Abstract
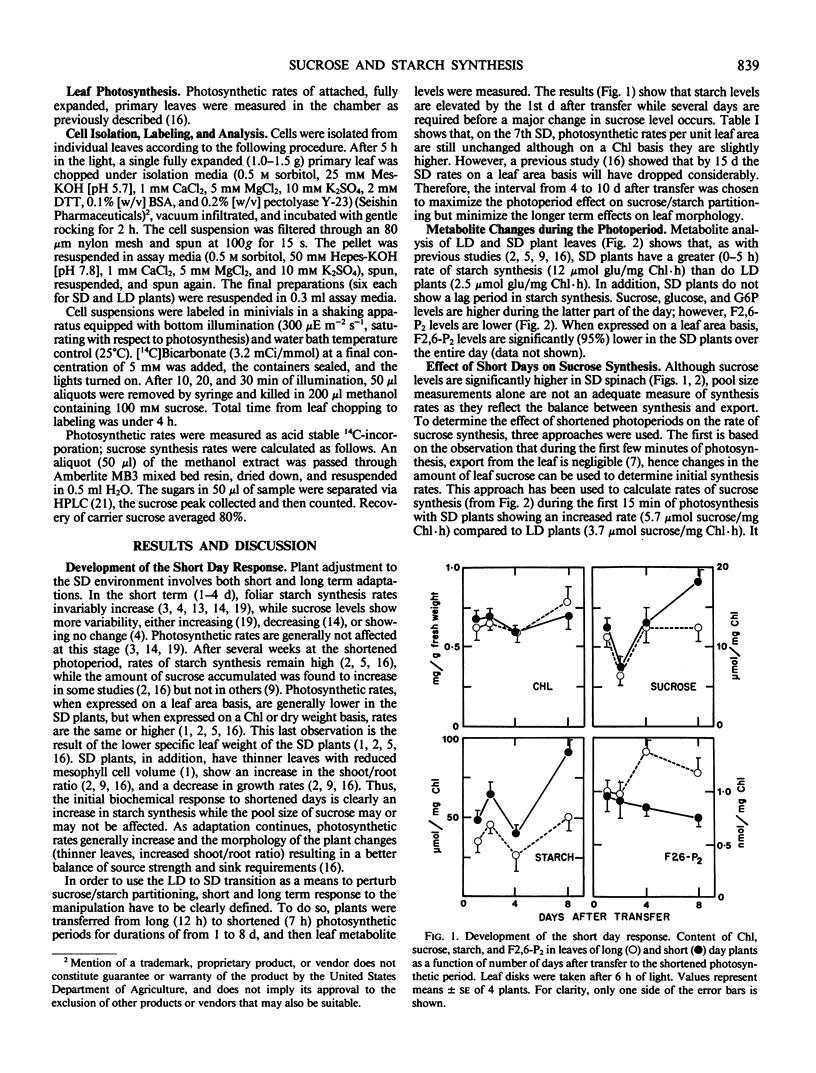
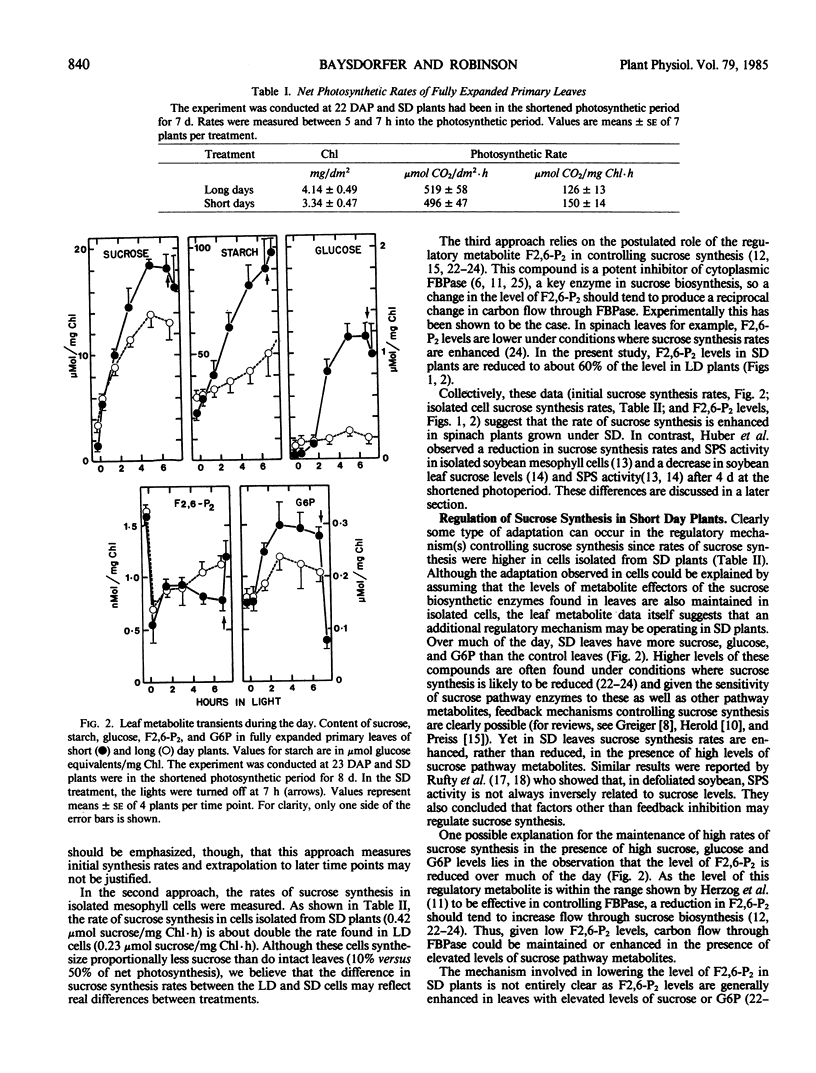
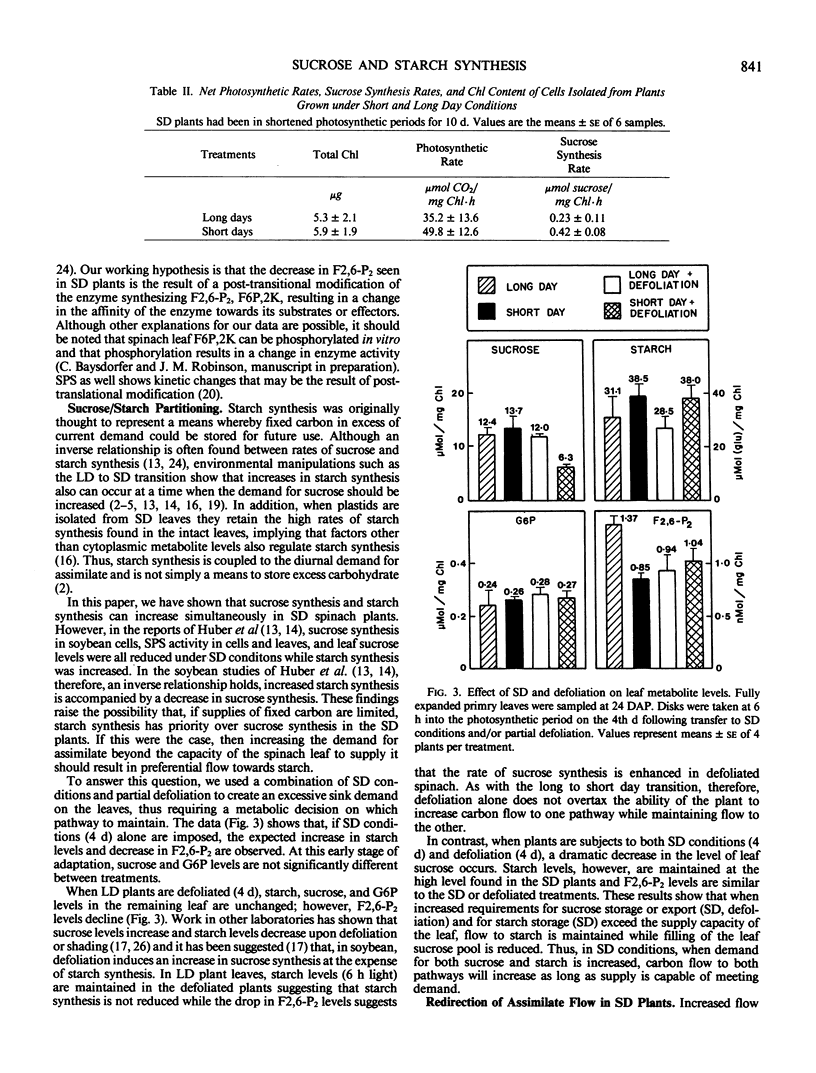
The flow of carbon into sucrose and starch was investigated in fully expanded primary leaves of spinach using the long to short day transition and partial defoliation as tools to manipulate sucrose/starch synthesis. Transfer from 12 hour to 7 hour photosynthetic periods resulted in a 4-fold increase in the initial rate of starch synthesis, a 50% increase in the initial rate of sucrose synthesis, a 30% increase in leaf sucrose, and a 40% decrease in fructose, 2,6-biphosphate. In addition, sucrose synthesis rates in cells isolated from shortened daylength plants are 80% higher than in cells isolated from control plants. These results show that, in spinach, an increase in the rates of both sucrose and starch synthesis can occur under short day conditions. In contrast, when short day plants are partially defoliated, starch levels remain high, fructose 2,6-biphosphate levels remain low, but the level of leaf sucrose drops by 50%. Thus, when demand exceeds supply, starch synthesis has priority over filling of leaf sucrose pools in the short day plant.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatterton N. J., Silvius J. E. Photosynthate Partitioning into Starch in Soybean Leaves: I. Effects of Photoperiod versus Photosynthetic Period Duration. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):749–753. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterton N. J., Silvius J. E. Photosynthate Partitioning into Starch in Soybean Leaves: II. IRRADIANCE LEVEL AND DAILY PHOTOSYNTHETIC PERIOD DURATION EFFECTS. Plant Physiol. 1981 Feb;67(2):257–260. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cséke C., Weeden N. F., Buchanan B. B., Uyeda K. A special fructose bisphosphate functions as a cytoplasmic regulatory metabolite in green leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog B., Stitt M., Heldt H. W. Control of Photosynthetic Sucrose Synthesis by Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphate : III. Properties of the Cytosolic Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphatase. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):561–565. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. C., Bickett D. M. Evidence for control of carbon partitioning by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):445–447. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. C., Israel D. W. Biochemical Basis for Partitioning of Photosynthetically Fixed Carbon between Starch and Sucrose in Soybean (Glycine max Merr.) Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1982 Mar;69(3):691–696. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. C., Rufty T. W., Kerr P. S. Effect of Photoperiod on Photosynthate Partitioning and Diurnal Rhythms in Sucrose Phosphate Synthase Activity in Leaves of Soybean (Glycine max L. [Merr.]) and Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1080–1084. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. M. Photosynthetic Carbon Metabolism in Leaves and Isolated Chloroplasts from Spinach Plants Grown under Short and Intermediate Photosynthetic Periods. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):397–409. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rufty T. W., Huber S. C. Changes in Starch Formation and Activities of Sucrose Phosphate Synthase and Cytoplasmic Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in Response to Source-Sink Alterations. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jun;72(2):474–480. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Kremer D. F. Changes of Sucrose-Phosphate Synthase Activity in Barley Primary Leaves during Light/Dark Transitions. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):910–912. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Kremer D. F., Harris W. G. Diurnal carbohydrate metabolism of barley primary leaves. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):165–169. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Gerhardt R., Kürzel B., Heldt H. W. A role for fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the regulation of sucrose synthesis in spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1139–1141. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Herzog B., Heldt H. W. Control of Photosynthetic Sucrose Synthesis by Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphate : I. Coordination of CO(2) Fixation and Sucrose Synthesis. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):548–553. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Kürzel B., Heldt H. W. Control of Photosynthetic Sucrose Synthesis by Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphate : II. Partitioning between Sucrose and Starch. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):554–560. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne J. H., Koller H. R. Influence of assimilate demand on photosynthesis, diffusive resistances, translocation, and carbohydrate levels of soybean leaves. Plant Physiol. 1974 Aug;54(2):201–207. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Lederer B., Bartrons R., Hers H. G. A kinetic study of pyrophosphate: fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase from potato tubers. Application to a microassay of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


