Abstract
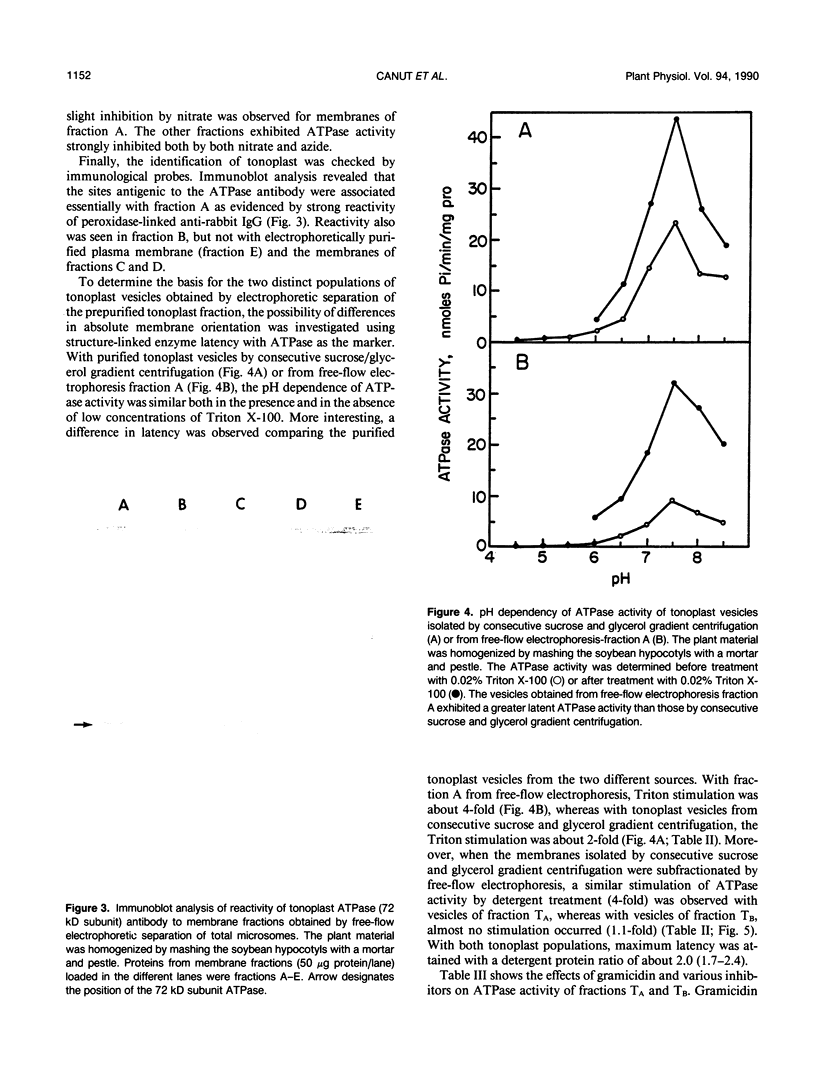
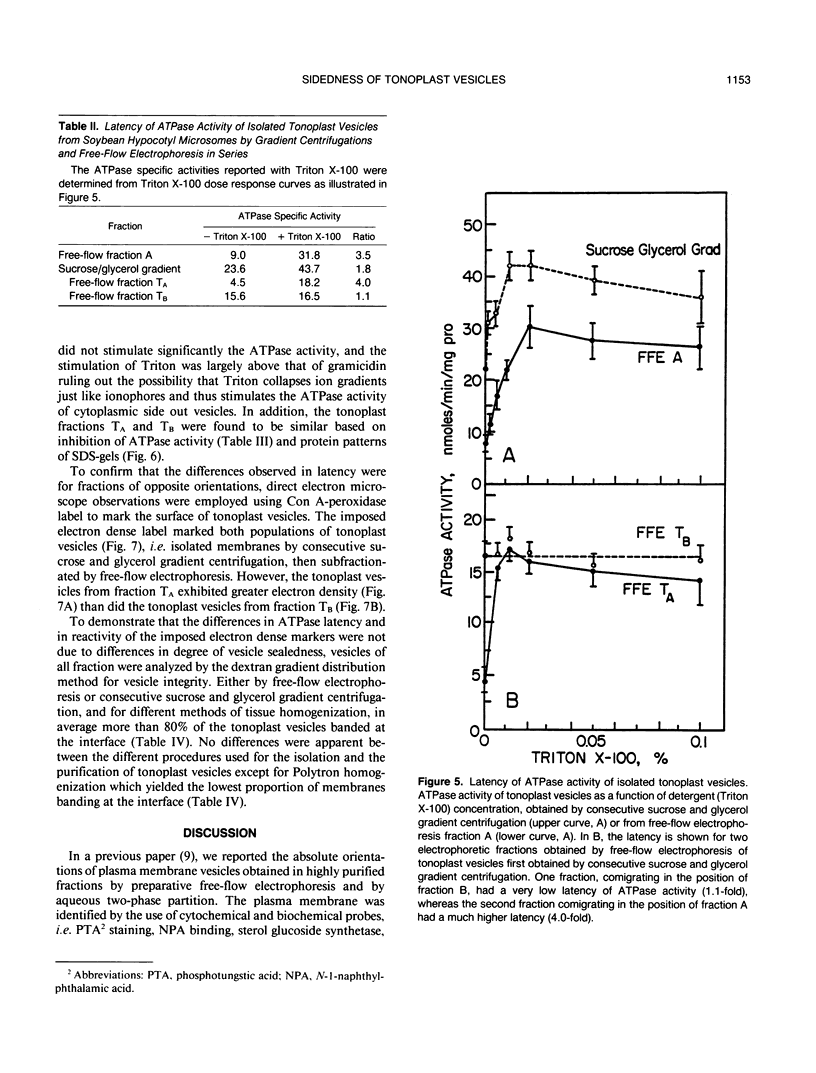
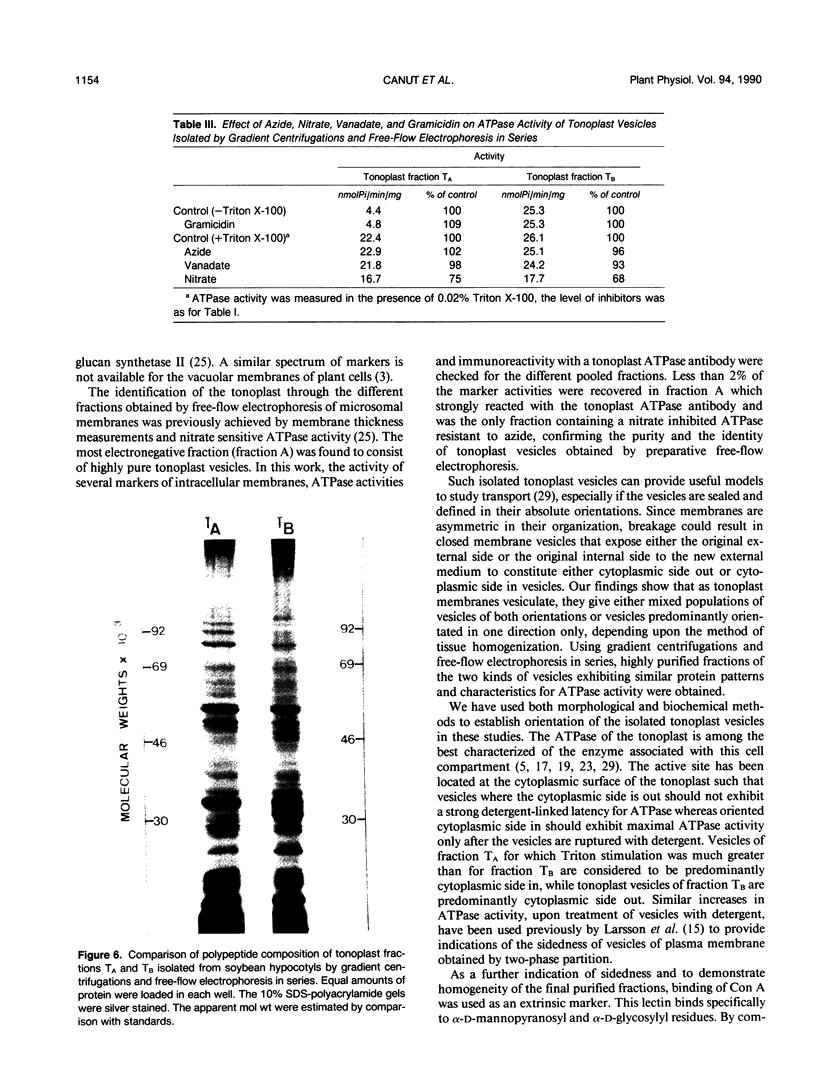
Tonoplast vesicles were purified from a microsomal fraction isolated from etiolated soybean hypocotyls (Glycine max L.) by preparative free-flow electrophoresis. Marker enzyme determinations and immunoblot analysis against the vacuolar-ATPase confirmed the nature and the purity of the isolated membranes. A purified tonoplast fraction also was obtained by consecutive sucrose and glycerol centrifugation which was further resolved into two different populations of vesicles (TA and TB) by free-flow electrophoresis. The determination of the sidedness of these different vesicles included concanavalin A binding as an imposed label, NADH-ferricyanide oxidoreductase cytochemistry, and ATPase latency. The tonoplast fractions, obtained by consecutive sucrose and glycerol gradient centrifugations, were found to consist of a mixture of two populations of vesicles of opposite sidedness. The least electronegative fraction obtained by free-flow electrophoresis (TB) consisted predominantly of cytoplasmic side out tonoplast vesicles while a fraction of greater electronegativity (TA) contained the cytoplasmic side in tonoplast vesicles. The relative amounts of each type of vesicle varied with the method of homogenization. Razor blade chopping, Polytron, and Waring Blendor homogenization gave predominantly cytoplasmic side out vesicles, whereas mashing with a mortar and pestle gave nearly equal amounts of the two populations of membrane vesicles of different orientation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbier-Brygoo H., Renaudin J. P., Guern J. The vacuolar membrane of plant cells: a newcomer in the field of biological membranes. Biochimie. 