Abstract
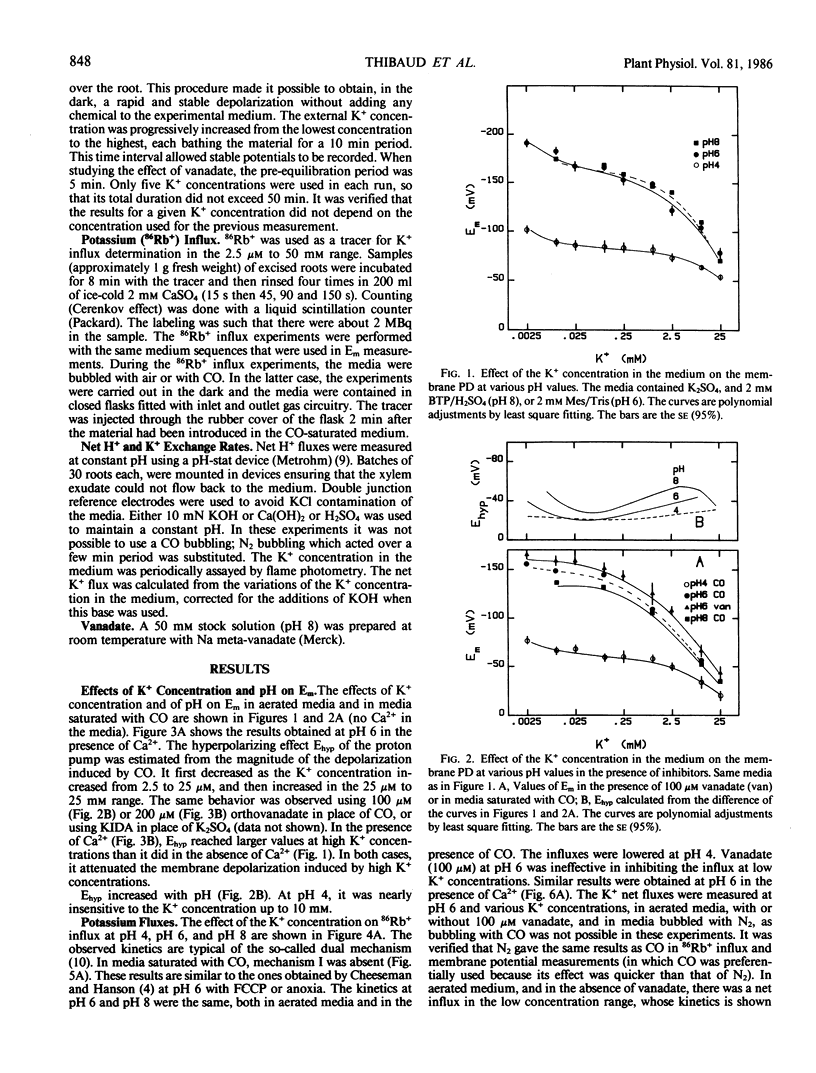
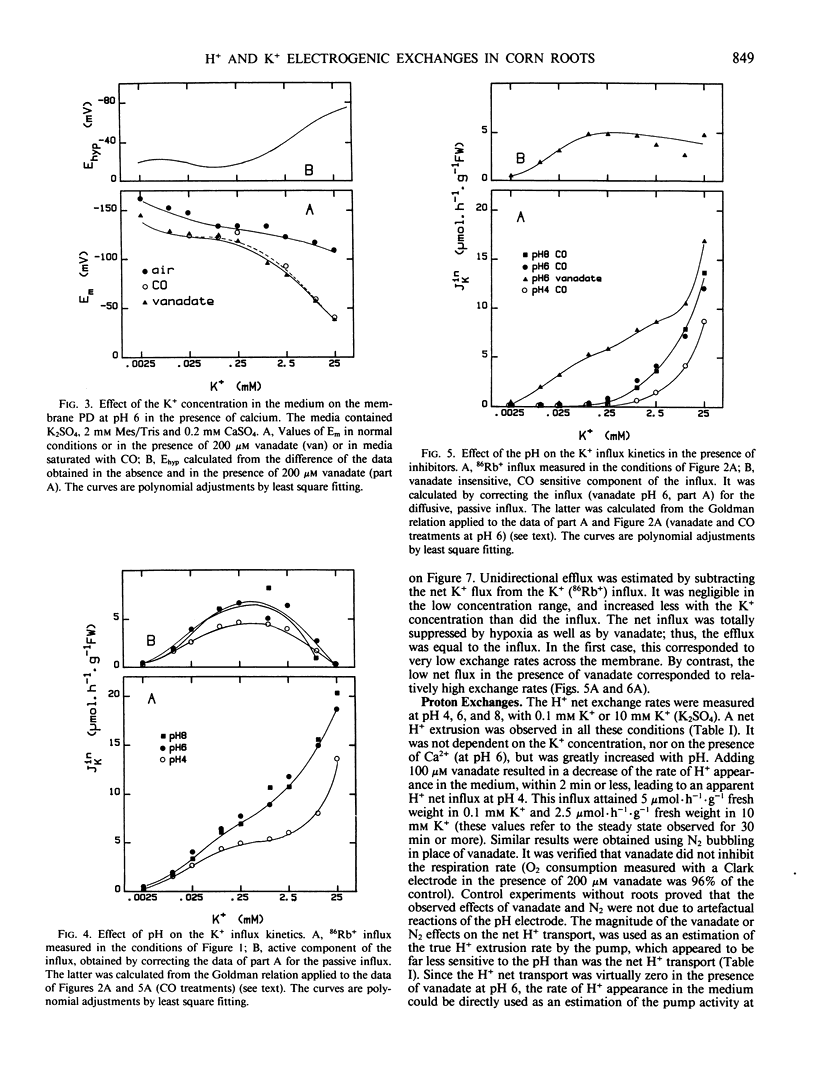
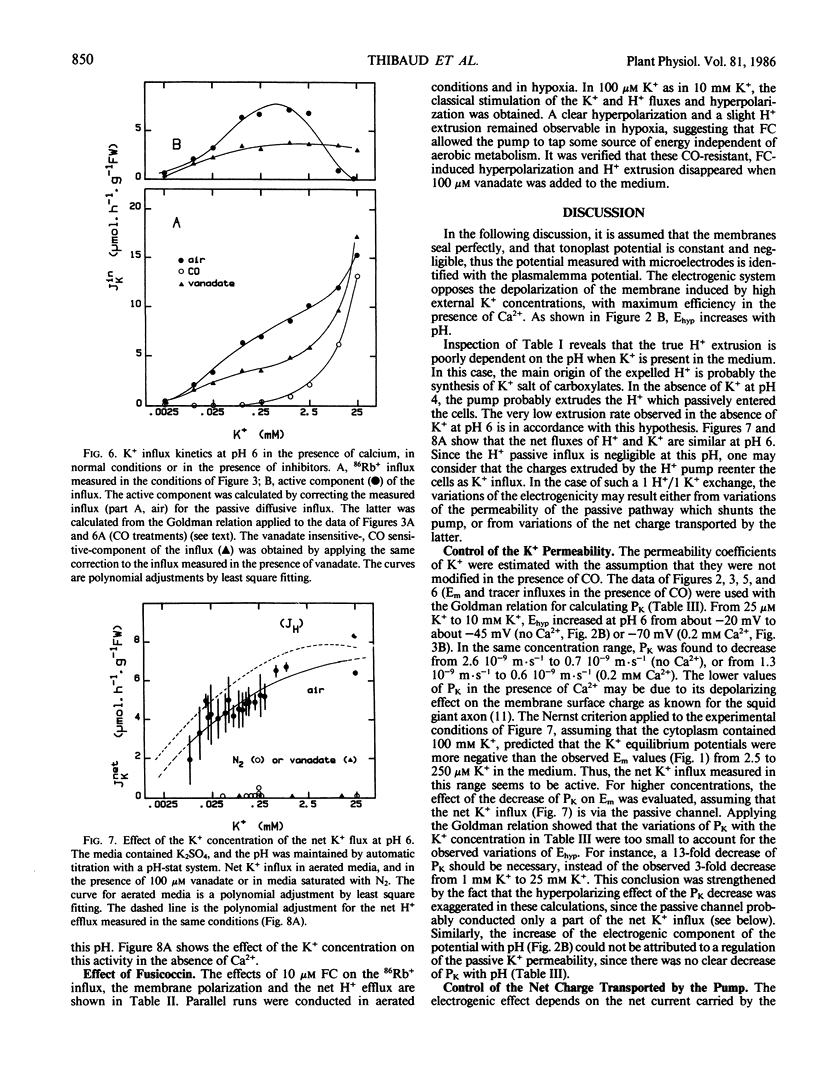
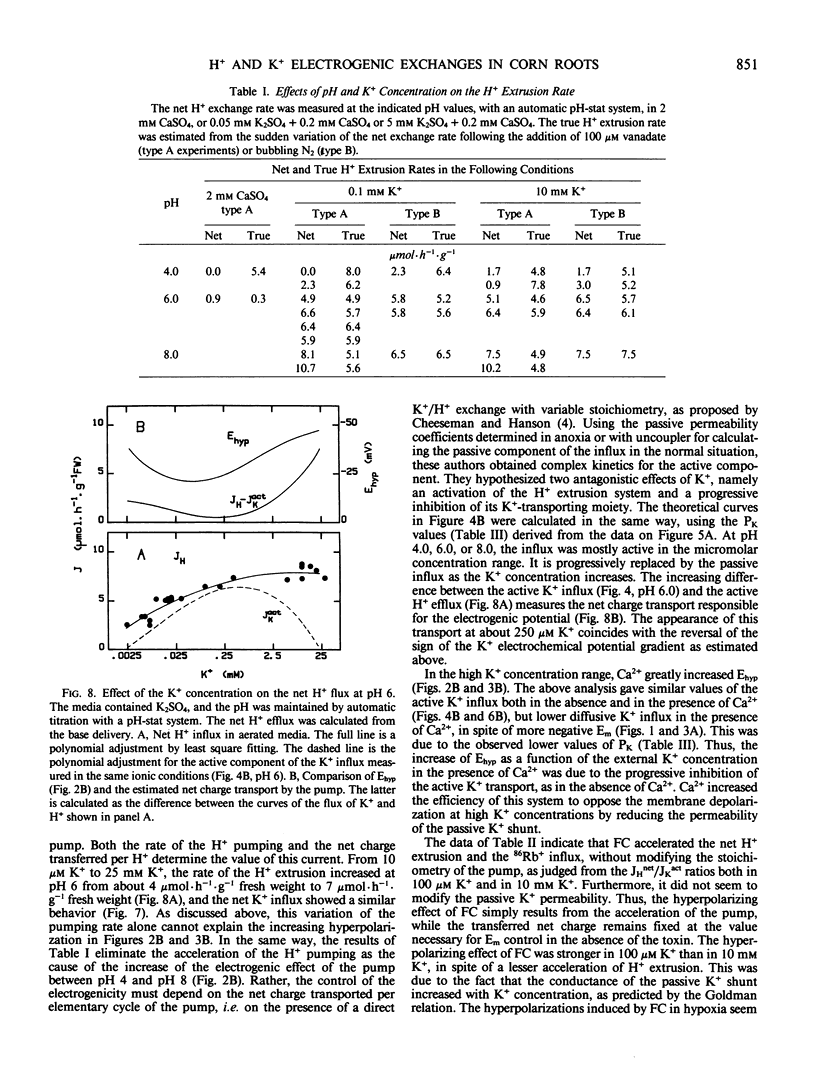
The membrane potential difference, the net H+ exchange rate, the K+ net flux, and the K+ (86Rb+) influx were measured in excised corn roots as functions of the K+ concentration in the medium at various pH values, in the presence of poorly permeant anions. The roots behaved as a K+/H+ exchange system. By comparing the results in normal or hypoxic conditions, or in the presence of vanadate, it was possible to distinguish the active components of membrane potential and transports from the passive ones. The magnitude of the electrogenic potential was not related to the active H+ extrusion rate. At pH 6, the variations of the electrogenic potential resulted from variations of the stoichiometry of the active H+/K+ exchange. The same relationship between this stoichiometry and the K+ concentration