Abstract
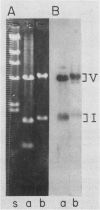
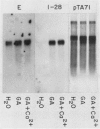
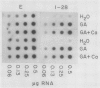
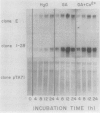
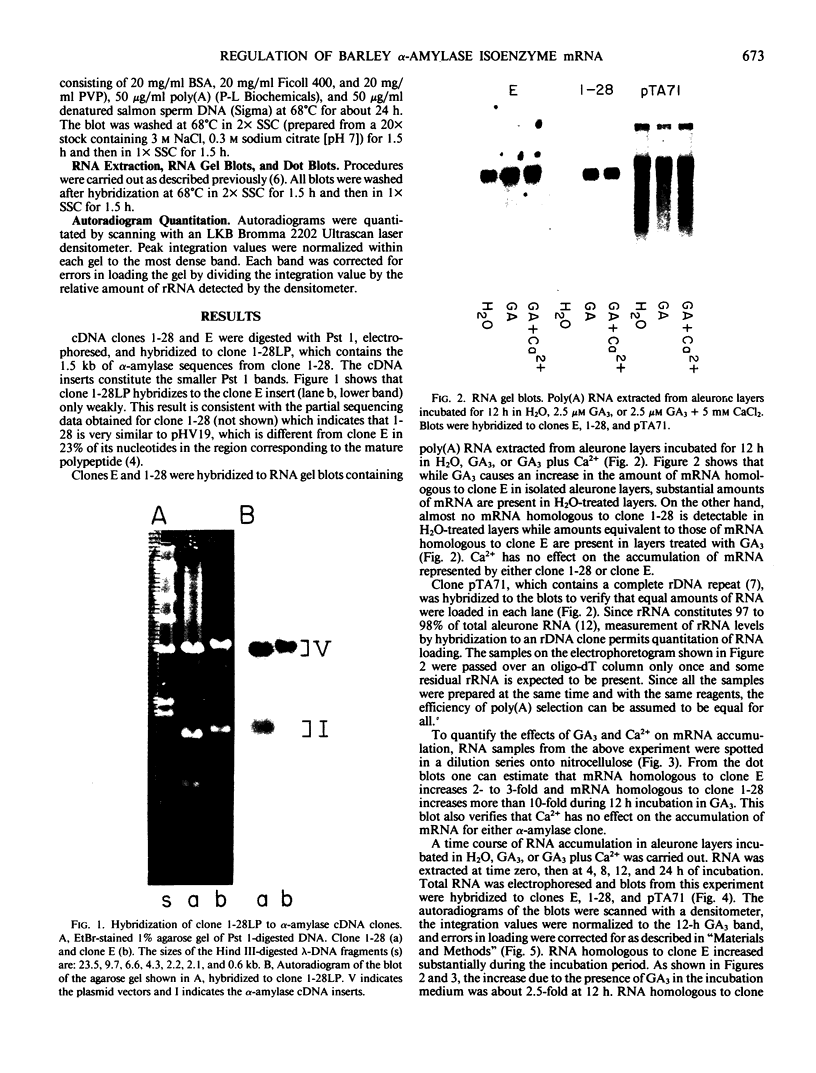
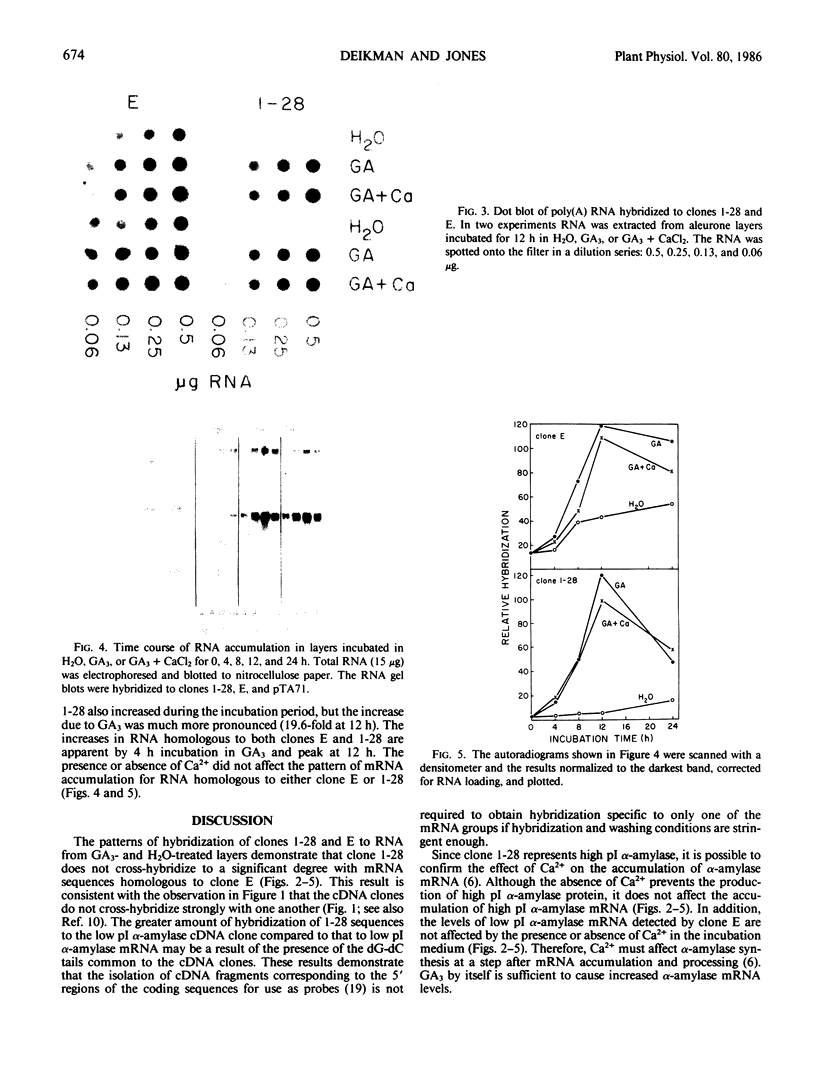
The effect of gibberellic acid and Ca2+ on the accumulation of α-amylase mRNAs in aleurone layers of barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv Himalaya) was studied using cDNA clones containing sequences of mRNAs for the high and low isoelectric point (pI) α-amylases. There is no significant hybridization between the two α-amylase cDNA clones under the hybridization and washing conditions employed. These clones were therefore used to monitor levels of mRNAs for high and low pI α-amylases. It is shown that although the synthesis of the high pI α-amylase proteins depends on the presence of Ca2+ in the incubation medium, the accumulation of mRNA for this group occurs to the same degree in the presence or the absence of Ca2+. The accumulation of low pI α-amylase mRNA is also not affected by the presence or absence of Ca2+ in the incubation medium. These results establish gibberellic acid, not Ca2+, as the principal regulator of α-amylase mRNA accumulation in barley aleurone, while Ca2+ controls high pI α-amylase synthesis at a later step in the biosynthetic pathway.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callis J., Ho T. H. Multiple molecular forms of the gibberellin-induced alpha-amylase from the aleurone layers of barley seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 1;224(1):224–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deikman J., Jones R. L. Control of alpha-amylase mRNA accumulation by gibberellic Acid and calcium in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):192–198. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach W. L., Bedbrook J. R. Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1869–1885. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. K., Swegle M., Dandekar A. M., Muthukrishnan S. Expression and regulation of alpha-amylase gene family in barley aleurones. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):579–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Higgins T. J. Characterization of the alpha-Amylases Synthesized by Aleurone Layers of Himalaya Barley in Response to Gibberellic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1647–1653. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Scandalios J. G., Varner J. E. Multiple forms of amylase induced by gibberellic acid in isolated barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1970 Apr;45(4):367–371. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. L., Carbonell J. Regulation of the synthesis of barley aleurone alpha-amylase by gibberellic Acid and calcium ions. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):213–218. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Chandra G. R., Maxwell E. S. Hormonal control of alpha-amylase gene expression in barley. Studies using a cloned CDNA probe. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2370–2375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Gill B. S., Swegle M., Chandra G. R. Structural genes for alpha-amylases are located on barley chromosomes 1 and 6. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13637–13639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Milliman C. Coordinate increase in major transcripts from the high pI alpha-amylase multigene family in barley aleurone cells stimulated with gibberellic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12234–12240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Milliman C. Isolation and sequence analysis of a barley alpha-amylase cDNA clone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8169–8174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C. Two barley alpha-amylase gene families are regulated differently in aleurone cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3731–3738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]