Abstract
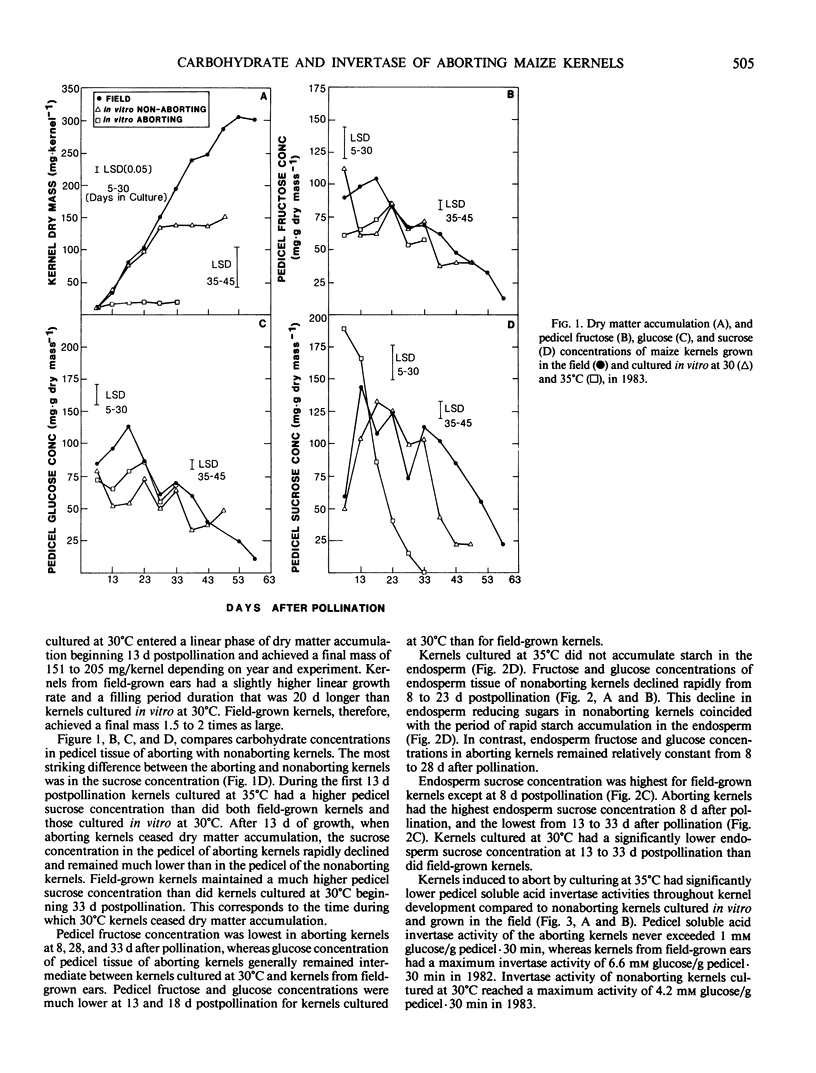
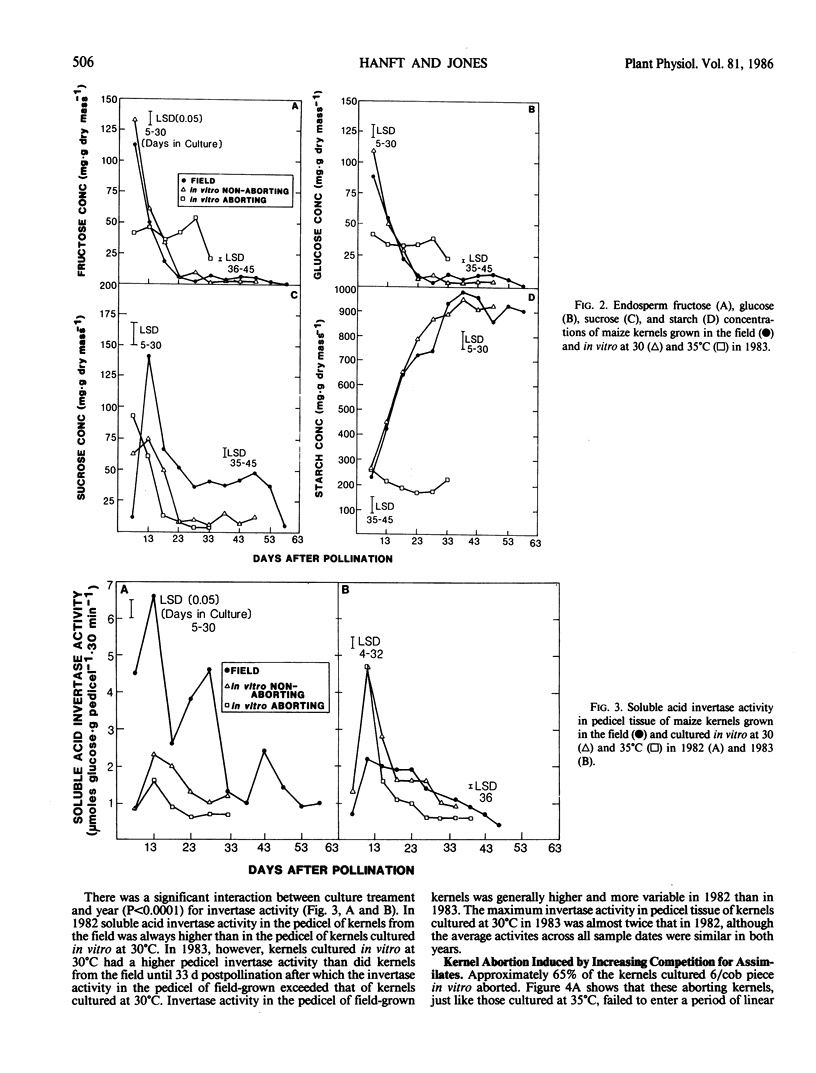
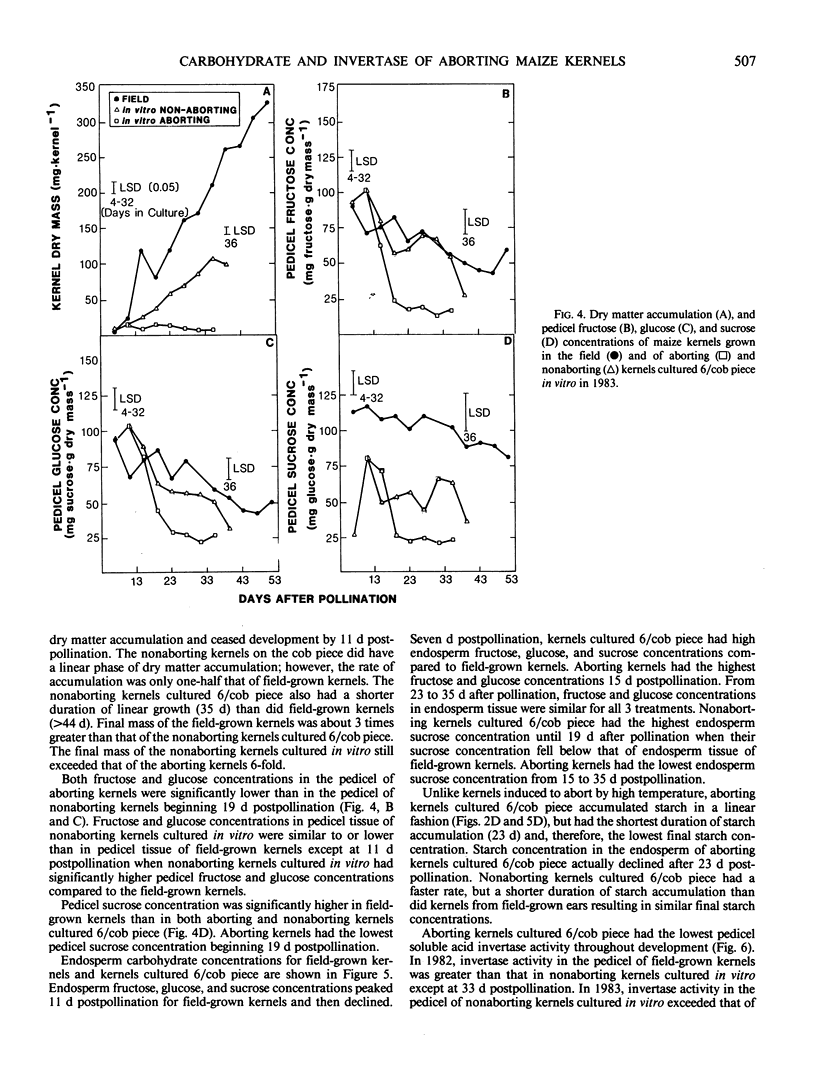
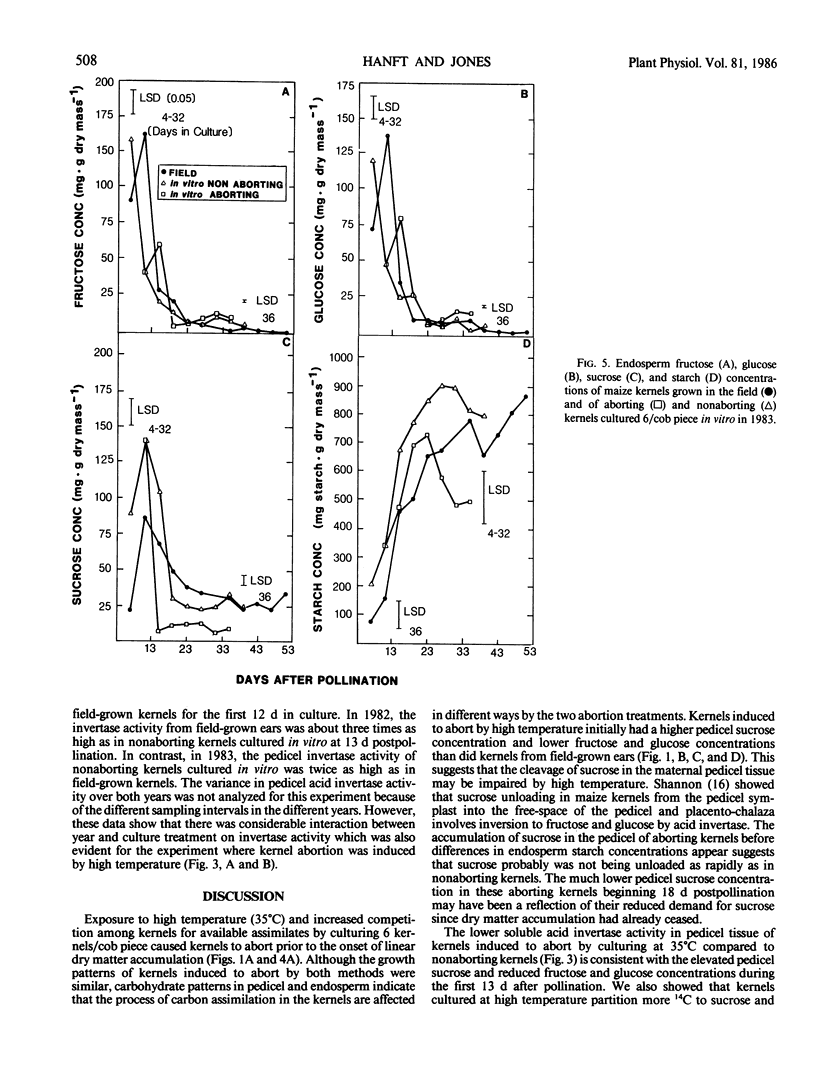
Kernels cultured in vitro were induced to abort by high temperature (35°C) and by culturing six kernels/cob piece. Aborting kernels failed to enter a linear phase of dry mass accumulation and had a final mass that was less than 6% of nonaborting field-grown kernels. Kernels induced to abort by high temperature failed to synthesize starch in the endosperm and had elevated sucrose concentrations and low fructose and glucose concentrations in the pedicel during early growth compared to nonaborting kernels. Kernels induced to abort by high temperature also had much lower pedicel soluble acid invertase activities than did nonaborting kernels. These results suggest that high temperature during the lag phase of kernel growth may impair the process of sucrose unloading in the pedicel by indirectly inhibiting soluble acid invertase activity and prevent starch synthesis in the endosperm. Kernels induced to abort by culturing six kernels/cob piece had reduced pedicel fructose, glucose, and sucrose concentrations compared to kernels from field-grown ears. These aborting kernels also had a lower pedicel soluble acid invertase activity