was observed in conditions ensuring different membrane polarizations (pH 6, pH 4, or pH 6 with fusicoccin). Both metabolic and Mg-ATPase specific inhibitors stopped the active H+ transport and the net K+ influx. Nevertheless, the tracer influx in the presence of vanadate remained higher than the passive influx calculated from the permeability coefficient determined in hypoxia. It is proposed that vanadate uncouples the K+ moiety of the H+/K+ antiport and allows it to mediate isotopic exchanges.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheeseman J. M., Hanson J. B. Energy-linked Potassium Influx as Related to Cell Potential in Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):842–845. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman J. M., Lafayette P. R., Gronewald J. W., Hanson J. B. Effect of ATPase inhibitors on cell potential and k influx in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jun;65(6):1139–1145. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.6.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. L., Ehrenstein G. Effect of divalent cations on potassium conductance of squid axons: determination of surface charge. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):447–463. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86396-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi-Caldogno F., Cerana R., Pugliarello M. C. Relationship between ATP Level and Activity of Fusicoccin-stimulated H/K-Exchange System in Plant Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1095–1098. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Wemmer D., Ray P. M., Jardetzky O. Regulation of Cytoplasmic and Vacuolar pH in Maize Root Tips under Different Experimental Conditions. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jun;69(6):1344–1347. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.6.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


