Abstract
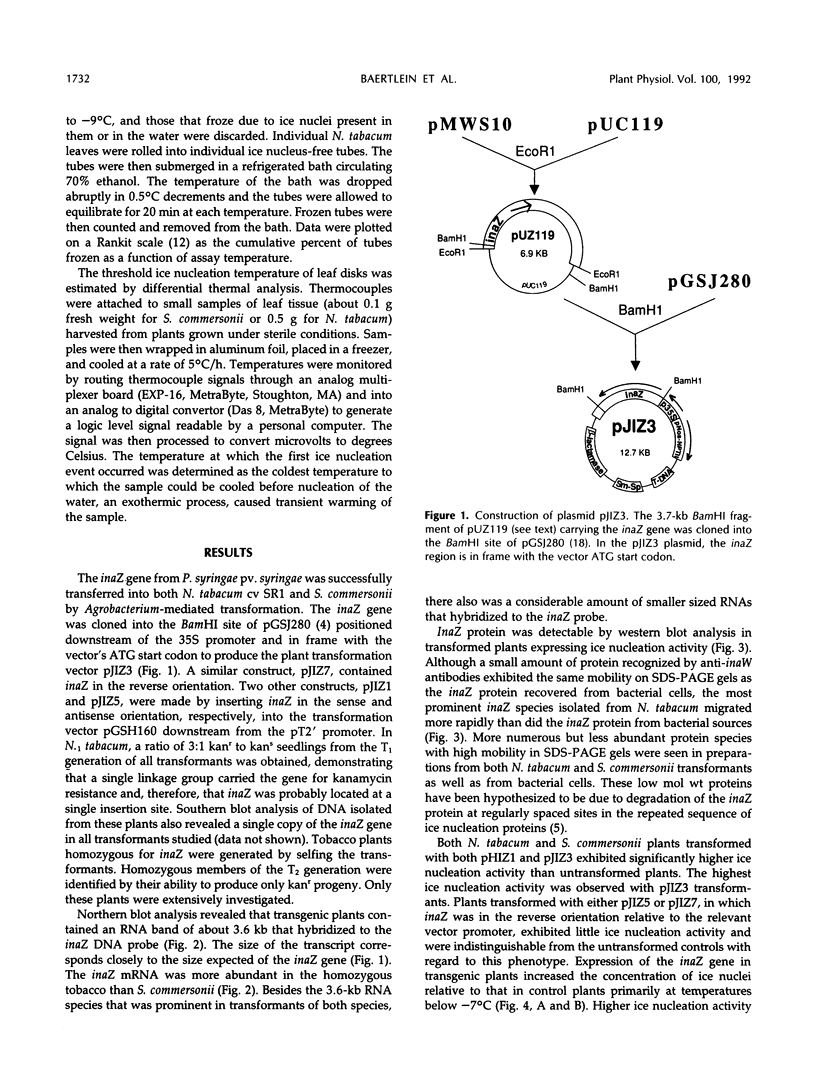
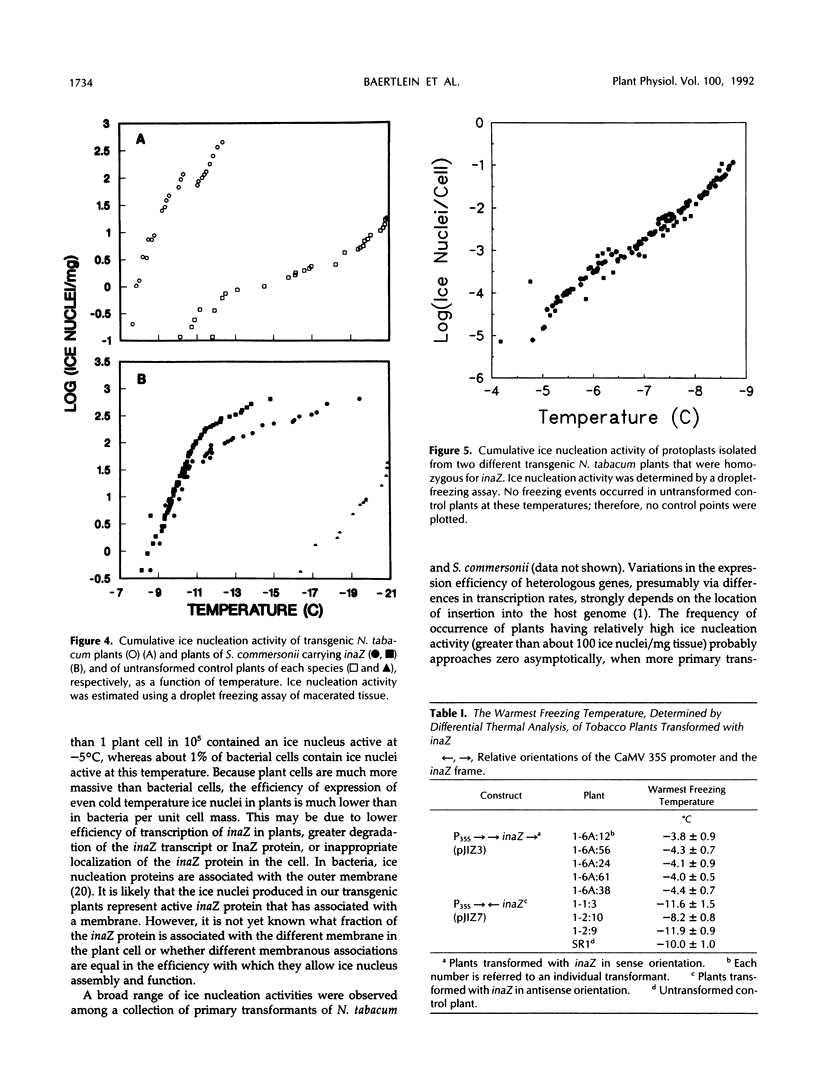
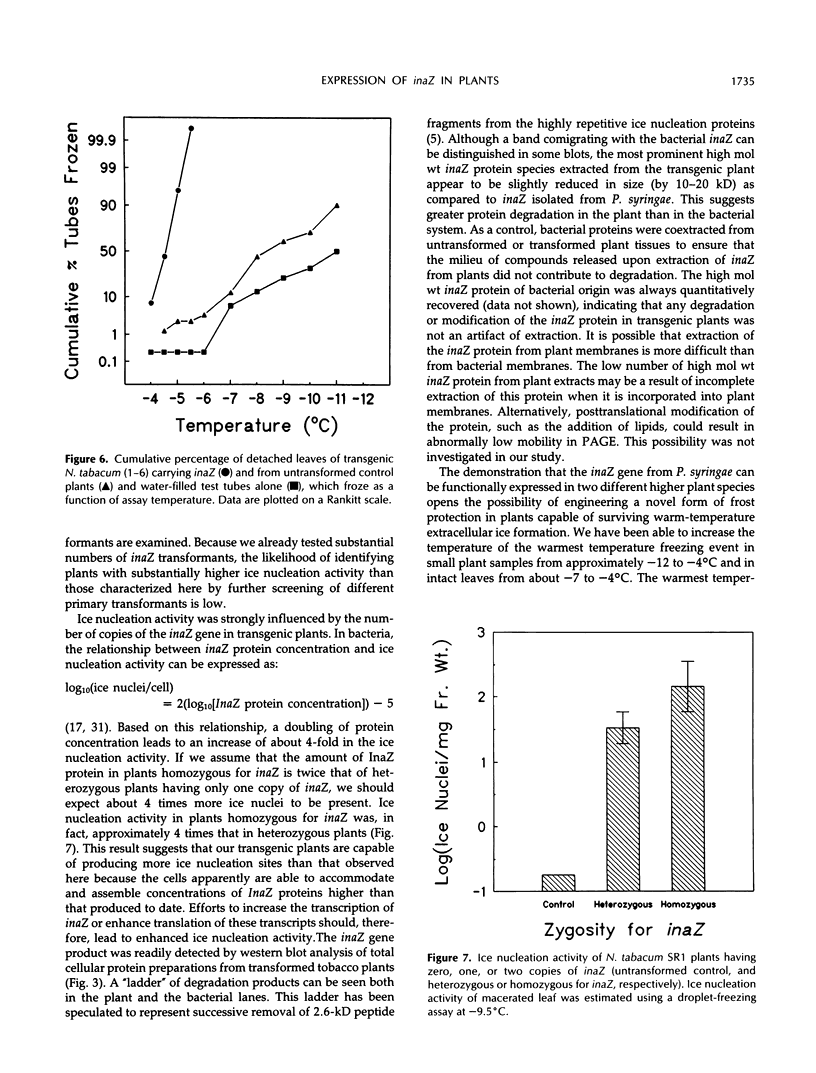
We have introduced an ice nucleation gene (inaZ) from Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae into Nicotiana tabacum, a freezing-sensitive species, and Solanum commersonii, a freezing-tolerant species. Transformants of both species showed increased ice nucleation activity over untransformed controls. The concentration of ice nuclei detected at −10.5°C in 15 different primary transformants of S. commersonii varied by over 1000-fold, and the most active transformant contained over 100 ice nuclei/mg of tissue. The temperature of the warmest freezing event in plant samples of small mass was increased from approximately −12°C in the untransformed controls to −4°C in inaZ-expressing transformants. The threshold nucleation temperature of samples from transformed plants did not increase appreciably with the mass of the sample. The most abundant protein detected in transgenic plants using immunological probes specific to the inaZ protein exhibited a higher mobility on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels than the inaZ protein from bacterial sources. However, some protein with a similar mobility to the inaZ protein could be detected. Although the warmest ice nucleation temperature detected in transgenic plants is lower than that conferred by this gene in P. syringae (−2°C), our results demonstrate that the ice nucleation gene of P. syringae can be expressed in plant cells to produce functional ice nuclei.
