Abstract
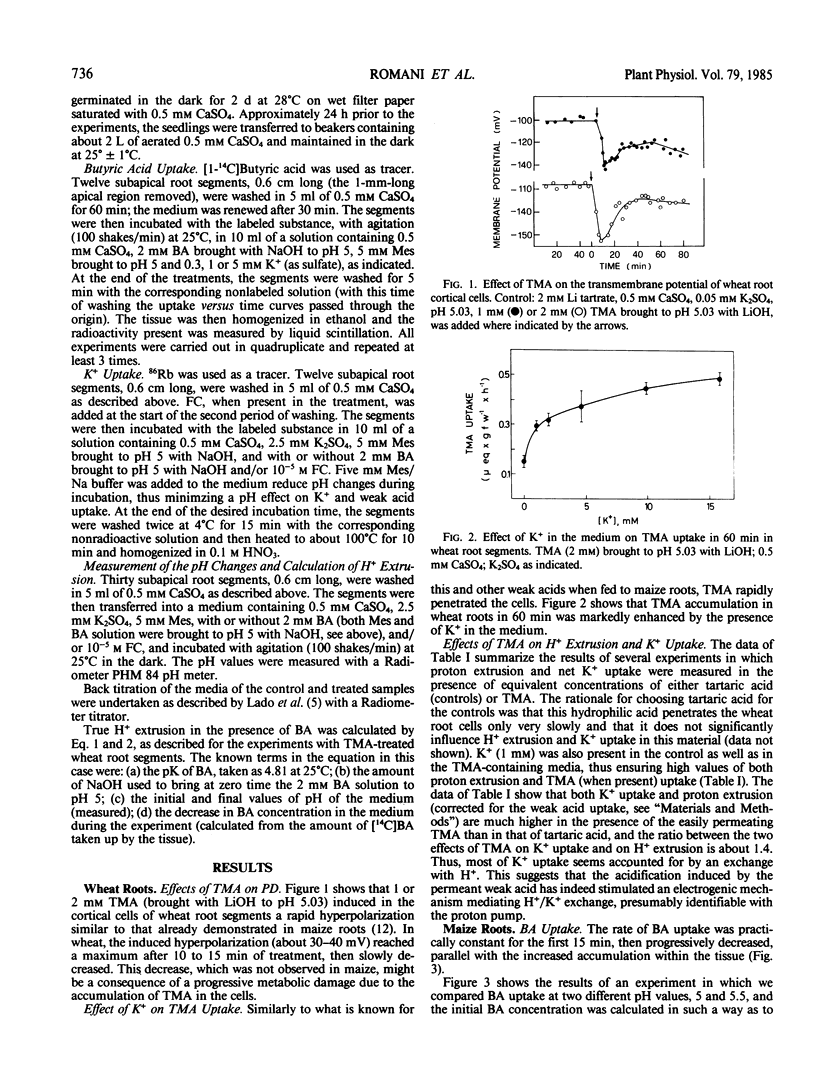
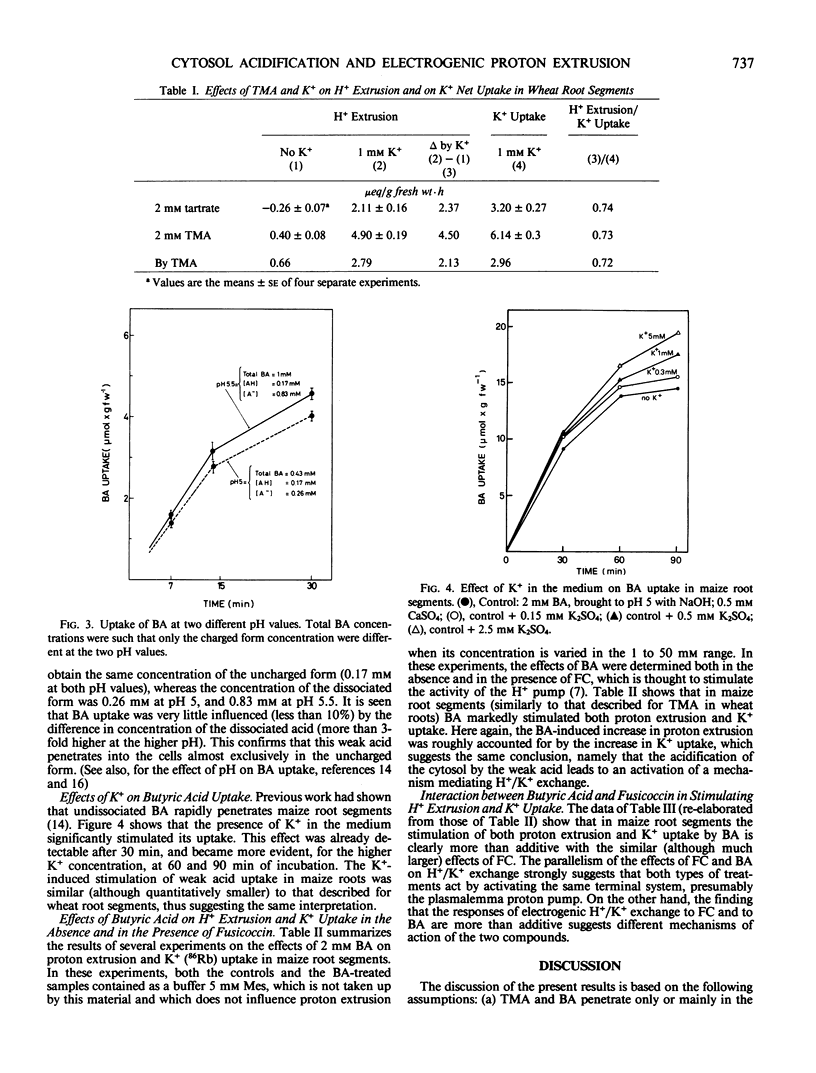
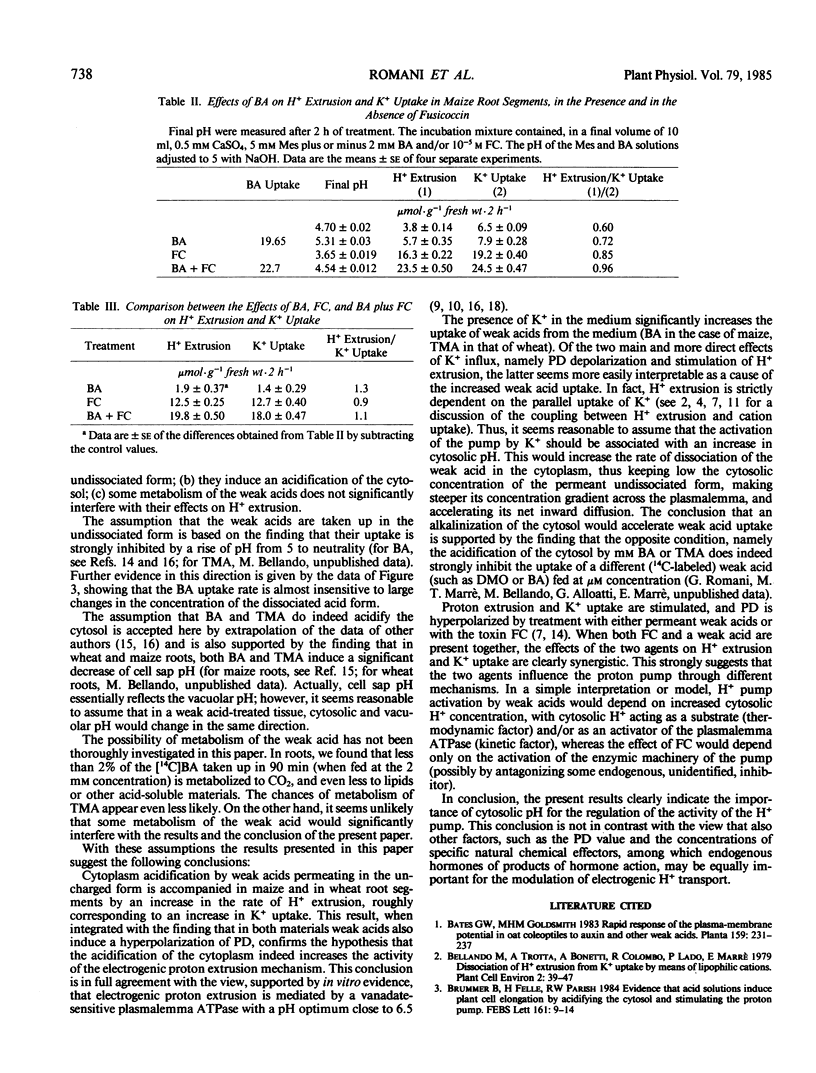
The rapid uptake of weak acids permeant in the uncharged form is accompanied in maize and wheat root segments by a hyperpolarization of the transmembrane electrical potential and an increase in K+ uptake, suggesting a stimulation of the plasmalemma H+ pump. The evaluation of weak acid-induced H+ extrusion must take into account the alkalinization of the medium due to the rapid uptake of the uncharged form of the acid, partially masking the proton pump-mediated extrusion of H+. The data corrected for this interference show that the lipophilic butyric acid and trimethyl acetic acid induce in maize and in wheat root segments a significant increase in `real' H+ extrusion, roughly matching the increase in net K+ uptake. The presence of K+ significantly increases the rate of uptake of the weak acid, possibly as a consequence of an alkalinization of the cytosol associated with K+ absorption. In maize root segments, the effects of fusicoccin and those of butyric acid on both K+ uptake and H+ extrusion are clearly synergistic, thus suggesting distinct modes of action. These results support the view that the activity of the plasmalemma H+ pump is regulated by the value of cytosolic pH.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Sanders D., Hansen U. P., Slayman C. L. Role of the plasma membrane proton pump in pH regulation in non-animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5903–5907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Partial purification and properties of the proton-translocating ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12826–12830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