compared to nonaborting kernels from the same cob piece and from field-grown ears. The low invertase activity in pedicel tissue of the aborting kernels was probably caused by a lack of substrate (sucrose) for the invertase to cleave due to the intense competition for available assimilates. In contrast to kernels cultured at 35°C, aborting kernels from cob pieces containing all six kernels accumulated starch in a linear fashion. These results indicate that kernels cultured six/cob piece abort because of an inadequate supply of sugar and are similar to apical kernels from field-grown ears that often abort prior to the onset of linear growth.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Felker F. C., Shannon J. C. Movement of C-labeled Assimilates into Kernels of Zea mays L: III. AN ANATOMICAL EXAMINATION AND MICROAUTORADIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF ASSIMILATE TRANSFER. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):864–870. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft J. M., Jones R. J. Kernel Abortion in Maize : II. Distribution of C among Kernel Carbohydrates. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):511–515. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Glasziou K. T. Sugar Accumulation Cycle in Sugar Cane. II. Relationship of Invertase Activity to Sugar Content & Growth Rate in Storage Tissue of Plants Grown in Controlled Environments. Plant Physiol. 1963 May;38(3):344–348. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchings S. K., del Rio C. E., Aufdemorte T. B., Meffert R. M., Lane J. J. The pulpal response to topically applied citric acid. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984 Aug;58(2):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(84)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacher J. A., Hatch M. D., Glasziou K. T. Sugar Accumulation Cycle in Sugar Cane. III. Physical & Metabolic Aspects of Cycle in Immature Storage Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1963 May;38(3):348–354. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.3.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon J. C. Movement of C-Labeled Assimilates into Kernels of Zea mays L: I. Pattern and Rate of Sugar Movement. Plant Physiol. 1972 Feb;49(2):198–202. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon J. C. Movement of C-Labeled Assimilates into Kernels of Zea mays L: II. Invertase Activity of the Pedicel and Placento-Chalazal Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1972 Feb;49(2):203–206. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


