Abstract
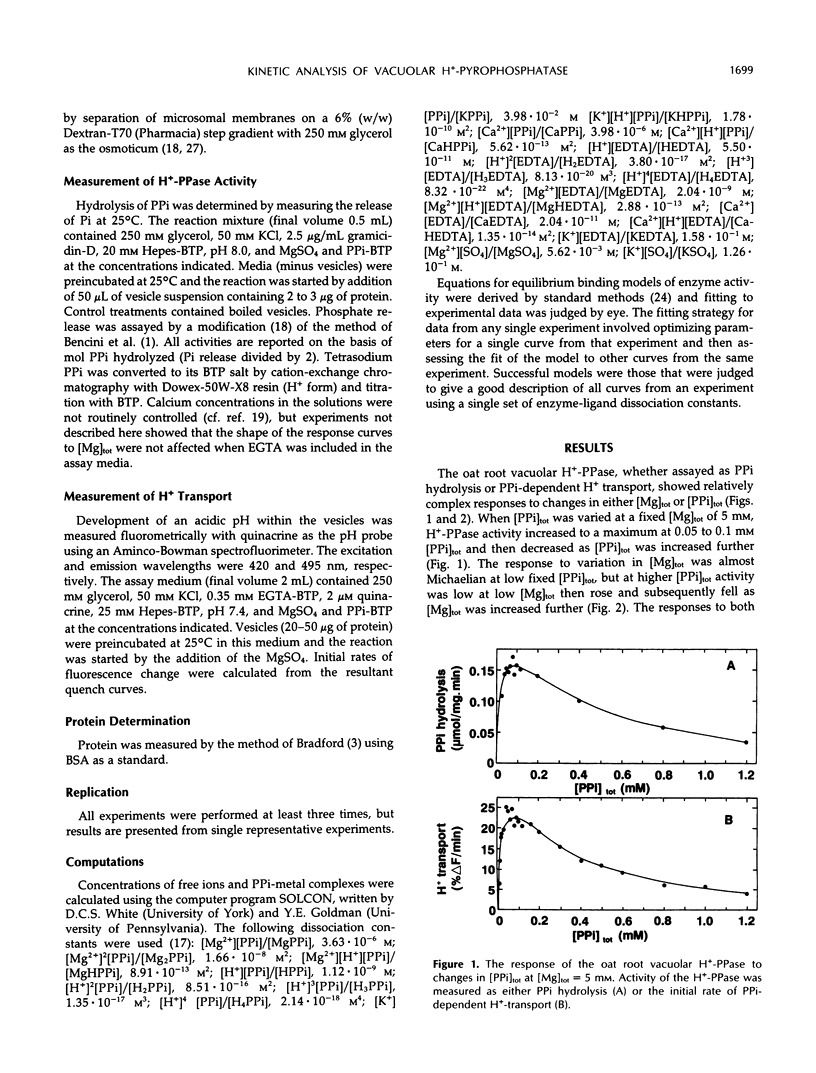
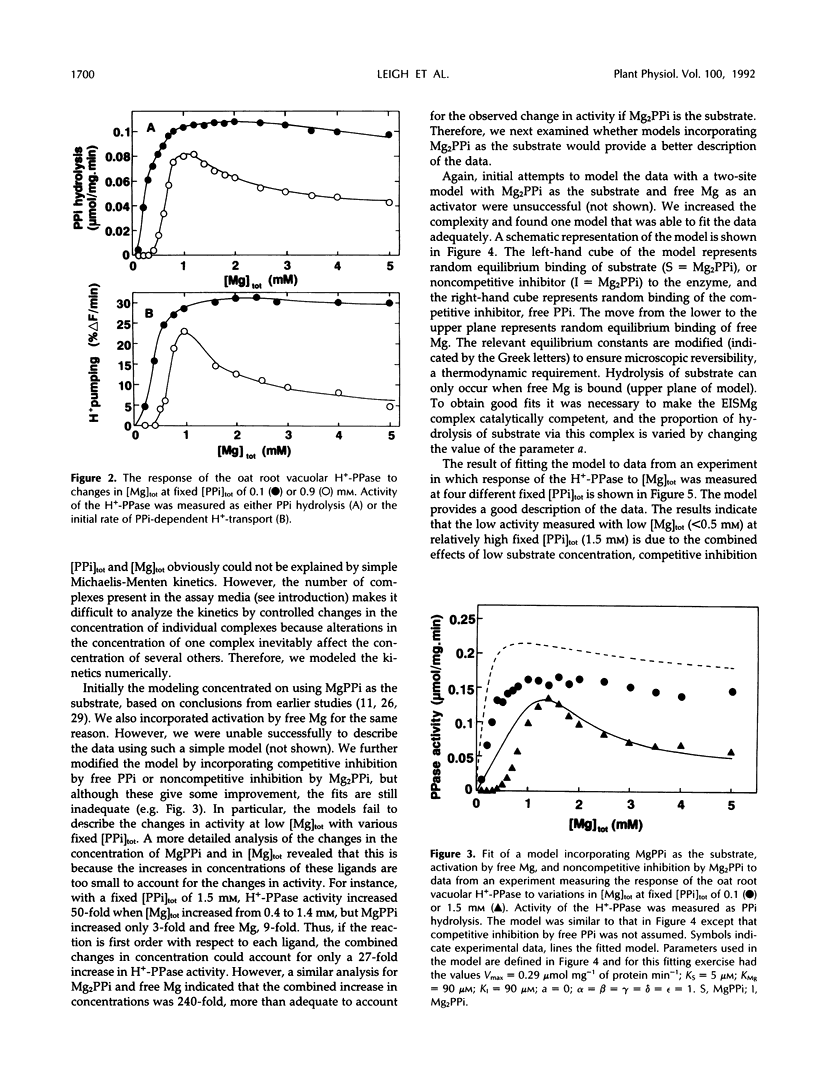
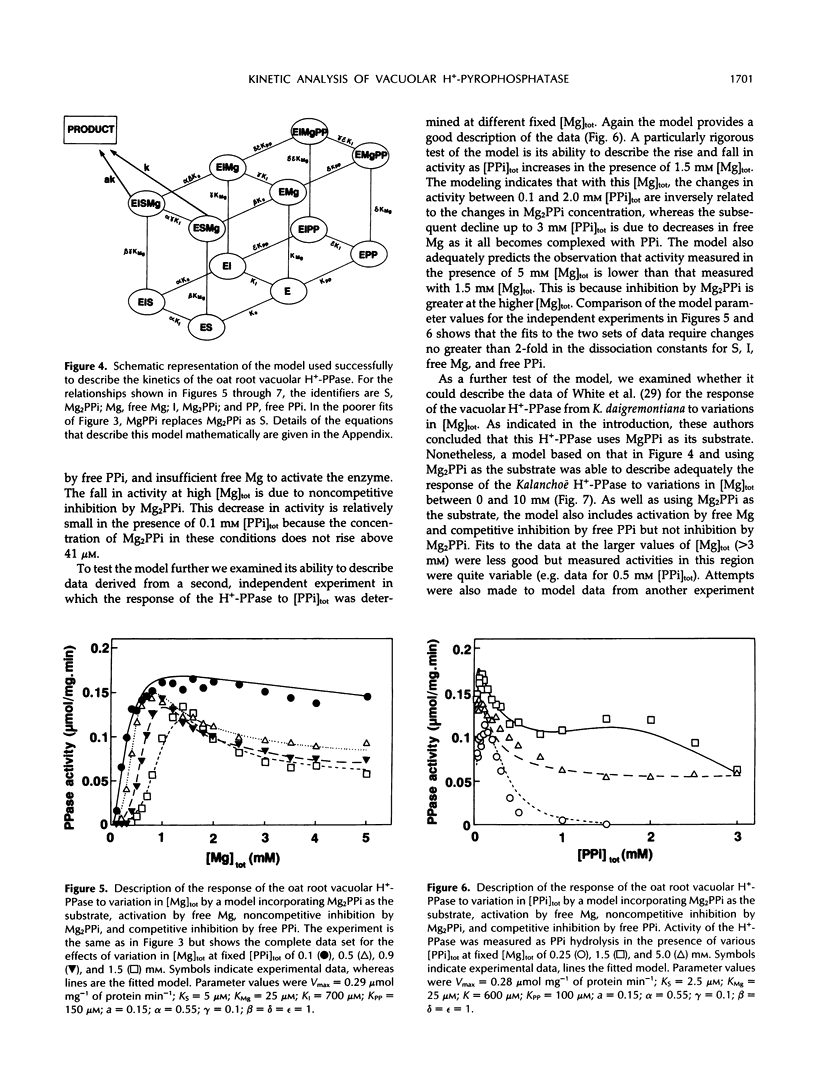
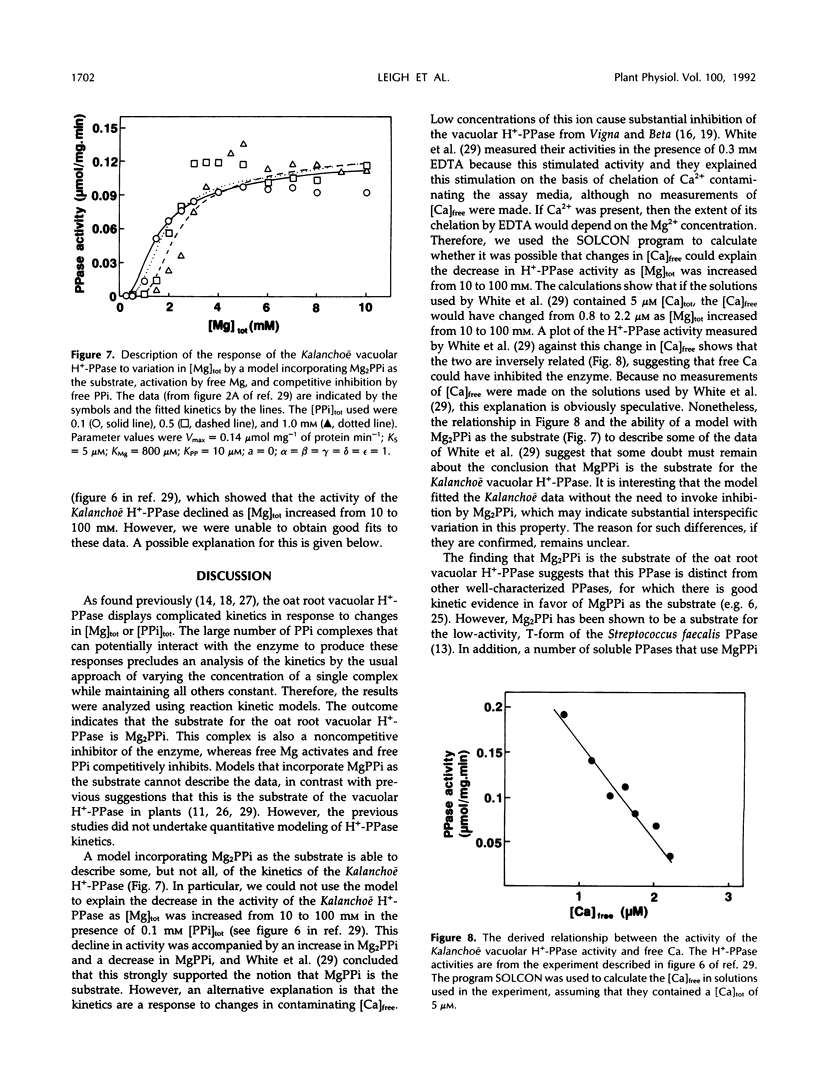
The responses of the vacuolar membrane (tonoplast) proton-pumping inorganic pyrophosphatase (H+-PPase) from oat (Avena sativa L.) roots to changes in Mg2+ and pyrophosphate (PPi) concentrations have been characterized. The kinetics were complex, and reaction kinetic models were used to determine which of the various PPi complexes were responsible for the observed responses. The results indicate that the substrate for the oat root vacuolar H+-PPase is Mg2PPi and that this complex is also a non-competitive inhibitor. In addition, the enzyme is activated by free Mg2+ and competitively inhibited by free PPi. This conclusion differs from that reached in previous studies, in which it was proposed that MgPPi is the substrate for plant vacuolar H+-PPases. However, models incorporating MgPPi as a substrate were unable to describe the kinetics of the oat H+-PPase. It is demonstrated that models incorporating Mg2PPi as the substrate can describe some of the published kinetics of the Kalanchoë daigremontiana vacuolar H+-PPase. Calculations of the likely concentrations of Mg2PPi in plant cytoplasm suggest that the substrate binding site of the oat vacuolar H+-PPase would be about 70% saturated in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bencini D. A., Wild J. R., O'Donovan G. A. Linear one-step assay for the determination of orthophosphate. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;132(2):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., McGuigan J. A. Estimation of the upper limit of the free magnesium concentration measured with Mg-sensitive microelectrodes in ferret ventricular muscle: (1) use of the Nicolsky-Eisenman equation and (2) in calibrating solutions of the appropriate concentration. Magnesium. 1988;7(3):154–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanson A., Pilet P. E. Target Molecular Size and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Analysis of the ATP-and Pyrophosphate-Dependent Proton Pumps from Maize Root Tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):934–938. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperman B. S. The mechanism of action of yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase. Methods Enzymol. 1982;87:526–548. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)87030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. M., Rea P. A., Sanders D. Vacuolar proton-pumping pyrophosphatase in Beta vulgaris shows vectorial activation by potassium. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):66–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80085-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P. W. Mechanisms of magnesium transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:259–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich R., Kurkdjian A., Guern J., Flügge U. I. Comparative studies on the electrical properties of the H+ translocating ATPase and pyrophosphatase of the vacuolar-lysosomal compartment. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2835–2841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. Y., Pan R. L. An essential arginyl residue in the tonoplast pyrophosphatase from etiolated mung bean seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jul;93(3):1128–1133. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R., Jokinen M. Kinetic model for the action of the inorganic pyrophosphatase from Streptococcus faecalis. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3526–3530. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeshima M. H(+)-translocating inorganic pyrophosphatase of plant vacuoles. Inhibition by Ca2+, stabilization by Mg2+ and immunological comparison with other inorganic pyrophosphatases. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 26;196(1):11–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Britten C. J., Jennings I. R., Calvert C. M., Skiera L. A., Leigh R. A., Sanders D. Regulation of vacuolar h-pyrophosphatase by free calcium : a reaction kinetic analysis. Plant Physiol. 1992 Dec;100(4):1706–1715. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.4.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Chromatographic resolution of h-translocating pyrophosphatase from h-translocating ATPase of higher plant tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):126–129. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Proton-Translocating Inorganic Pyrophosphatase in Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Tonoplast Vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):46–52. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian V., Poole R. J. Purification of an h-translocating inorganic pyrophosphatase from vacuole membranes of red beet. Plant Physiol. 1989 Sep;91(1):34–38. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unguryte A., Smirnova I. N., Baykov A. A. Kinetic models for the action of cytosolic and mitochondrial inorganic pyrophosphatases of rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Sep;273(2):292–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Leigh R. A., Kaestner K. H., Sze H. Electrogenic h-pumping pyrophosphatase in tonoplast vesicles of oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):497–502. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Marshall J., Smith J. A. Substrate kinetics of the tonoplast h-translocating inorganic pyrophosphatase and its activation by free mg. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jul;93(3):1063–1070. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.3.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


