Abstract
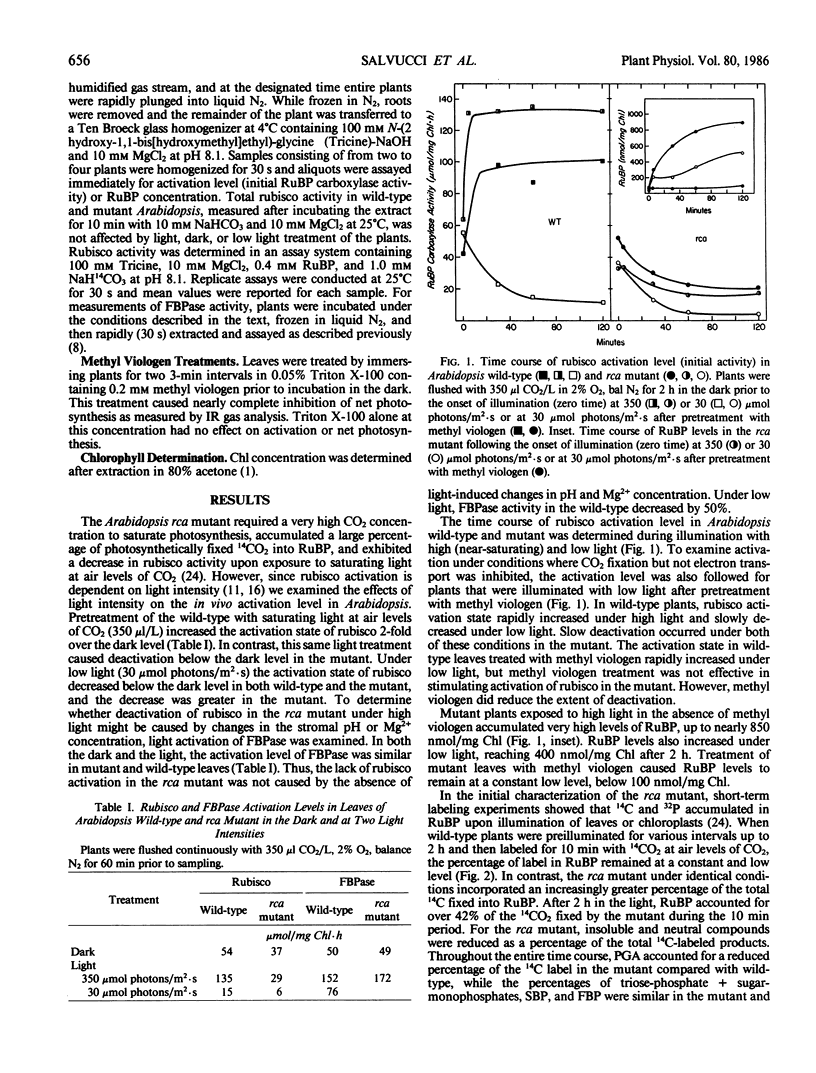
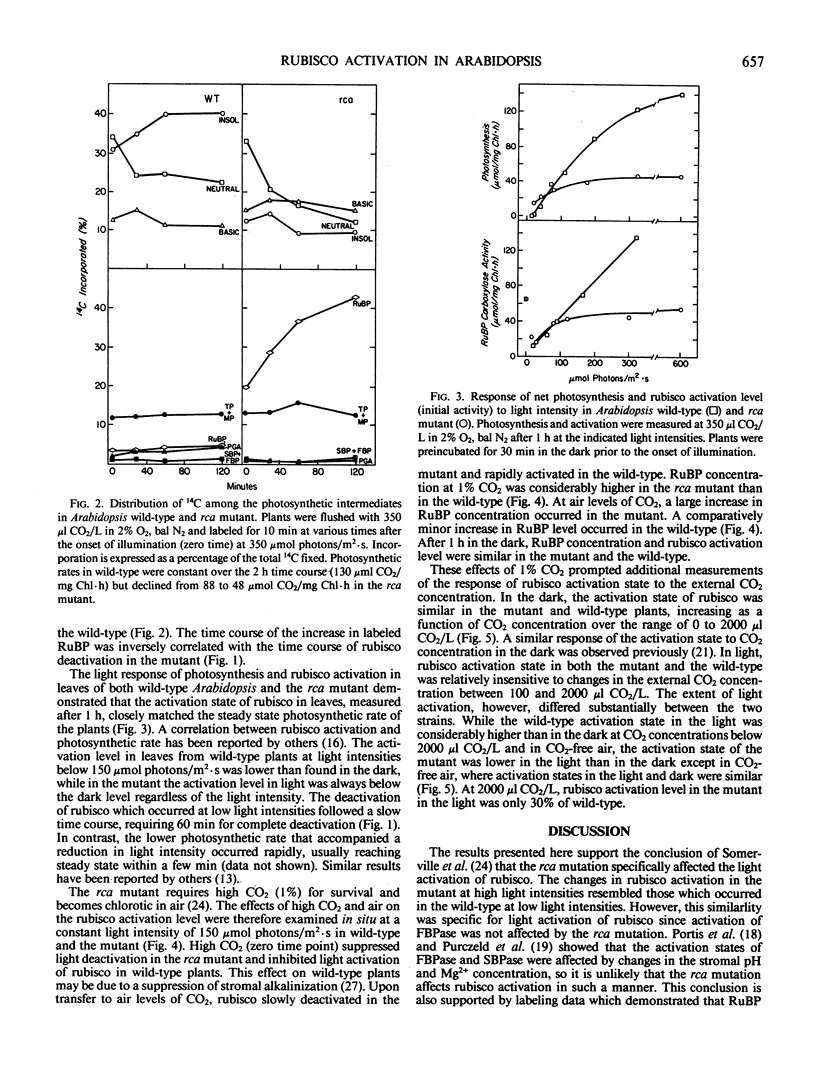
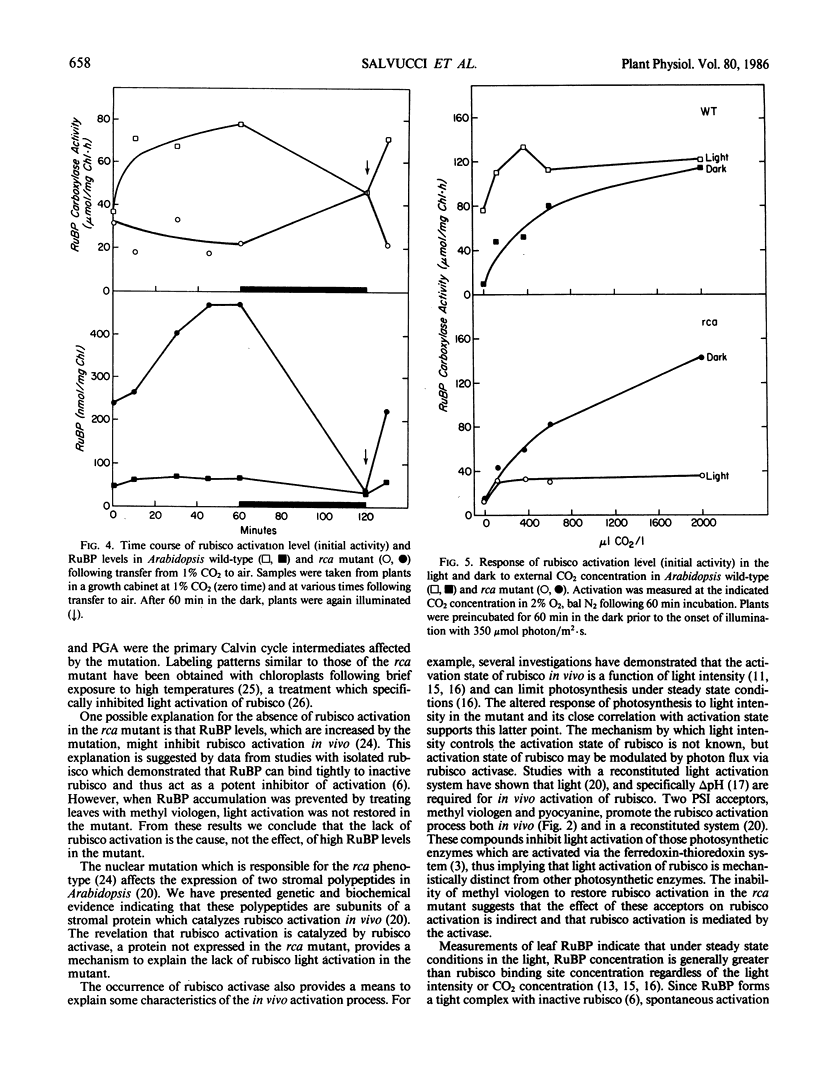
The requirements for activation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) were investigated in leaves of Arabidopsis wild-type and a mutant incapable of light activating rubisco in vivo. Upon illumination with saturating light intensities, the activation state of rubisco increased 2-fold in the wild-type and decreased in the mutant. Activation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate phosphatase was unaffected by the mutation. Under low light, rubisco deactivated in both the wild-type and the mutant. Deactivation of rubisco in the mutant under high and low light led to the accumulation of high concentrations of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. Inhibiting photosynthesis with methyl viologen prevented ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate accumulation but was ineffective in restoring rubisco activation to the mutant. Net photosynthesis and the rubisco activation level were closely correlated and saturated at a lower light intensity in the mutant than in wild-type. At CO2 concentrations between 100 and 2000 microliters per liter, the activation state was a function of the CO2 concentration in the dark but was independent of CO2 concentration in the light. High CO2 concentration (1%) suppressed activation in the wild-type and deactivation in the mutant. These results support the concept that rubisco activation in vivo is not a spontaneous process but is catalyzed by a specific protein. The absence of this protein, rubisco activase, is responsible for the altered characteristics of rubisco activation in the mutant.