Abstract
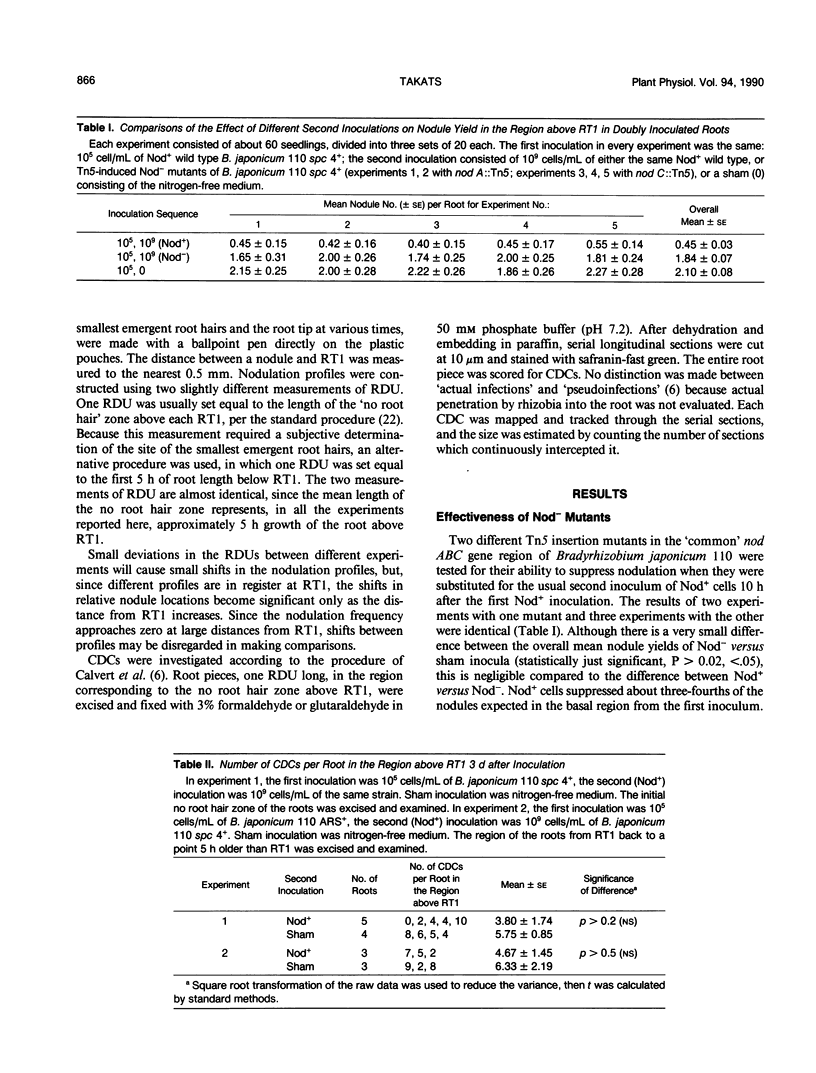
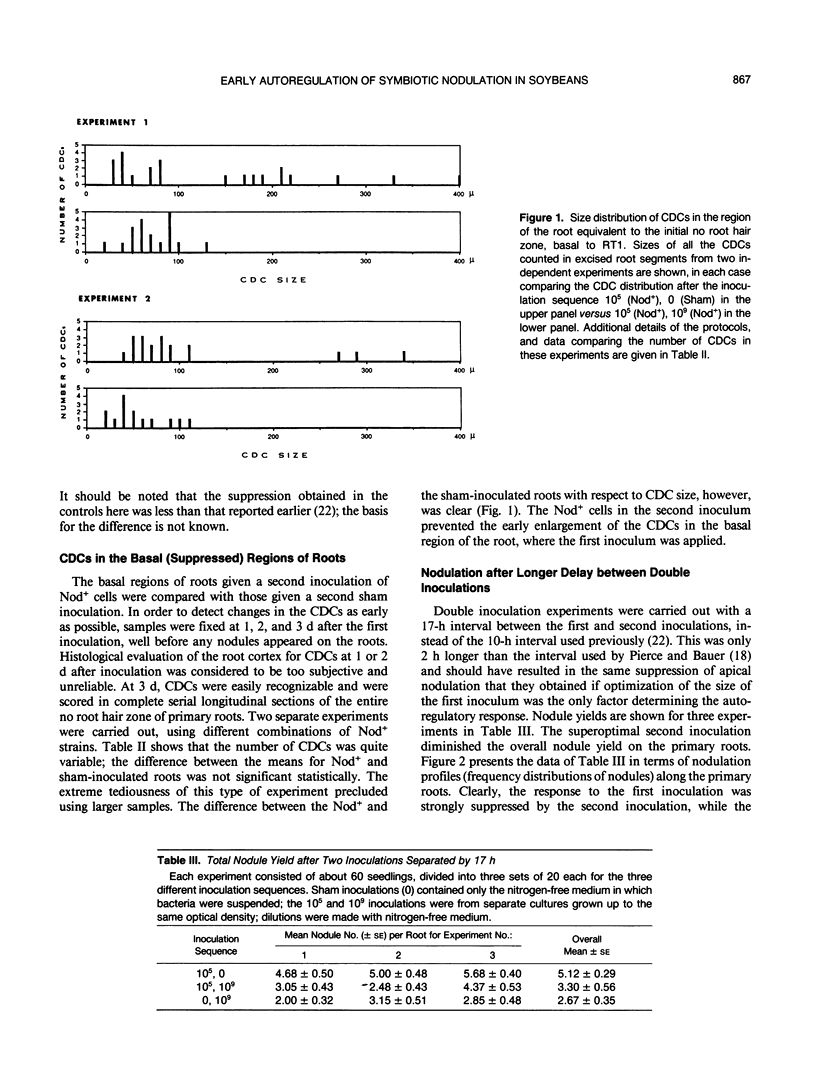
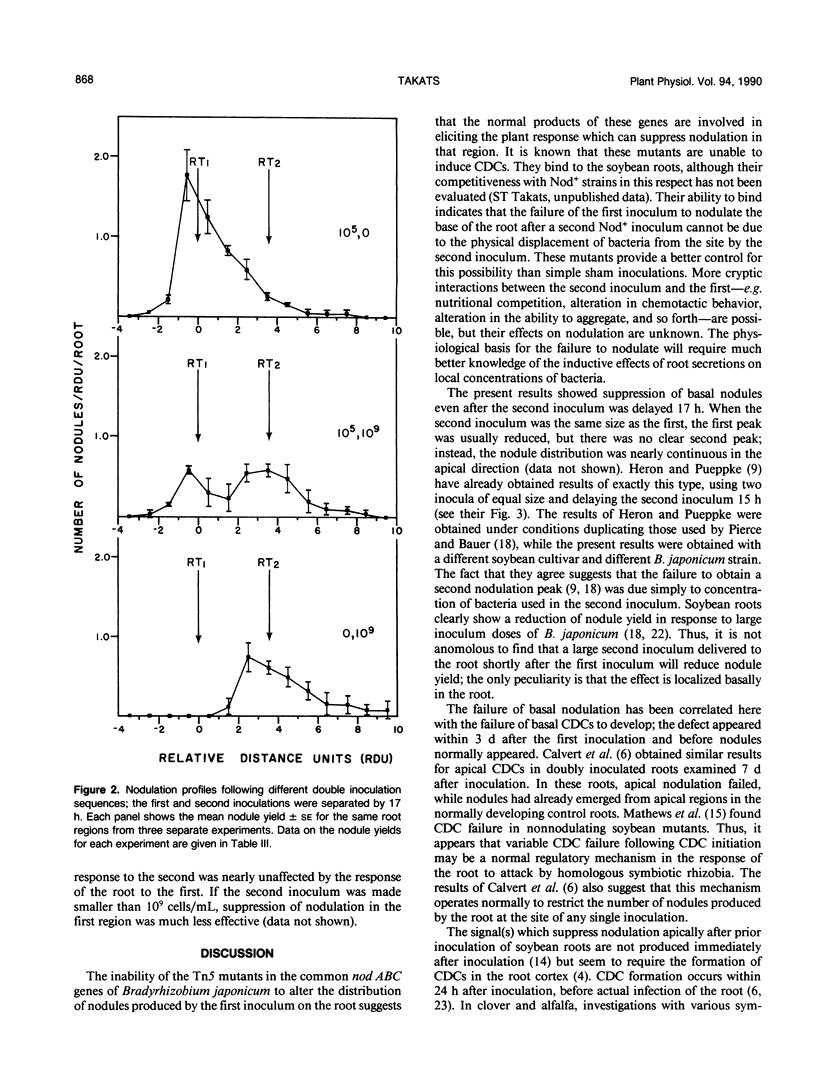
Autoregulation of symbiotic root nodulation in soybean seedlings (Glycine max L. Merrill cv Pride 216) was studied following double inoculation of primary roots with Bradyrhizobium japonicum 110. When the second inoculation was given 10 or 17 hours after the first, the nodulation in the first-inoculated region of the root was suppressed. The effect was eliminated if B. japonicum 110 containing Tn5 insertions in the `common' nod ABC genes was used for the second inoculation, indicating the requirement for changes in the root mediated by these bacterial genes. When the root cortex in the suppressed basal region was examined 3 days after inoculation, cell division centers were present in numbers not significantly different from the numbers in control roots given a sham second inoculation; their size distribution, however, showed a failure of enlargement compared with controls.
