Abstract
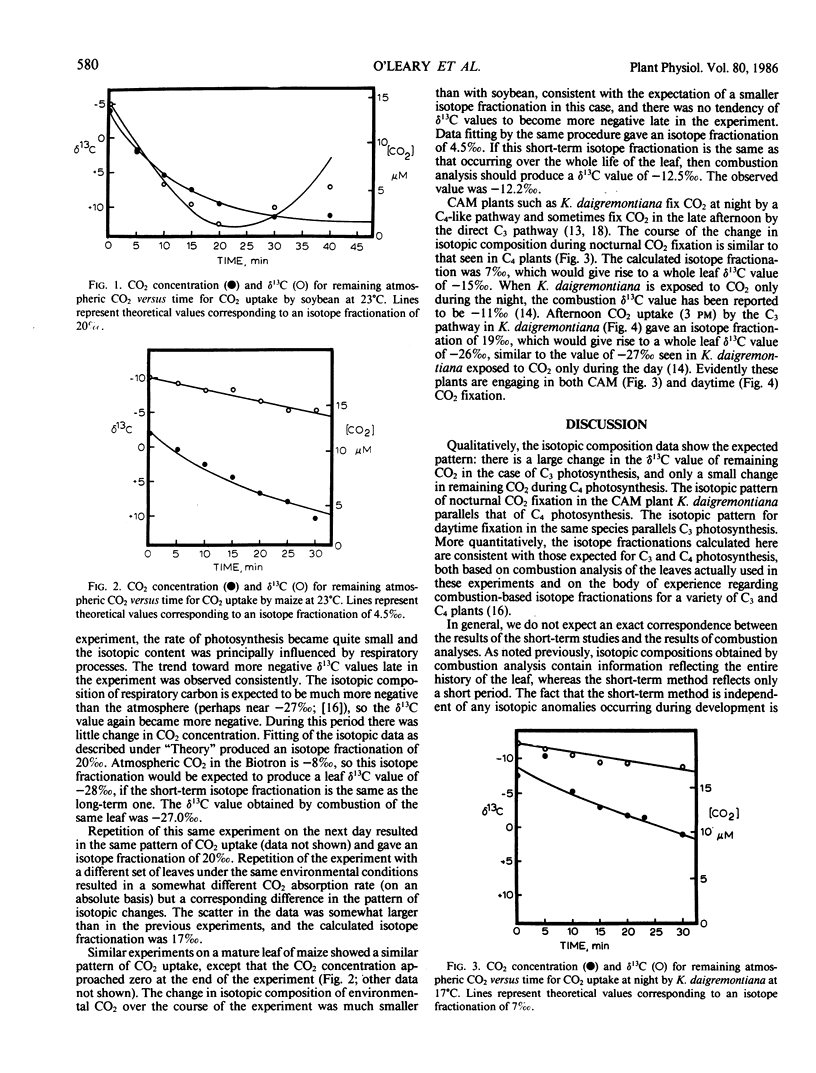
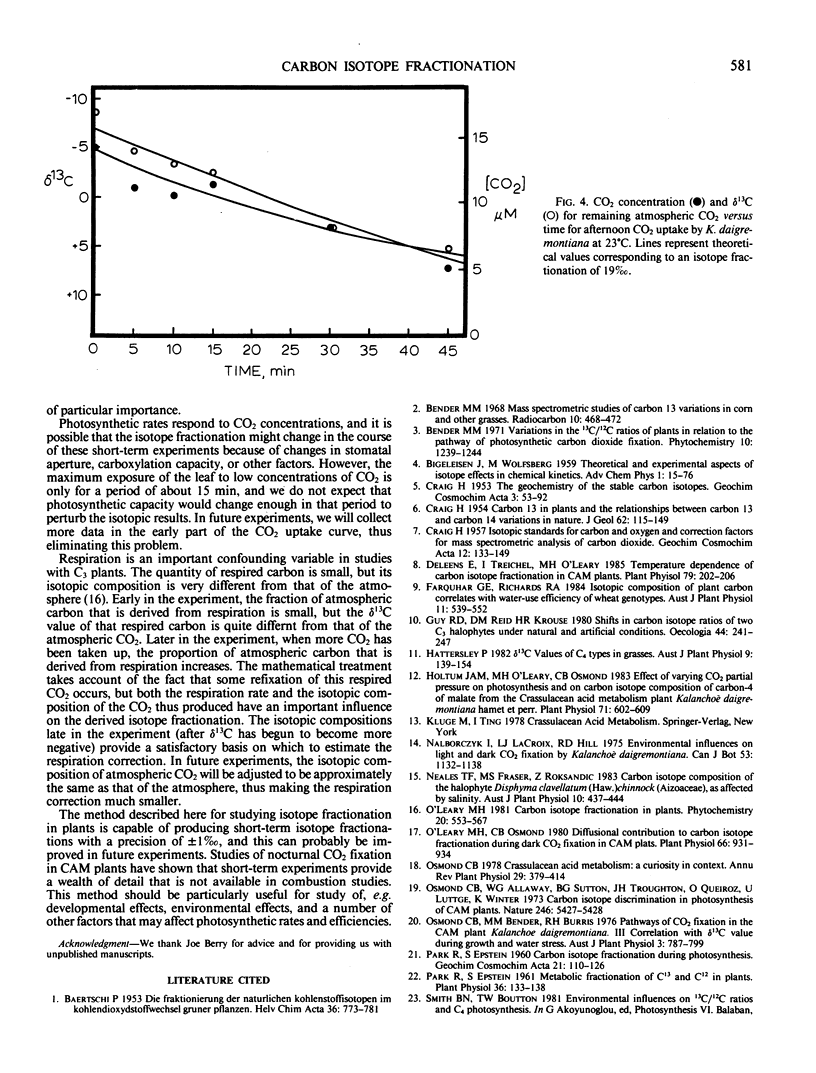
Combustion-based studies of the carbon-13 content of plants give only an integrated, long-term value for the isotope fractionation associated with photosynthesis. A method is described here which permits determination of this isotope fractionation in 2 to 3 hours. To accomplish this, the plant is enclosed in a glass chamber, and the quantity and isotopic content of the CO2 remaining in the atmosphere are monitored during photosynthesis. Isotope fractionation studies by this method give results consistent with what is expected from combustion studies of C3, C4, and Crassulacean acid metabolism plants. This method will make possible a variety of new studies of environmental and species effects in carbon isotope fractionation.
