Abstract
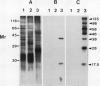
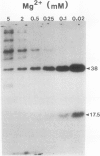
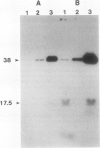
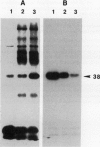
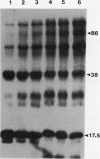
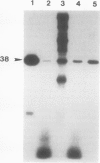
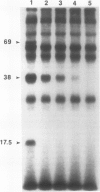
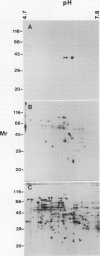
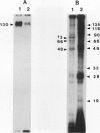
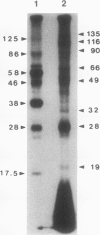
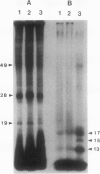
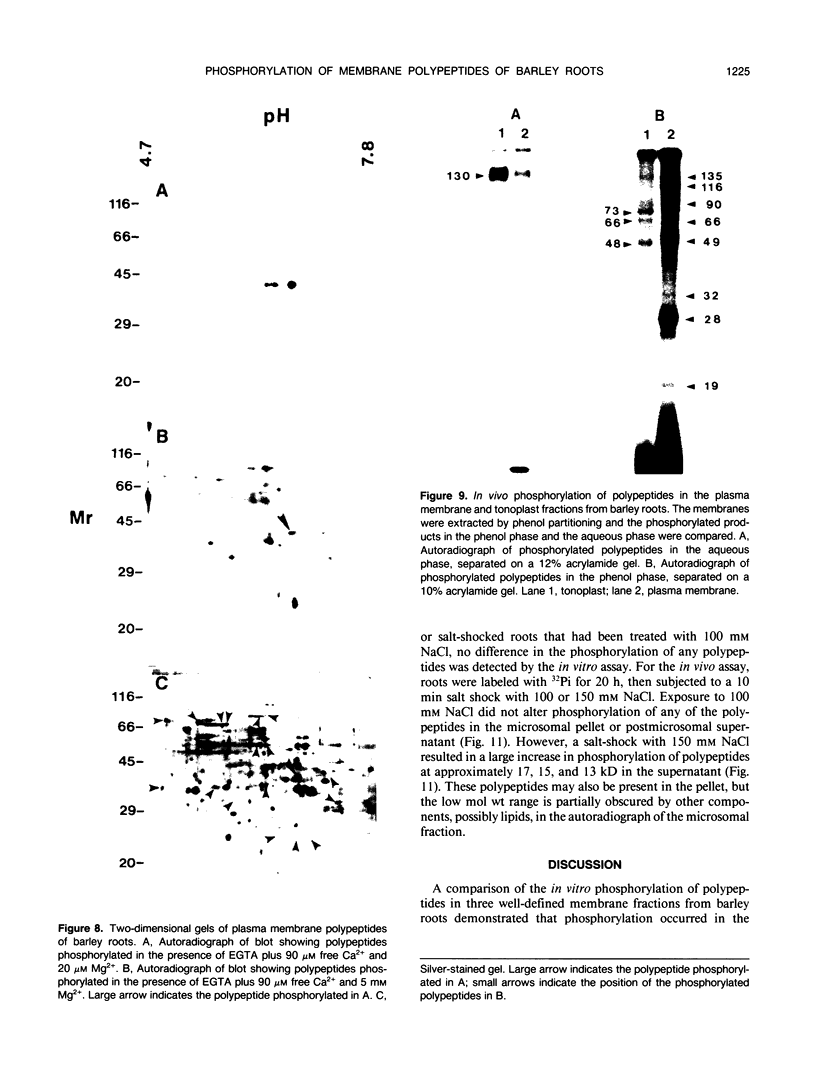
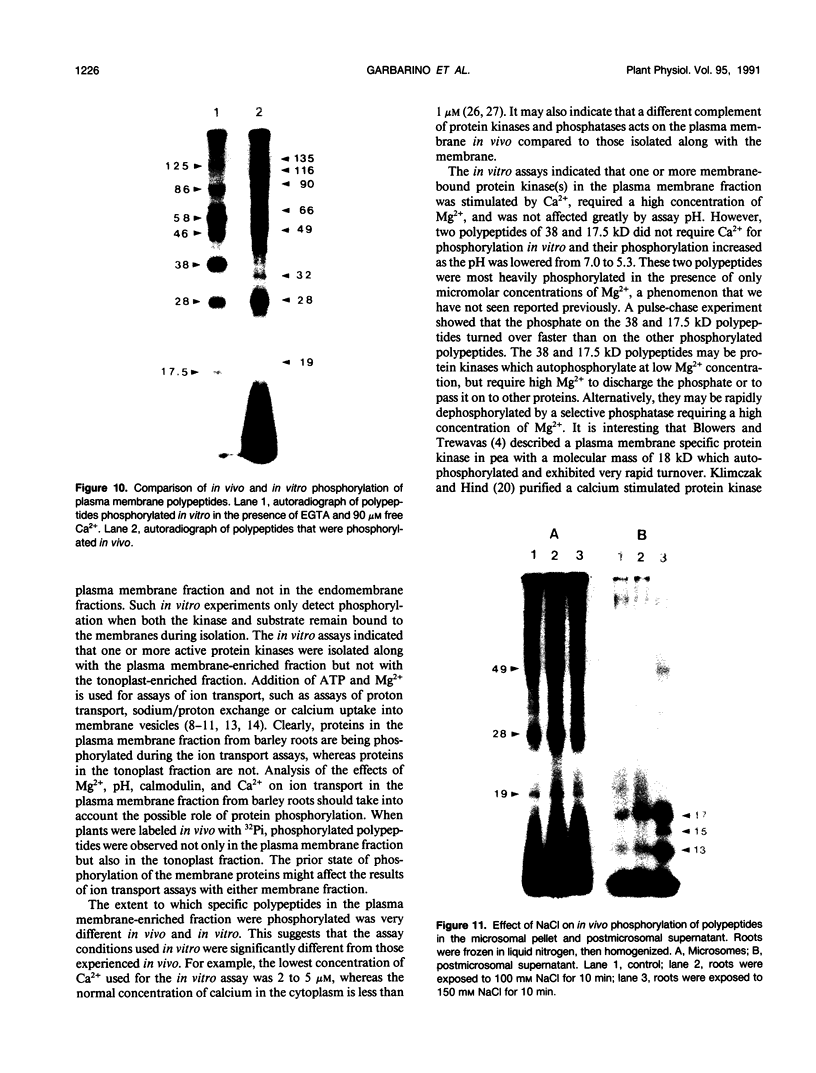
Phosphorylation of polypeptides in membrane fractions from barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv CM 72) roots was compared in in vitro and in vivo assays to assess the potential role of protein kinases in modification of membrane transport. Membrane fractions enriched in endoplasmic reticulum, tonoplast, and plasma membrane were isolated using sucrose gradients and the membrane polypeptides separated using sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. When the membrane fractions were incubated with γ-[32P]ATP, phosphorylation occurred almost exclusively in the plasma membrane fraction. Phosphorylation of a band at 38 kilodaltons increased as the concentration of Mg2+ was decreased from millimolar to micromolar levels. Phosphorylation of bands at 125, 86, 58, 46, and 28 kilodaltons required millimolar Mg2+ concentrations and was greatly enhanced by Ca2+. When roots of intact plants were labeled with [32P]orthophosphate, polypeptides at approximately 135, 116, 90, 46 to 53, 32, 28, and 19 kilodaltons were labeled in the plasma membrane fraction and polypeptides at approximately 73, 66, and 48 kilodaltons were labeled in the tonoplast fraction. Treatment of the roots of intact plants with 150 millimolar NaCl resulted in increased phosphorylation of some polypeptides while treatment with 100 mm NaCl had no effect.