Full text
PDF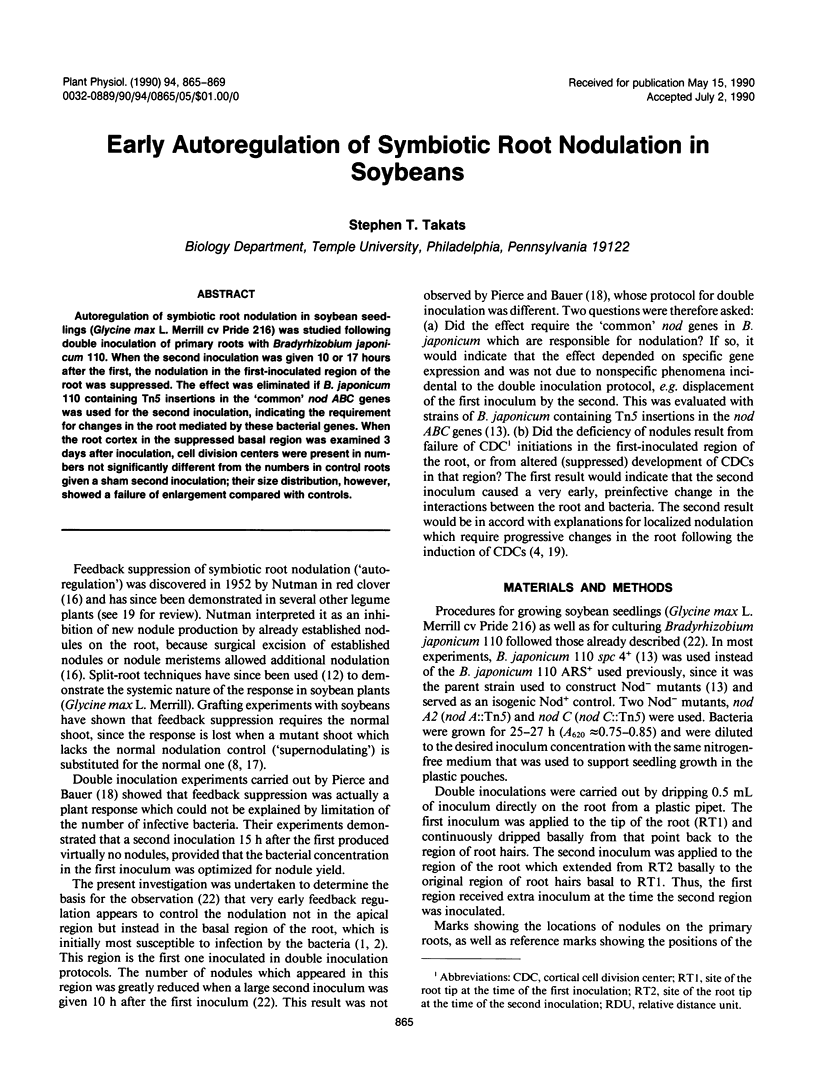

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bhagwat A. A., Bauer W. D. Transient susceptibility of root cells in four common legumes to nodulation by rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Turgeon B. G., Bauer W. D. Early Events in the Infection of Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr) by Rhizobium japonicum: I. LOCALIZATION OF INFECTIBLE ROOT CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1027–1031. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caetano-Anollés G., Lagares A., Bauer W. D. Rhizobium meliloti exopolysaccharide Mutants Elicit Feedback Regulation of Nodule Formation in Alfalfa. Plant Physiol. 1990 Feb;92(2):368–374. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delves A. C., Mathews A., Day D. A., Carter A. S., Carroll B. J., Gresshoff P. M. Regulation of the soybean-Rhizobium nodule symbiosis by shoot and root factors. Plant Physiol. 1986 Oct;82(2):588–590. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron D. S., Pueppke S. G. Regulation of nodulation in the soybean-Rhizobium symbiosis : strain and cultivar variability. Plant Physiol. 1987 Aug;84(4):1391–1396. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Bhuvaneswari T. V., Torrey J. G., Bisseling T. Early nodulin genes are induced in alfalfa root outgrowths elicited by auxin transport inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1244–1248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bohlool B. B. Suppression of nodule development of one side of a split-root system of soybeans caused by prior inoculation of the other side. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):125–130. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik N. S., Bauer W. D. When does the self-regulatory response elicited in soybean root after inoculation occur? Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):537–539. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J. E., Nakao P., Bohlool B. B., Gresshoff P. M. Lack of Systemic Suppression of Nodulation in Split Root Systems of Supernodulating Soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) Mutants. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1347–1352. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce M., Bauer W. D. A rapid regulatory response governing nodulation in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):286–290. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent L., Huang S. Z., Rolfe B. G., Djordjevic M. A. Split-Root Assays Using Trifolium subterraneum Show that Rhizobium Infection Induces a Systemic Response That Can Inhibit Nodulation of Another Invasive Rhizobium Strain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1611–1619. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1611-1619.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Wingender R., John M., Wieneke U., Schell J. Rhizobium meliloti nodA and nodB genes are involved in generating compounds that stimulate mitosis of plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8578–8582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