1986 Mar;68(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr R., Sandelius A. S., Crane F. L., Morré D. J. Redox reactions of tonoplast and plasma membranes isolated from soybean hypocotyls by free-flow electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 3;852(2-3):254–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(86)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. B., O'neill S. D., Spanswick R. M. H-ATPase Activity from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris: I. Identification and Characterization of an Anion-Sensitive H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):538–544. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller T., Dürr M., Wiemken A. Asymmetric distribution of concanavalin A binding sites on yeast plasmalemma and vacuolar membrane. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Aug;109(1-2):115–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00425122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canut H., Brightman A., Boudet A. M., Morré D. J. Plasma membrane vesicles of opposite sidedness from soybean hypocotyls by preparative free-flow electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1988 Feb;86(2):631–637. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.2.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulley J. R. Determination of inorganic phosphate in the presence of detergents or protein. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Leonard R. T. Effect of vanadate, molybdate, and azide on membrane-associated ATPase and soluble phosphatase activities of corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1335–1340. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandala S., Taiz L. Characterization of the subunit structure of the maize tonoplast ATPase. Immunological and inhibitor binding studies. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12850–12855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandala S., Taiz L. Partial purification of a tonoplast ATPase from corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jun;78(2):327–333. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morré D. J., Vigil E. L., Frantz C., Goldenberg H., Crane F. L. Cytochemical demonstration of glutaraldehyde-resistant NADH-ferricyanide oxido-reductase activities in rat-liver plasma membranes and Golgi apparatus. Cytobiologie. 1978 Dec;18(2):213–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. J., Briskin D. P., Krátký Z., Johnstone R. M. Density gradient localization of plasma membrane and tonoplast from storage tissue of growing and dormant red beet : characterization of proton-transport and ATPase in tonoplast vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):549–556. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland J. C., Lembi C. A., Morré D. J. Phosphotungstic acid-chromic acid as a selective electron-dense stain for plasma membranes of plant cells. Stain Technol. 1972 Jul;47(4):195–200. doi: 10.3109/10520297209116484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandelius A. S., Penel C., Auderset G., Brightman A., Millard M., Morré D. J. Isolation of highly purified fractions of plasma membrane and tonoplast from the same homogenate of soybean hypocotyls by free-flow electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):177–185. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]