Full text
PDF



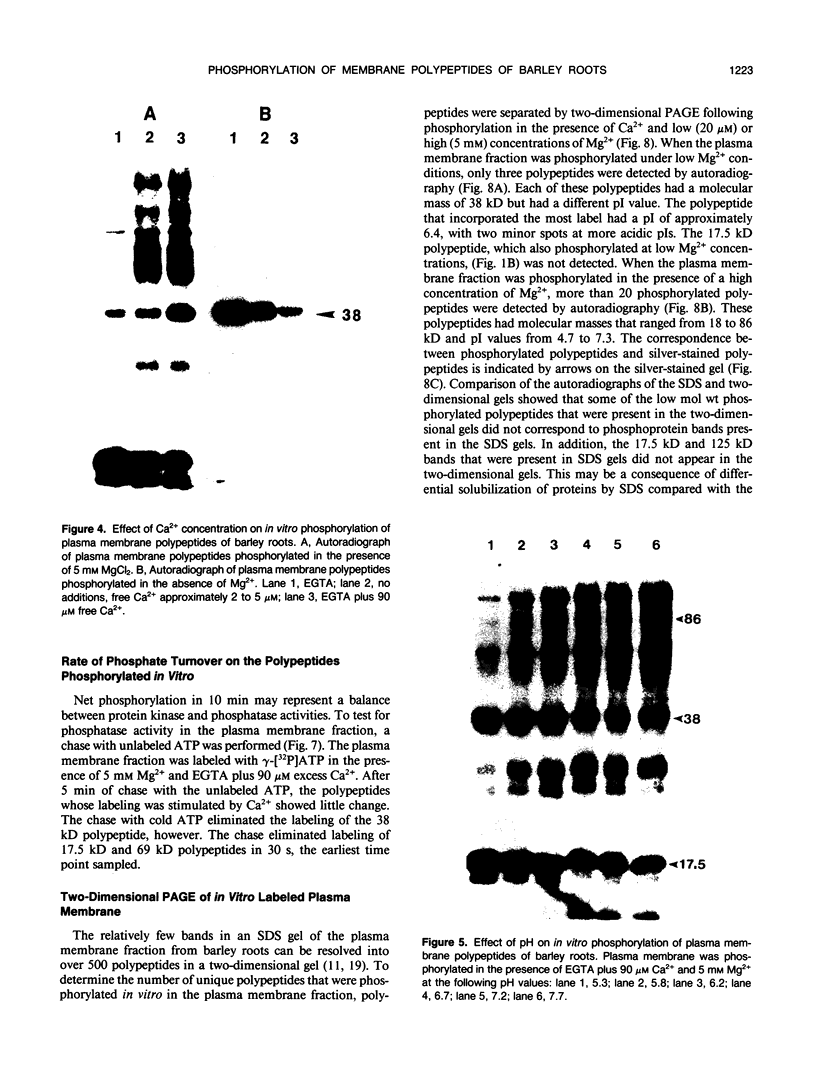



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blowers D. P., Boss W. F., Trewavas A. J. Rapid Changes in Plasma Membrane Protein Phosphorylation during Initiation of Cell Wall Digestion. Plant Physiol. 1988 Feb;86(2):505–509. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers D. P., Trewavas A. J. Autophosphorylation of plasma membrane bound calcium calmodulin dependent protein kinase from pea seedlings and modification of catalytic activity by autophosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):691–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers D. P., Trewavas A. J. Rapid cycling of autophosphorylation of a ca-calmodulin regulated plasma membrane located protein kinase from pea. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1279–1285. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. J., Dupont F. M. Lipid Composition of Plasma Membranes and Endomembranes Prepared from Roots of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) : Effects of Salt. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):955–961. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Bush D. S., Windle J. J., Jones R. L. Calcium and proton transport in membrane vesicles from barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1990 Sep;94(1):179–188. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Hurkman W. J. Separation of the Mg-ATPases from the Ca-Phosphatase Activity of Microsomal Membranes Prepared from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):857–862. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Tanaka C. K., Hurkman W. J. separation and Immunological Characterization of Membrane Fractions from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Mar;86(3):717–724. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M. Variable Effects of Nitrate on ATP-Dependent Proton Transport by Barley Root Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):526–534. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Norlyn J. D. Seawater-based crop production: a feasibility study. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):249–251. doi: 10.1126/science.197.4300.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. NaCl Induces a Na/H Antiport in Tonoplast Vesicles from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):231–236. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. Rapid induction of na/h exchange activity in barley root tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Fornari C. S., Tanaka C. K. A Comparison of the Effect of Salt on Polypeptides and Translatable mRNAs in Roots of a Salt-Tolerant and a Salt-Sensitive Cultivar of Barley. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1444–1456. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K., Dupont F. M. The effects of salt stress on polypeptides in membrane fractions from barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1263–1273. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K. Solubilization of plant membrane proteins for analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):802–806. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K. The effects of salt on the pattern of protein synthesis in barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):517–524. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimczak L. J., Hind G. Biochemical Similarities between Soluble and Membrane-Bound Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinases of Barley. Plant Physiol. 1990 Apr;92(4):919–923. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.4.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klucis E., Polya G. M. Localization, solubilization and characterization of plant membrane-associated calcium-dependent protein kinases. Plant Physiol. 1988 Sep;88(1):164–171. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladror U. S., Zielinski R. E. Protein kinase activities in tonoplast and plasmalemma membranes from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):151–158. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny-Baron G., Scherer G. F. Phospholipid-stimulated protein kinase in plants. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18052–18059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Reddy A. S. Calcium messenger system in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1987;6(1):47–103. doi: 10.1080/07352688709382247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short T. W., Briggs W. R. Characterization of a Rapid, Blue Light-Mediated Change in Detectable Phosphorylation of a Plasma Membrane Protein from Etiolated Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jan;92(1):179–185. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]