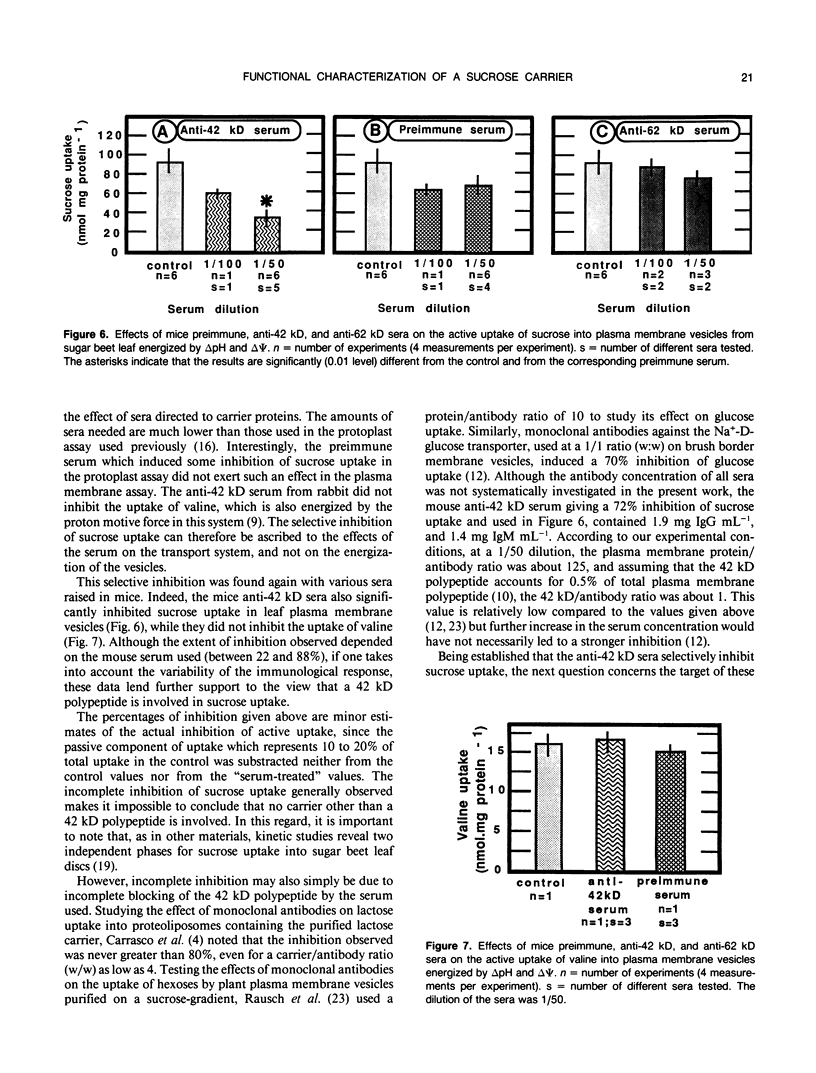
Abstract
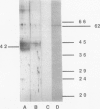
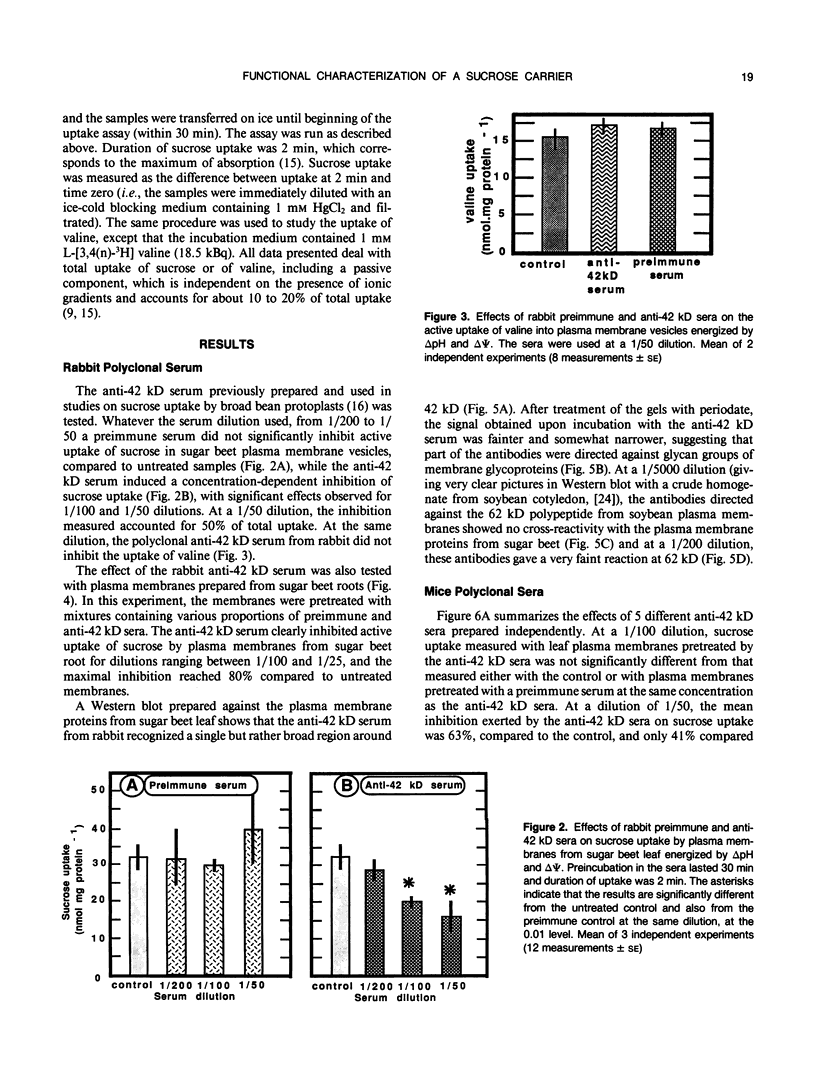
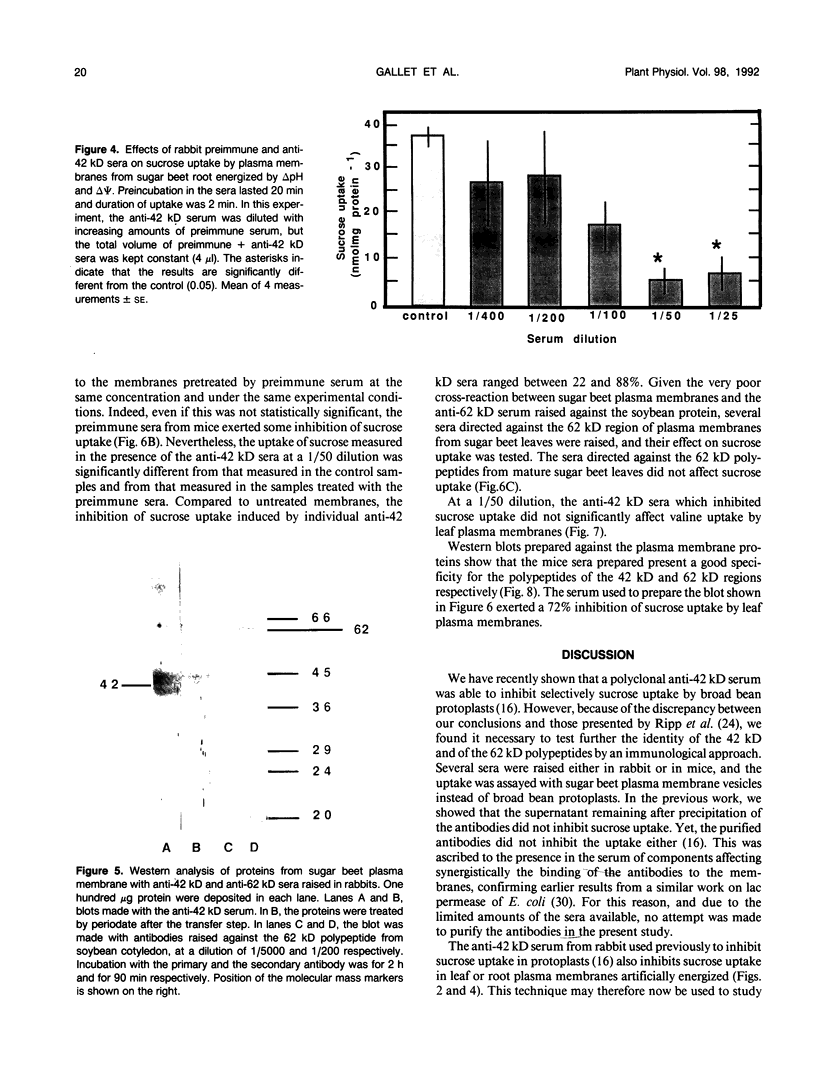
Several polyclonal sera were raised in rabbits and in mice against putative sucrose carrier proteins, i.e. a 42 kilodalton (O Gallet, R Lemoine, C Larsson, S Delrot [1989] Biochim Biophys Acta 978: 56-64) and a 62 kD (KG Ripp, PV Viitanen, WD Hitz, VR Fransceschi [1988] Plant Physiol 88: 1435-1445) polypeptide of the plasma membrane. The effects of these sera on the active uptake of sucrose and of valine into purified plasma membrane vesicles from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) leaves and roots were studied. At a dilution of 1/50, the anti-42 kilodalton sera consistently inhibited sucrose uptake in plasma membranes from leaves or from roots. They had no effect on valine uptake. Under the same experimental conditions, the anti-62 kilodalton sera had no effect on active uptake of sucrose. The data further support the view that a 42 kilodalton polypeptide is a component of the transport system mediating sucrose uptake across the plasma membrane of plant cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bearden J. C., Jr Quantitation of submicrogram quantities of protein by an improved protein-dye binding assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 26;533(2):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush D. R. Proton-Coupled Sucrose Transport in Plasmalemma Vesicles Isolated from Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris L. cv Great Western) Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1989 Apr;89(4):1318–1323. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.4.1318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Tahara S. M., Patel L., Goldkorn T., Kaback H. R. Preparation, characterization, and properties of monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6894–6898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsell H., Korn K., Raszeja-Specht A., Bernotat-Danielowski S., Ollig D. Monoclonal antibodies against the renal Na+-D-glucose cotransporter. Identification of antigenic polypeptides and demonstration of functional coupling of different Na+-cotransport systems. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18419–18429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Levin A., Branton D. Copper staining: a five-minute protein stain for sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):308–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. W., Lucas W. J. A Reanalysis of the Two-Component Phloem Loading System in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1982 Mar;69(3):734–739. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch T., Raszeja-Specht A., Koepsell H. Identification of an Mr 75000 component of the H+/D-glucose cotransporter from Zea mays with monoclonal antibodies directed against the mammalian Na+/D-glucose cotransporter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 16;985(2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripp K. G., Viitanen P. V., Hitz W. D., Franceschi V. R. Identification of membrane protein associated with sucrose transport into cells of developing soybean cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1435–1445. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmalstig J. G., Geiger D. R. Phloem Unloading in Developing Leaves of Sugar Beet : I. Evidence for Pathway through the Symplast. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):237–241. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmalstig J. G., Geiger D. R. Phloem Unloading in Developing Leaves of Sugar Beet : II. Termination of Phloem Unloading. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):49–52. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turgeon R., Gowan E. Phloem Loading in Coleus blumei in the Absence of Carrier-Mediated Uptake of Export Sugar from the Apoplast. Plant Physiol. 1990 Nov;94(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.3.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Lever J. E. Monoclonal antibodies that bind the renal Na+/glucose symport system. 1. Identification. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5783–5790. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]