Abstract
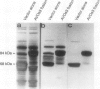
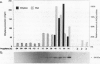
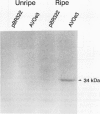
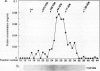
Fruit ripening involves a series of changes in gene expression regulated by the phytohormone ethylene. AVOe3, a ripening-related gene in avocado fruit (Persea americana Mill. cv Hass), was characterized with regard to its ethylene-regulated expression. The AVOe3 mRNA and immunopositive protein were induced in mature fruit within 12 hours of propylene treatment. The AVOe3 mRNA levels reached a maximum 1 to 2 days before the ethylene climacteric, whereas the immunopositive protein continued to accumulate. RNA selected by the pAVOe3 cDNA clone encoded a polypeptide with molecular mass of 34 kilodaltons, corresponding to the molecular mass of the AVOe3 protein determined by immunoblots. The protein was soluble, remaining in solution at 100,000 gravity and eluted as a monomer on gel filtration. Because of its pattern of induction and relationship to an ethylene-related gene of tomato, the possible involvement of AVOe3 in ethylene biosynthesis is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A. B., Christoffersen R. E. Synthesis and processing of cellulase from ripening avocado fruit. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):830–835. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozak K. R., Yu H., Sirevåg R., Christoffersen R. E. Sequence analysis of ripening-related cytochrome P-450 cDNAs from avocado fruit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3904–3908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britsch L., Grisebach H. Purification and characterization of (2S)-flavanone 3-hydroxylase from Petunia hybrida. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 2;156(3):569–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzi C., Gillespie D. Fast blots: immobilization of DNA and RNA from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:582–587. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Stepień P. P., Tso J. Y., Brousseau R., Narang S., Thomas D. Y., Wu R. Synthesis of human insulin gene. VIII. Construction of expression vectors for fused proinsulin production in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A. J., Bouzayen M., Grierson D. Identification of a tomato gene for the ethylene-forming enzyme by expression in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7434–7437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth M. J., Bird C. R., Ray J., Schuch W., Grierson D. Structure and expression of an ethylene-related mRNA from tomato. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):731–739. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanellis A. K., Solomos T., Mattoo A. K. Hydrolytic Enzyme Activities and Protein Pattern of Avocado Fruit Ripened in Air and in Low Oxygen, with and without Ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1989 May;90(1):259–266. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kende H. Enzymes of ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1989 Sep;91(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln J. E., Fischer R. L. Diverse mechanisms for the regulation of ethylene-inducible gene expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Apr;212(1):71–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00322446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Hoffman N. E., Yang S. F. Promotion by Ethylene of the Capability to Convert 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic Acid to Ethylene in Preclimacteric Tomato and Cantaloupe Fruits. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):407–411. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarvey D. J., Yu H., Christoffersen R. E. Nucleotide sequence of a ripening-related cDNA from avocado fruit. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jul;15(1):165–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00017736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'keefe D. P., Leto K. J. Cytochrome P-450 from the Mesocarp of Avocado (Persea americana). Plant Physiol. 1989 Apr;89(4):1141–1149. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.4.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitrit Y., Riov J., Blumenfeld A. Regulation of Ethylene Biosynthesis in Avocado Fruit during Ripening. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):130–135. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanu P., Reinhardt D., Boller T. Analysis and cloning of the ethylene-forming enzyme from tomato by functional expression of its mRNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2007–2013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker M. L., Laties G. G. Interrelationship of Gene Expression, Polysome Prevalence, and Respiration during Ripening of Ethylene and/or Cyanide-Treated Avocado Fruit. Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):307–315. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Straeten D., Van Wiemeersch L., Goodman H. M., Van Montagu M. Cloning and sequence of two different cDNAs encoding 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4859–4863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. R. An improved method for the detection of peroxidase-conjugated antibodies on immunoblots. J Virol Methods. 1989 Apr-May;24(1-2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]