Full text
PDF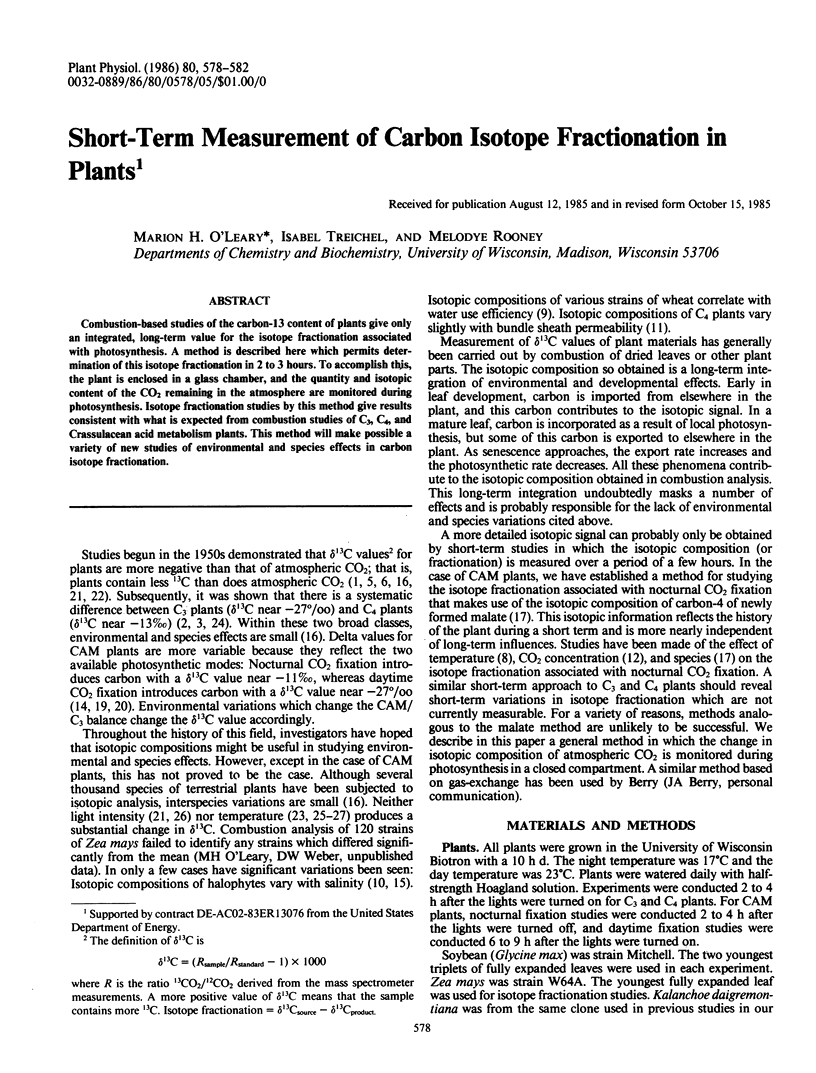


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deleens E., Treichel I., O'leary M. H. Temperature Dependence of Carbon Isotope Fractionation in CAM Plants. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):202–206. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtum J. A., O'leary M. H., Osmond C. B. Effect of Varying CO(2) Partial Pressure on Photosynthesis and on Carbon Isotope Composition of Carbon-4 of Malate from the Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Plant Kalanchoë daigremontiana Hamet et Perr. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):602–609. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'leary M. H., Osmond C. B. Diffusional Contribution to Carbon Isotope Fractionation during Dark CO(2) Fixation in CAM Plants. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):931–934. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park R., Epstein S. Metabolic fractionation of C & C in plants. Plant Physiol. 1961 Mar;36(2):133–138. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