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahr J. T., Jensen R. G. Activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in intact chloroplasts by CO2 and light. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 15;185(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Ogren W. L. A Sensitive Assay Procedure for Simultaneous Determination of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase and Oxygenase Activities. Plant Physiol. 1981 Feb;67(2):237–245. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Miziorko H. M. Carbamate formation on the epsilon-amino group of a lysyl residue as the basis for the activation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by CO2 and Mg2+. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5321–5328. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Lorimer G. H. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:507–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Jensen R. G., O'leary J. W., Berry J. A. Photosynthesis and Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Concentrations in Intact Leaves of Xanthium strumarium L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):968–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Jensen R. G. Photosynthesis and Activation of Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase in Wheat Seedlings : Regulation by CO(2) and O(2). Plant Physiol. 1983 Apr;71(4):955–960. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.4.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Jr, Chon C. J., Mosbach A., Heldt H. W. Fructose-and sedoheptulosebisphosphatase. The sites of a possible control of CO2 fixation by lightdependent changes of the stromal Mg2+ concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 10;461(2):313–325. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purczeld P., Chon C. J., Portis A. R., Jr, Heldt H. W., Heber U. The mechanism of the control of carbon fixation by the pH in the chloroplast stroma. Studies with nitrite-mediated proton transfer across the envelope. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 13;501(3):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Bahr J. T., Jensen R. G. Measurement of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate from spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):876–879. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville C. R., Portis A. R., Ogren W. L. A Mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana Which Lacks Activation of RuBP Carboxylase In Vivo. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):381–387. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdan K., Heldt H. W., Milovancev M. The role of pH in the regulation of carbon fixation in the chloroplast stroma. Studies on CO2 fixation in the light and dark. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 11;396(2):276–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


