Abstract
A procedure is described for the purification of the enzyme indol-3-ylacetylglucose:myo-inositol indol-3-ylacetyltransferase (IAA-myo-inositol synthase). This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of indol-3-ylacetate from 1-0-indol-3-ylacetyl-β-d-glucose to myo-inositol to form indol-3-ylacetyl-myo-inositol and glucose. A hexokinase or glucose oxidase based assay system is described. The enzyme has been purified approximately 16,000-fold, has an isoelectric point of pH 6.1 and yields three catalytically inactive bands upon acrylamide gel electrophoresis of the native protein. The enzyme shows maximum transferase activity with myo-inositol but shows some transferase activity with scyllo-inositol and myo-inosose-2. No transfer of IAA occurs with myo-inositol-d-galactopyranose, cyclohexanol, mannitol, or glycerol as acyl acceptor. The affinity of the enzyme for 1-0-indol-3-ylacetyl-β-d-glucose is, Km = 30 micromolar, and for myo-inositol is, Km = 4 millimolar. The enzyme does not catalyze the exchange incorporation of glucose into IAA-glucose indicating the reaction mechanism involves binding of IAA glucose to the enzyme with subsequent hydrolytic cleavage of the acyl moiety by the hydroxyl of myo-inositol to form IAA myo-inositol ester.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
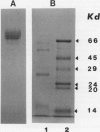
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisnell J. R., Bandurski R. S. Translocation of radiolabeled indole-3-acetic acid and indole-3-acetyl-myo-inositol from kernel to shoot of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1988;86:79–84. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcuera L. J., Bandurski R. S. Biosynthesis of Indol-3-yl-acetyl-myo-inositol Arabinoside in Kernels of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1664–1666. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcuera L. J., Michalczuk L., Bandurski R. S. Enzymic synthesis of indol-3-ylacetyl-myo-inositol galactoside. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 1;207(2):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2070283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcuera L. J., Michalczuk L., Bandurski R. S. Enzymic synthesis of indol-3-ylacetyl-myo-inositol galactoside. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 1;207(2):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2070283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domagalski W., Schulze A., Bandurski R. S. Isolation and characterization of esters of indole-3-acetic acid from the liquid endosperm of the horse chestnut (Aesculus species). Plant Physiol. 1987;84:1107–1113. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehmann A. Identification of 2-O (indole-3-acetyl)-D-glucopyranose, 4-O-(indole-3-acetyl)-D-glucopyranose and 6-O-(indole-3-acetyl)-D-glucopyranose from kernels of Zea mays by gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Carbohydr Res. 1974 May;34(1):99–114. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)80374-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehmann A. The van urk-Salkowski reagent--a sensitive and specific chromogenic reagent for silica gel thin-layer chromatographic detection and identification of indole derivatives. J Chromatogr. 1977 Feb 11;132(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)89300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Cohen J. D., Bandurski R. S. Concentration and Metabolic Turnover of Indoles in Germinating Kernels of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):415–421. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. J., Bandurski R. S. [3H]Indole-3-acetyl-myo-inositol hydrolysis by extracts of Zea mays L. vegetative tissue. Plant Physiol. 1986;80:374–377. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keglević D., Pokorny M. The chemical synthesis of 1-O-(indol-3'-ylacetyl)-beta-D-glucopyranose. The higher activity of the glucoside in comparison with exogenous indol-3-ylacetic acid in plant-section elongation tests. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;114(4):827–832. doi: 10.1042/bj1140827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keglević D. Synthesis of 1-O-(indol-3-ylacetyl)- -D-glucopyranose and its rearrangement into 2-O-(indol-3-ylacetyl)-D-glucopyranose. Carbohydr Res. 1971 Dec;20(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoszynski M., Bandurski R. S. Transport and metabolism of indole-3-acetyl-myo-inositol-galactoside in seedlings of Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1986;80:961–964. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopcewicz J., Ehmann A., Bandurski R. S. Enzymatic Esterification of Indole-3-acetic Acid to myo-Inositol and Glucose. Plant Physiol. 1974 Dec;54(6):846–851. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.6.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk S., Bandurski R. S. Isomerization of 1-O-indol-3-ylacetyl-beta-D-glucose. Enzymatic hydrolysis of 1-O, 4-O, and 6-O-indol-3-ylacetyl-beta-D-glucose and the enzymatic synthesis of indole-3-acetyl glycerol by a hormone metabolizing complex. Plant Physiol. 1990;94:4–12. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.1.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Nicholls P. B., Bandurski R. S. A partial characterization of indoleacetylinositols from ZEA mays. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 8;20(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90448-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leznicki A. J., Bandurski R. S. Enzymic synthesis of indole-3-acetyl-1-O-beta-d-glucose. I. Partial purification and characterization of the enzyme from Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1988;88:1474–1480. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leznicki A. J., Bandurski R. S. Enzymic synthesis of indole-3-acetyl-1-O-beta-d-glucose. II. Metabolic characteristics of the enzyme. Plant Physiol. 1988;88:1481–1485. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowacki J., Bandurski R. S. Myo-Inositol Esters of Indole-3-acetic Acid as Seed Auxin Precursors of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):422–427. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogita Z. I., Markert C. L. A miniaturized system for electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):233–241. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piskornik Z., Bandurski R. S. Purification and Partial Characterization of a Glucan Containing Indole-3-acetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jul;50(1):176–182. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack D., Gross W. Properties and Activity Changes of Chlorogenic Acid:Glucaric Acid Caffeoyltransferase From Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Plant Physiol. 1990 Jan;92(1):41–47. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZENK M. H. I-(Indole-3-acetyl)-beta-D-glucose, a new compound in the metabolism of indole-3-acetic acid in plants. Nature. 1961 Jul 29;191:493–494. doi: 10.1038/191493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]