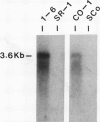
Full text
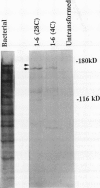
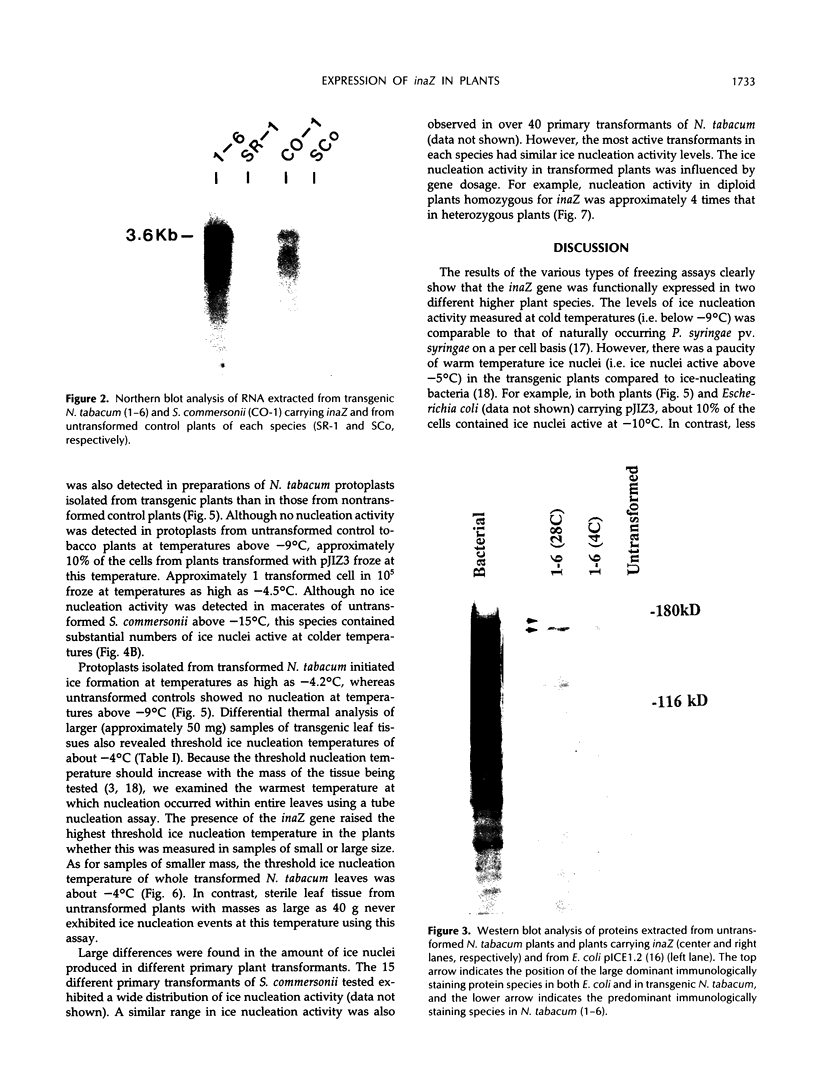
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G. Development of plant promoter expression vectors and their use for analysis of differential activity of nopaline synthase promoter in transformed tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):86–91. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger C. A., Mueller G. M., Wolber P. K. Immunological characterization of ice nucleation proteins from Pseudomonas syringae, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Erwinia herbicola. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):669–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.669-675.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S. S., Baker L. S., Upper C. D. Ice nucleation temperature of individual leaves in relation to population sizes of ice nucleation active bacteria and frost injury. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):259–265. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S. S., Nordheim E. V., Arny D. C., Upper C. D. Lognormal distribution of epiphytic bacterial populations on leaf surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.695-700.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren P. B., Frederick R., Govindarajan A. G., Panopoulos N. J., Staskawicz B. J., Lindow S. E. An ice nucleation reporter gene system: identification of inducible pathogenicity genes in Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1291–1301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindow S. E. Competitive Exclusion of Epiphytic Bacteria by IcePseudomonas syringae Mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2520–2527. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2520-2527.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindow S. E., Lahue E., Govindarajan A. G., Panopoulos N. J., Gies D. Localization of ice nucleation activity and the iceC gene product in Pseudomonas syringae and Escherichia coli. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1989 Sep-Oct;2(5):262–272. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-2-262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur P. The role of intracellular freezing in the death of cells cooled at supraoptimal rates. Cryobiology. 1977 Jun;14(3):251–272. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(77)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orser C., Staskawicz B. J., Panopoulos N. J., Dahlbeck D., Lindow S. E. Cloning and expression of bacterial ice nucleation genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.359-366.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajashekar C. B., Li P. H., Carter J. V. Frost injury and heterogeneous ice nucleation in leaves of tuber-bearing solanum species : ice nucleation activity of external source of nucleants. Plant Physiol. 1983 Apr;71(4):749–755. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southworth M. W., Wolber P. K., Warren G. J. Nonlinear relationship between concentration and activity of a bacterial ice nucleation protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15211–15216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolber P. K., Deininger C. A., Southworth M. W., Vandekerckhove J., van Montagu M., Warren G. J. Identification and purification of a bacterial ice-nucleation protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7256–7260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]