Abstract
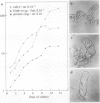
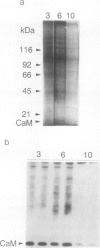
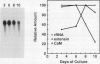
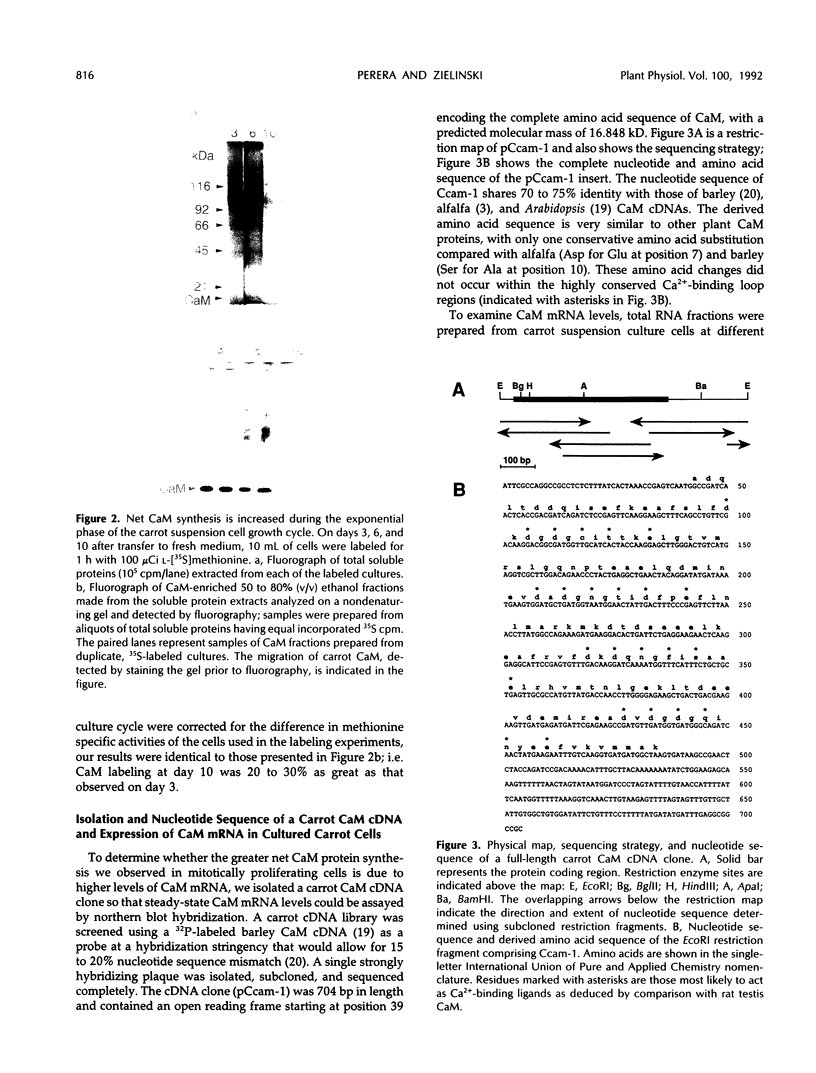
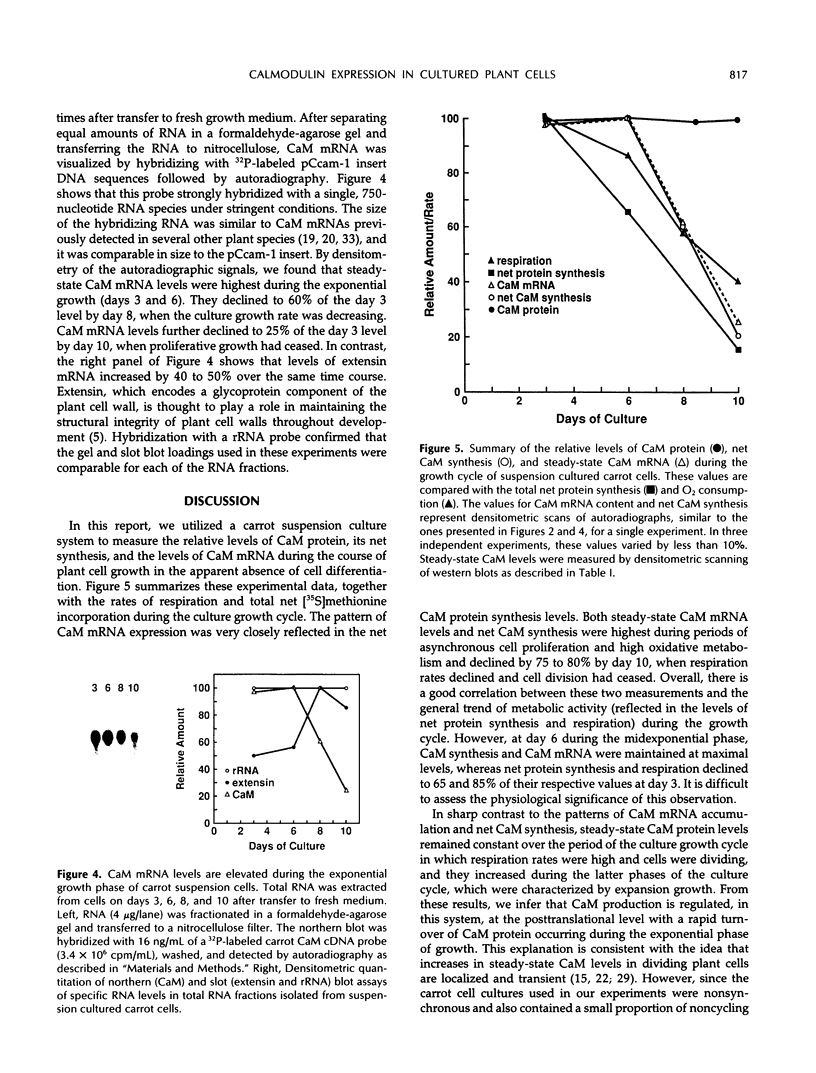
The expression of calmodulin mRNA and protein were measured during a growth cycle of carrot (Daucus carota L.) cells grown in suspension culture. A full-length carrot calmodulin cDNA clone isolated from a λgt10 library was used to measure steady-state calmodulin mRNA levels. During the exponential phase of culture growth when mitotic activity and oxidative respiration rates were maximal, calmodulin mRNA levels were 4- to 5-fold higher than they were during the later stages of culture growth, when respiration rates were lower and growth was primarily by cell expansion. Net calmodulin polypeptide synthesis, as measured by pulse-labeling in vivo with [35S]methionine, paralleled the changes in calmodulin steady-state mRNA level during culture growth. As a consequence, net calmodulin polypeptide synthesis declined 5- to 10-fold during the later stages of culture growth. The qualitative spectrum of polypeptides synthesized and accumulated by the carrot cells during the course of a culture cycle, however, remained largely unchanged. Calmodulin polypeptide levels, in contrast to its net synthesis, remained relatively constant during the exponential phases of the culture growth cycle and increased during the later stages of culture growth. Our data are consistent with increased calmodulin polypeptide turnover associated with periods of rapid cell proliferation and high levels of respiration.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett M. J., Long S. R. Nucleotide sequence of an alfalfa calmodulin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3395–3395. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Jemiolo D. K., Kretsinger R. H. Interaction of calcium and calmodulin in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 26;623(2):257–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chafouleas J. G., Lagacé L., Bolton W. E., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Means A. R. Changes in calmodulin and its mRNA accompany reentry of quiescent (G0) cells into the cell cycle. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Varner J. E. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for carrot extensin and a proline-rich 33-kDa protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4399–4403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsbrough P. B., Cullis C. A. Characterisation of the genes for ribosomal RNA in flax. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1301–1309. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregori L., Marriott D., Putkey J. A., Means A. R., Chau V. Bacterially synthesized vertebrate calmodulin is a specific substrate for ubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2562–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregori L., Marriott D., West C. M., Chau V. Specific recognition of calmodulin from Dictyostelium discoideum by the ATP, ubiquitin-dependent degradative pathway. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5232–5235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haderlie L. C., Widholm J. M., Slife F. W. Effect of glyphosate on carrot and tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):40–43. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C., Ma Y., Buchbinder B. U., Pyne J. W., Sun S. M., Bliss F. A. Messenger RNA for G1 protein of French bean seeds: Cell-free translation and product characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3196–3200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F. Antigenic structure of calmodulin: production and characterization of antisera specific for plant calmodulins or Ca2+-replete vs. Ca2+-free calmodulins. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(1):3–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Sasaki Y., Tanaka T., Endo T., Ohno S., Fujii Y., Nagata T. N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide, a calmodulin antagonist, inhibits cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4354–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson C. P., Fisk R. Z. Hybridization probe size control: optimized 'oligolabelling'. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6295–6295. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling V., Perera I., Zielinski R. E. Primary structures of Arabidopsis calmodulin isoforms deduced from the sequences of cDNA clones. Plant Physiol. 1991 Aug;96(4):1196–1202. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.4.1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling V., Zielinski R. E. Cloning of cDNA Sequences Encoding the Calcium-Binding Protein, Calmodulin, from Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Physiol. 1989 Jun;90(2):714–719. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.2.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. H., Roberts D. M. Analysis of the state of posttranslational calmodulin methylation in developing pea plants. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jul;93(3):880–887. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Reddy A. S. Calcium messenger system in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1987;6(1):47–103. doi: 10.1080/07352688709382247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen C. D., Means A. R. Calmodulin is involved in regulation of cell proliferation. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3961–3968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02738.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eldik L. J., Wolchok S. R. Conditions for reproducible detection of calmodulin and S100 beta in immunoblots. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):752–759. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eldik L. J., Zendegui J. G., Marshak D. R., Watterson D. M. Calcium-binding proteins and the molecular basis of calcium action. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;77:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62463-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Van Eldik L. J., Smith R. E., Vanaman T. C. Calcium-dependent regulatory protein of cyclic nucleotide metabolism in normal and transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2711–2715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widholm J. M. The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain Technol. 1972 Jul;47(4):189–194. doi: 10.3109/10520297209116483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zendegui J. G., Zielinski R. E., Watterson D. M., Van Eldik L. J. Biosynthesis of calmodulin in normal and virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):883–889. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski R. E. Calmodulin mRNA in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) : Apparent Regulation by Cell Proliferation and Light. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):937–943. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski R. E., Werneke J. M., Jenkins M. E. Coordinate Expression of Rubisco Activase and Rubisco during Barley Leaf Cell Development. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jun;90(2):516–521. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.2.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]