Abstract
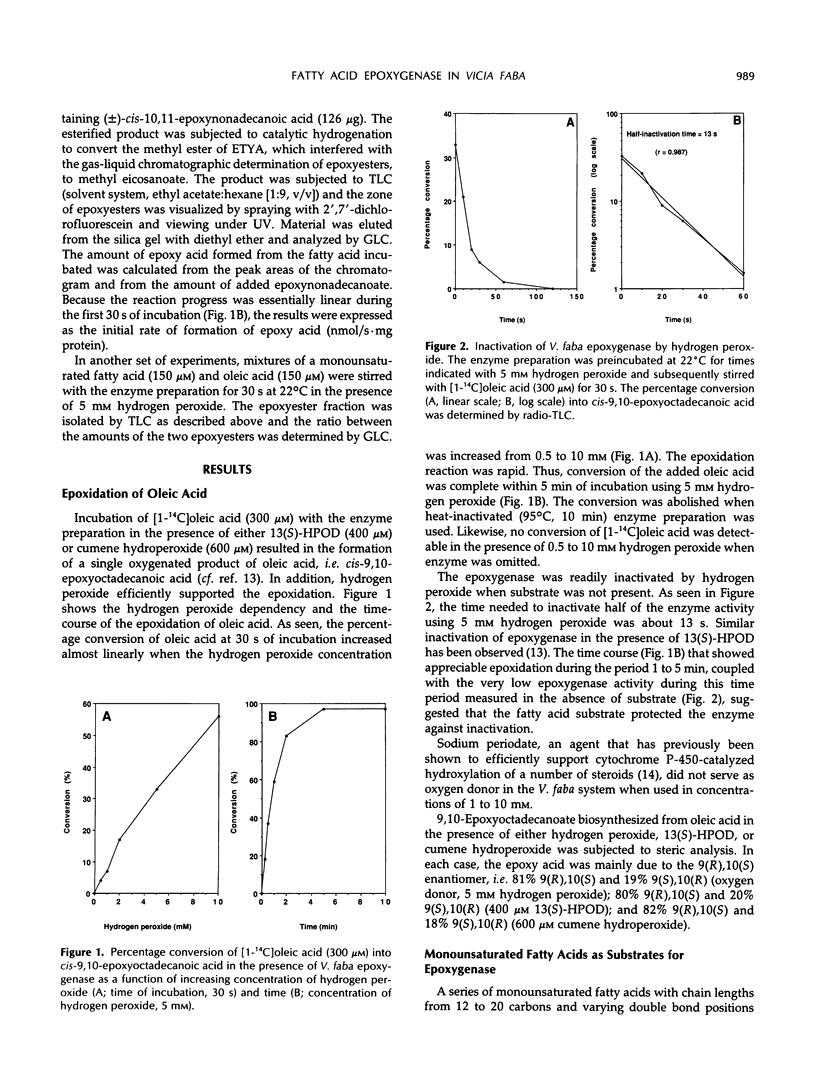
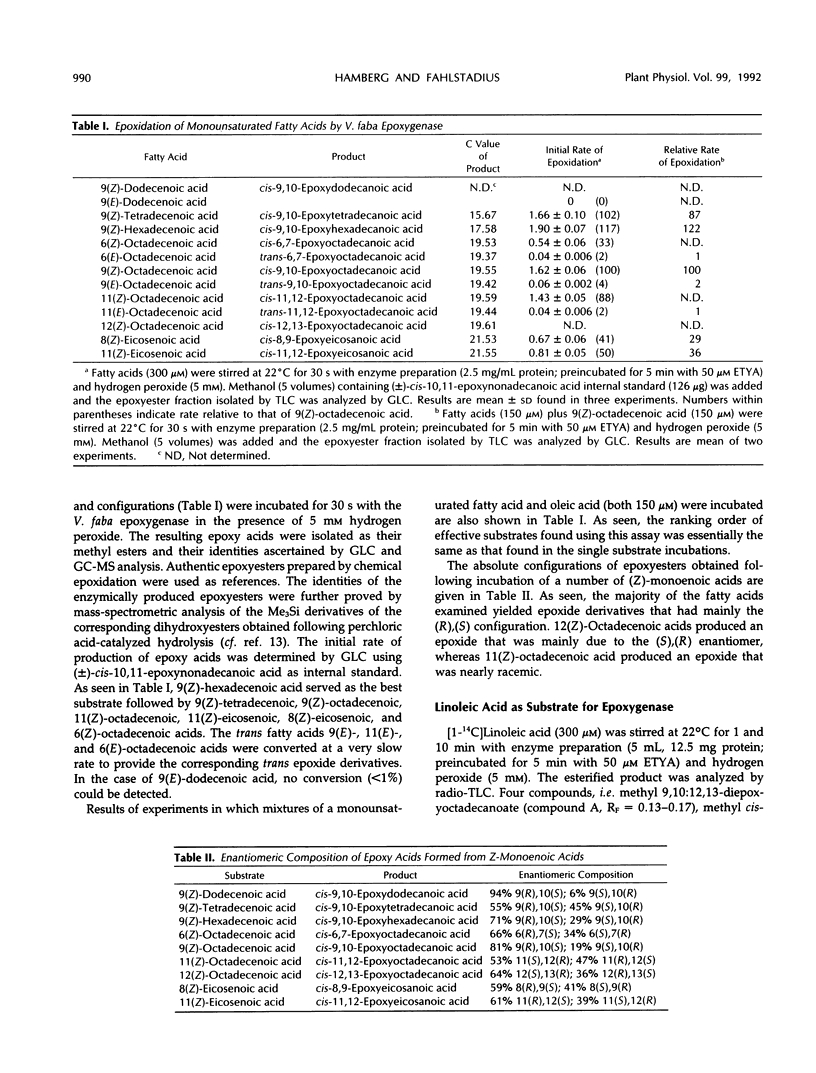
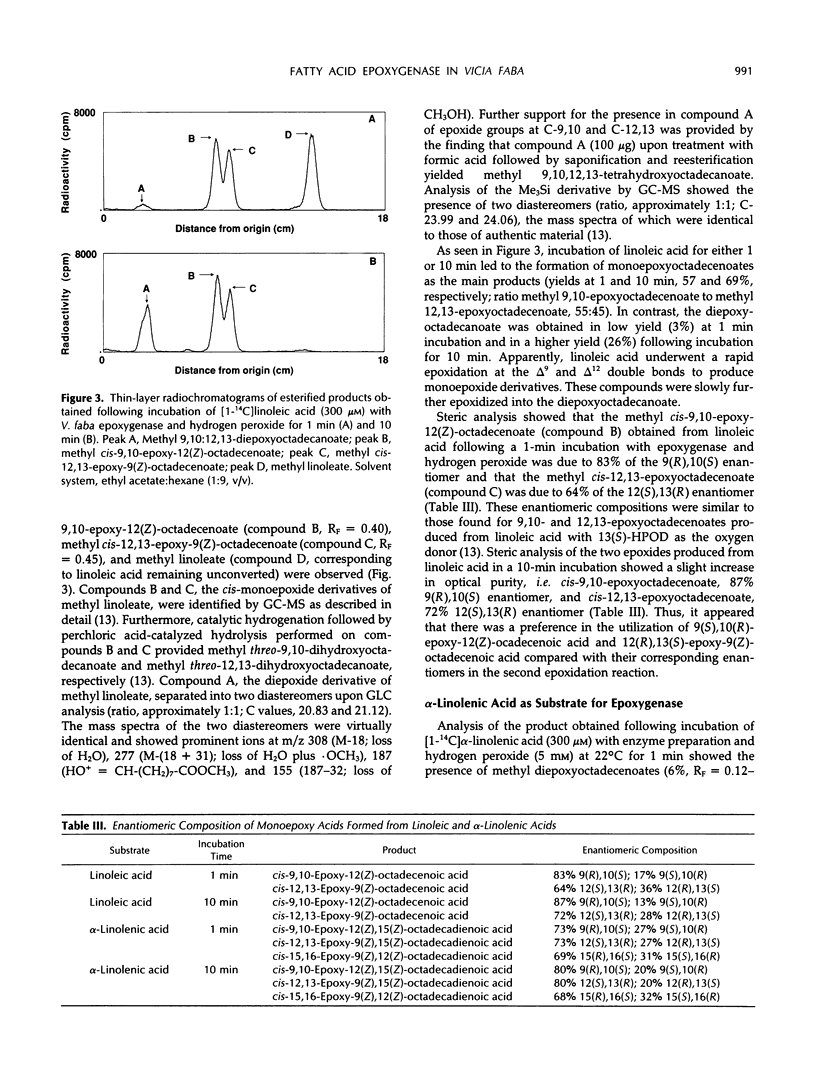
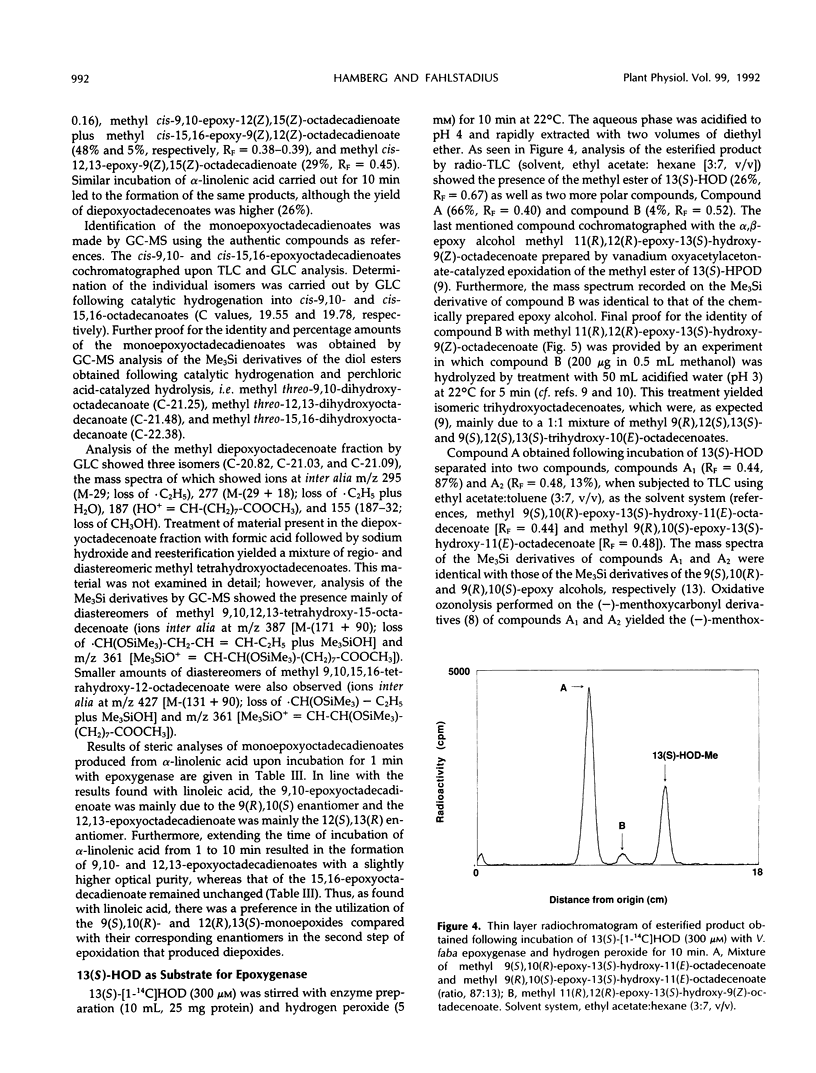
Seeds of broad bean (Vicia faba L.) contain a hydroperoxide-dependent fatty acid epoxygenase. Hydrogen peroxide served as an effective oxygen donor in the epoxygenase reaction. Fifteen unsaturated fatty acids were incubated with V. faba epoxygenase in the presence of hydrogen peroxide and the epoxy fatty acids produced were identified. Examination of the substrate specificity of the epoxygenase using a series of monounsaturated fatty acids demonstrated that (Z)-fatty acids were rapidly epoxidized into the corresponding cis-epoxy acids, whereas (E)-fatty acids were converted into their trans-epoxides at a very slow rate. In the series of (Z)-monoenoic acids, the double bond position as well as the chain length influenced the rate of epoxidation. The best substrates were found to be palmitoleic, oleic, and myristoleic acids. Steric analysis showed that most of the epoxy acids produced from monounsaturated fatty acids as well as from linoleic and α-linolenic acids had mainly the (R),(S) configuration. Exceptions were C18 acids having the epoxide group located at C-12/13, in which cases the (S),(R) enantiomers dominated. 