Abstract
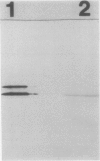
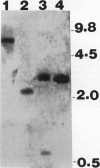
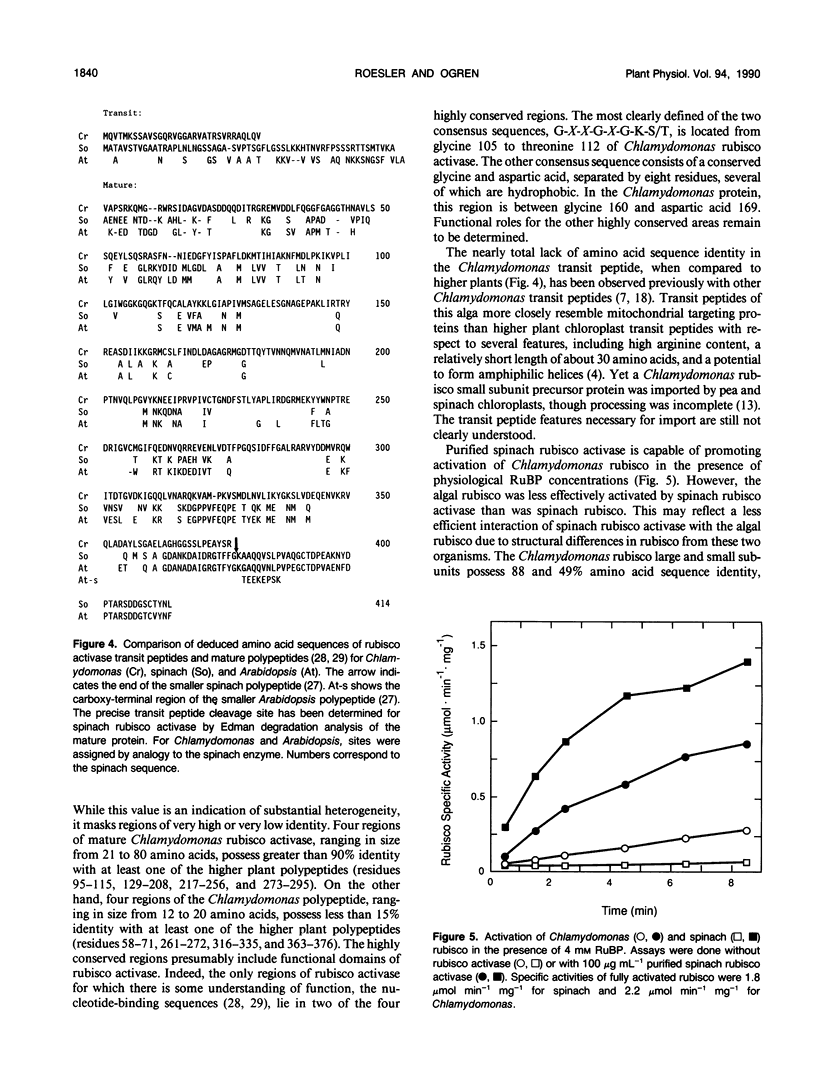
Immunoblot analysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) activase from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii indicated the presence of a single polypeptide. This observation contrasts with the Spinacea oleracea (spinach) and Arabidopsis thaliana proteins, in which two polypeptide species are generated by alternative pre-mRNA splicing. A Chlamydomonas rubisco activase cDNA clone containing the entire coding region was isolated and sequenced. The open reading frame encoded a 408 amino acid, 45 kilodalton polypeptide that included a chloroplast transit peptide. The presumptive mature polypeptide possessed 62% and 65% amino acid sequence identity, respectively, with the spinach and Arabidopsis mature polypeptides. The Chlamydomonas rubisco activase transit peptide possessed almost no amino acid sequence identity with the higher plant transit peptides. The nucleotide sequence of Chlamydomonas rubisco activase cDNA provided no evidence for alternative mRNA splicing, consistent with the immunoblot evidence for only one polypeptide. Genomic DNA blot analysis indicated the presence of a single Chlamydomonas rubisco activase gene. In the presence of spinach rubisco activase, a lower extent and rate of activation were obtained in vitro with Chlamydomonas rubisco than with spinach rubisco. We conclude Chlamydomonas rubisco activase comprises a single polypeptide which differs considerably from the higher plant polypeptides with respect to primary structure.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger M. R., Kaplan A., Berry J. A. Internal Inorganic Carbon Pool of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: EVIDENCE FOR A CARBON DIOXIDE-CONCENTRATING MECHANISM. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):407–413. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast DNA region of Chlamydomonas reinhardii containing the gene of the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase and parts of its flanking genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):775–793. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén L. G., Rochaix J. D., von Heijne G. Chloroplast transit peptides from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii share features with both mitochondrial and higher plant chloroplast presequences. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 29;260(2):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80094-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste-Royal G., Gibbs S. P. Immunocytochemical Localization of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase in the Pyrenoid and Thylakoid Region of the Chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):602–606. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Miziorko H. M. Carbamate formation on the epsilon-amino group of a lysyl residue as the basis for the activation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by CO2 and Mg2+. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5321–5328. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant S., Bogorad L. The Cu(II)-repressible plastidic cytochrome c. Cloning and sequence of a complementary DNA for the pre-apoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9062–9067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkind M. L., Wessler S. R., Schmidt G. W. Functional determinants in transit sequences: import and partial maturation by vascular plant chloroplasts of the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):226–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. M., Derocher J., Cattolico R. A. Analysis of Chromophytic and Rhodophytic Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Indicates Extensive Structural and Functional Similarities among Evolutionarily Diverse Algae. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):939–946. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Jr Rubisco activase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 4;1015(1):15–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90211-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Salvucci M. E., Ogren W. L. Activation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase at Physiological CO(2) and Ribulosebisphosphate Concentrations by Rubisco Activase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):967–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. P., Streusand V. J., Chatfield J. M., Portis A. R. Purification and assay of rubisco activase from leaves. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1008–1014. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler K. R., Ogren W. L. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Phosphoribulokinase : Sequence, Purification, and Kinetics. Plant Physiol. 1990 May;93(1):188–193. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Portis A. R., Ogren W. L. Light and CO(2) Response of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Activation in Arabidopsis Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):655–659. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville C. R., Portis A. R., Ogren W. L. A Mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana Which Lacks Activation of RuBP Carboxylase In Vivo. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):381–387. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spreitzer R. J., Mets L. Photosynthesis-deficient Mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii with Associated Light-sensitive Phenotypes. Plant Physiol. 1981 Mar;67(3):565–569. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streusand V. J., Portis A. R. Rubisco Activase Mediates ATP-Dependent Activation of Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):152–154. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werneke J. M., Chatfield J. M., Ogren W. L. Alternative mRNA splicing generates the two ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase polypeptides in spinach and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1989 Aug;1(8):815–825. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.8.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werneke J. M., Chatfield J. M., Ogren W. L. Catalysis of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Activation by the Product of a Rubisco Activase cDNA Clone Expressed in Escherichia coli. Plant Physiol. 1988 Aug;87(4):917–920. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.4.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werneke J. M., Ogren W. L. Structure of an Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA encoding rubisco activase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2871–2871. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werneke J. M., Zielinski R. E., Ogren W. L. Structure and expression of spinach leaf cDNA encoding ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):787–791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Perrot B., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. The structure of the gene for the large subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from spinach chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3251–3270. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]