Leckman J. F., Cohen D. J. Familial relationship between Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome, attention deficit disorder, learning disabilities, speech disorders, and stuttering. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1993 Sep;32(5):1044–1050. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199309000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Raymond C. L., Stevenson J. M., Leckman J. F. A family study of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):154–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Towbin K. E., Leckman J. F., Zahner G. E., Cohen D. J. Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Evidence supporting a genetic relationship. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1986 Dec;43(12):1180–1182. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1986.01800120066013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson B. S., Leckman J. F., Duncan J. S., Wetzles R., Riddle M. A., Hardin M. T., Cohen D. J. Corpus callosum morphology from magnetic resonance images in Tourette's syndrome. Psychiatry Res. 1994 Jun;55(2):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0925-4927(94)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson B., Riddle M. A., Cohen D. J., Katz L. D., Smith J. C., Hardin M. T., Leckman J. F. Reduced basal ganglia volumes in Tourette's syndrome using three-dimensional reconstruction techniques from magnetic resonance images. Neurology. 1993 May;43(5):941–949. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.5.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. A., Kidd K. K., Cohen D. J., Pauls D. L., Leckman J. F. A twin study of Tourette syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985 Aug;42(8):815–820. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790310077011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch S. L., Baer L., Cosgrove G. R., Jenike M. A. Neurosurgical treatment of Tourette's syndrome: a critical review. Compr Psychiatry. 1995 Mar-Apr;36(2):141–156. doi: 10.1016/s0010-440x(95)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch S. L., Jenike M. A., Alpert N. M., Baer L., Breiter H. C., Savage C. R., Fischman A. J. Regional cerebral blood flow measured during symptom provocation in obsessive-compulsive disorder using oxygen 15-labeled carbon dioxide and positron emission tomography. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Jan;51(1):62–70. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950010062008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle M. A., Rasmusson A. M., Woods S. W., Hoffer P. B. SPECT imaging of cerebral blood flow in Tourette syndrome. Adv Neurol. 1992;58:207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M., Doran M., Trimble M., Lees A. J. The treatment of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome by limbic leucotomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Aug;53(8):691–694. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.8.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer H. S., Reiss A. L., Brown J. E., Aylward E. H., Shih B., Chee E., Harris E. L., Reader M. J., Chase G. A., Bryan R. N. Volumetric MRI changes in basal ganglia of children with Tourette's syndrome. Neurology. 1993 May;43(5):950–956. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.5.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R. M., Parker B. A., Szechtman H. Role of the corpus callosum in expression of behavioral asymmetries induced by a unilateral dopamine lesion of the substantia nigra in the rat. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 23;609(1-2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90895-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swedo S. E., Pietrini P., Leonard H. L., Schapiro M. B., Rettew D. C., Goldberger E. L., Rapoport S. I., Rapoport J. L., Grady C. L. Cerebral glucose metabolism in childhood-onset obsessive-compulsive disorder. Revisualization during pharmacotherapy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Sep;49(9):690–694. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820090018003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talairach J., Bancaud J., Geier S., Bordas-Ferrer M., Bonis A., Szikla G., Rusu M. The cingulate gyrus and human behaviour. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1973 Jan;34(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(73)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Divitiis E., D'Errico A., Cerillo A. Stereotactic surgery in Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1977;(Suppl 24):73–73. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-8482-0_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]