13(S)-Hydroxy-9(Z),11(E)-octadecadienoic acid incubated with epoxygenase afforded the epoxy alcohol 9(S),10(R)-epoxy-13(S)-hydroxy-11(E)-octadecenoic acid as the major product. Smaller amounts of the diastereomeric epoxy alcohol 9(R),10(S)-epoxy-13(S)-hydroxy-11(E)-octadecenoic acid as well as the α,β-epoxy alcohol 11(R),12(R)-epoxy-13(S)-hydroxy-9(Z)-octadecenoic acid were also obtained. The soluble fraction of homogenate of V. faba seeds contained an epoxide hydrolase activity that catalyzed the conversion of cis-9,10-epoxyoctadecanoic acid into threo-9,10-dihydroxyoctadecanoic acid.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blee E., Schuber F. Stereochemistry of the epoxidation of fatty acids catalyzed by soybean peroxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1354–1360. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80937-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blée E., Schuber F. Efficient epoxidation of unsaturated fatty acids by a hydroperoxide-dependent oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12887–12894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croteau R., Kolattukudy P. E. Biosynthesis of hydroxyfatty acid polymers. Enzymatic epoxidation of 18-hydroxyoleic acid to 18-hydroxy-cis-9,10-epoxystearic acid by a particulate preparation from spinach (Spinacia oleracea). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahlstadius P., Hamberg M. A gas-liquid chromatographic method for steric analysis of epoxy acids. Chem Phys Lipids. 1989 Jul;51(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(89)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahlstadius P. cis-9,10-epoxystearic acid in human leukocytes: isolation and quantitative determination. Lipids. 1988 Nov;23(11):1015–1018. doi: 10.1007/BF02535645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Fahlstadius P. Allene oxide cyclase: a new enzyme in plant lipid metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Feb 1;276(2):518–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90753-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Hamberg G. Hydroperoxide-dependent epoxidation of unsaturated fatty acids in the broad bean (Vicia faba L.). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Dec;283(2):409–416. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90662-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M. Steric analysis of hydroperoxides formed by lipoxygenase oxygenation of linoleic acid. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrycay E. G., Gustafsson J. A., Ingelman-Sundberg M., Ernster L. Sodium periodate, sodium chloride, organic hydroperoxides, and H2O2 as hydroxylating agents in steroid hydroxylation reactions catalyzed by partially purified cytochrome P-450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson B. D., MacRae E. A., Ferguson I. B. Estimation of hydrogen peroxide in plant extracts using titanium(IV). Anal Biochem. 1984 Jun;139(2):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


