Abstract
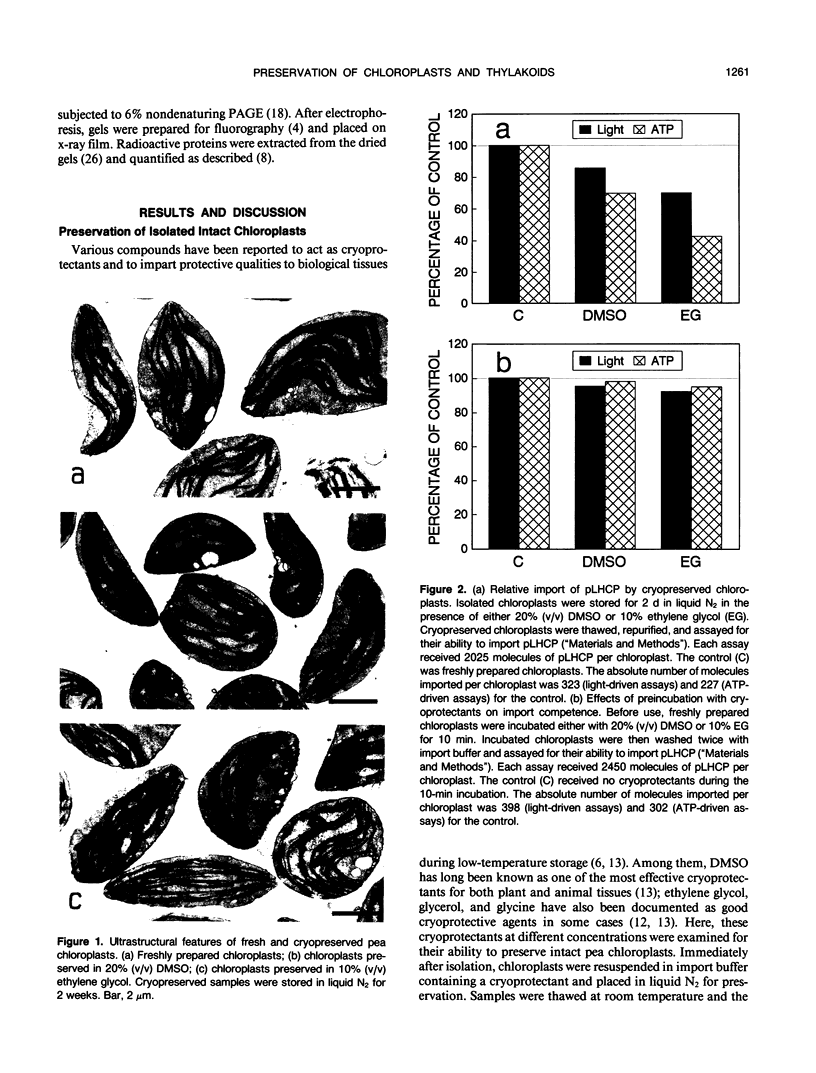
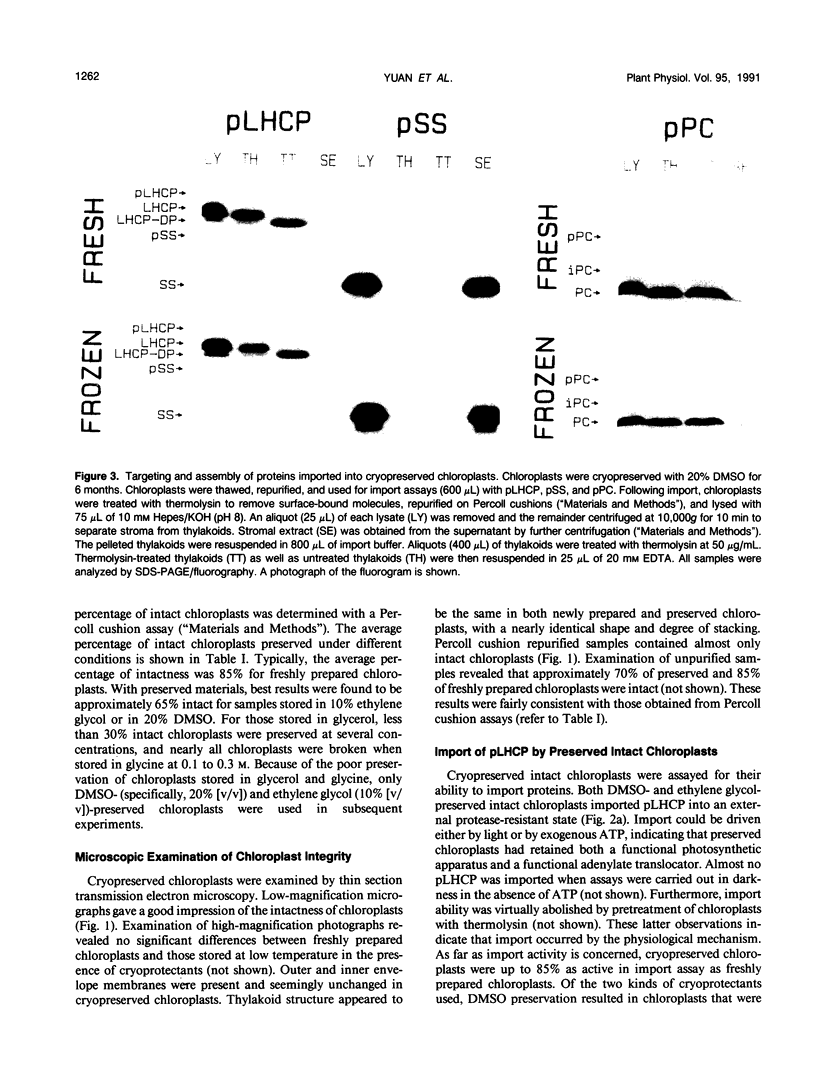
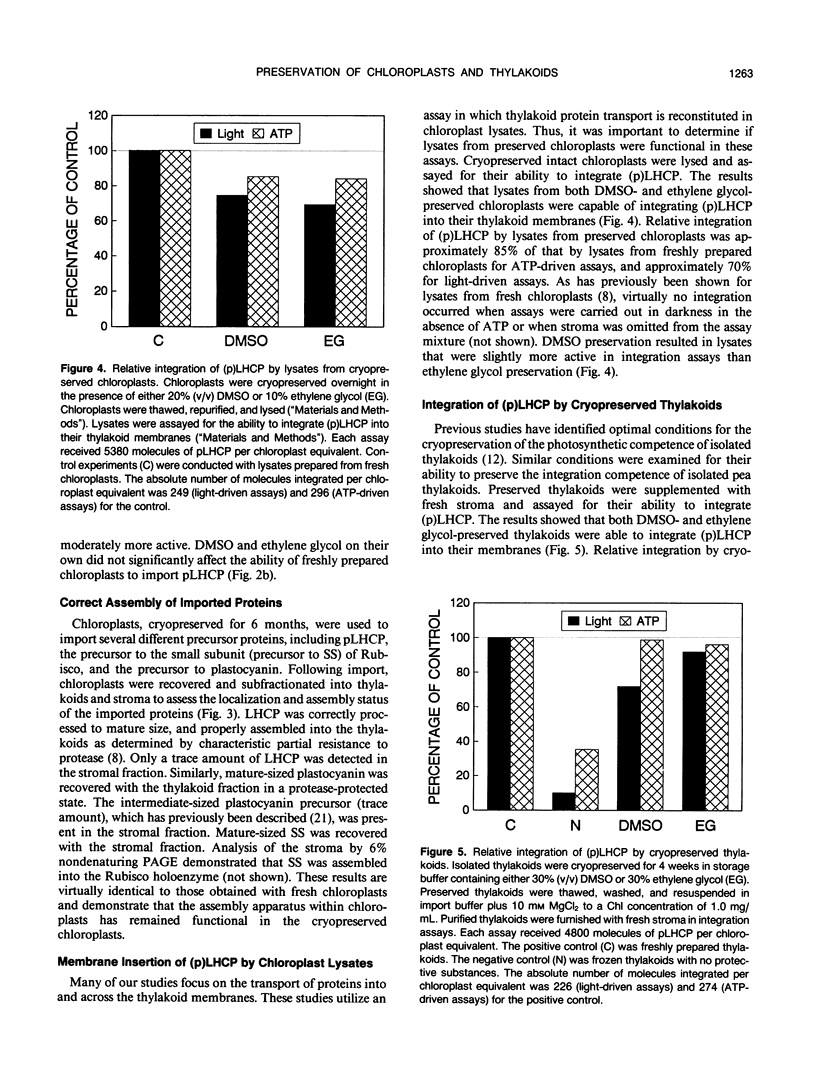
A method is presented for preservation of isolated intact chloroplasts and isolated thylakoids for use in chloroplast protein import and thylakoid protein integration studies. Chloroplasts of pea (Pisum sativum) were preserved by storage in liquid nitrogen in the presence of a cryoprotective agent. Dimethyl sulfoxide was the most effective of several cryoprotectants examined. Approximately 65 to 70% of chloroplasts stored in liquid nitrogen in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide remained intact upon thawing and were fully functional for the import of precursor proteins. Imported proteins were correctly localized within these chloroplasts, a process that for two of the proteins tested involved transport into the thylakoids. Lysate obtained from preserved chloroplasts was functional for protein integration assays. Preserved chloroplasts retained import and localization capability for up to 6 months of storage. Thylakoids were preserved by a modification of a method previously described (Farkas DL, Malkin S [1979] Plant Physiol 64: 942-947) for preservation of photosynthetic competence. Preserved thylakoids were nearly as active for protein integration studies as freshly prepared thylakoids. The ability to store chloroplasts and subfractions for extended periods will facilitate investigations of plastid protein biogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Smith S. M. Synthesis of the small subunit of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase from genes cloned into plasmids containing the SP6 promoter. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):709–715. doi: 10.1042/bj2400709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaya D., Jagendorf A. T. Optimal conditions for translation by thylakoid-bound polysomes from pea chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):832–838. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R. Structure and expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding a chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2960–2964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Fulsom D. R., Viitanen P. V. An imported thylakoid protein accumulates in the stroma when insertion into thylakoids is inhibited. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14225–14232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K. Import of proteins into chloroplasts. Membrane integration of a thylakoid precursor protein reconstituted in chloroplast lysates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14804–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K. Light-Harvesting Chlorophyll a/b Protein : Membrane Insertion, Proteolytic Processing, Assembly into LHC II, and Localization to Appressed Membranes Occurs in Chloroplast Lysates. Plant Physiol. 1988 Apr;86(4):1120–1126. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Werner-Washburne M., Lubben T. H., Keegstra K. Precursors to two nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins bind to the outer envelope membrane before being imported into chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3691–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas D. L., Malkin S. Cold storage of isolated class C chloroplasts: optimal conditions for stabilization of photosynthetic activities. Plant Physiol. 1979 Dec;64(6):942–947. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.6.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulson D. R., Cline K. A Soluble Protein Factor is Required in Vitro for Membrane Insertion of the Thylakoid Precursor Protein, pLHCP. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1146–1153. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullet J. E., Klein R. R., Grossman A. R. Optimization of protein synthesis in isolated higher plant chloroplasts. Identification of paused translation intermediates. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Mar 3;155(2):331–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan L. A., Cline K. A stromal protein factor maintains the solubility and insertion competence of an imported thylakoid membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):603–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S., Bauerle C., Hageman J., Keegstra K., Weisbeek P. The role of the transit peptide in the routing of precursors toward different chloroplast compartments. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen P. V., Doran E. R., Dunsmuir P. What is the role of the transit peptide in thylakoid integration of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein? J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15000–15007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




