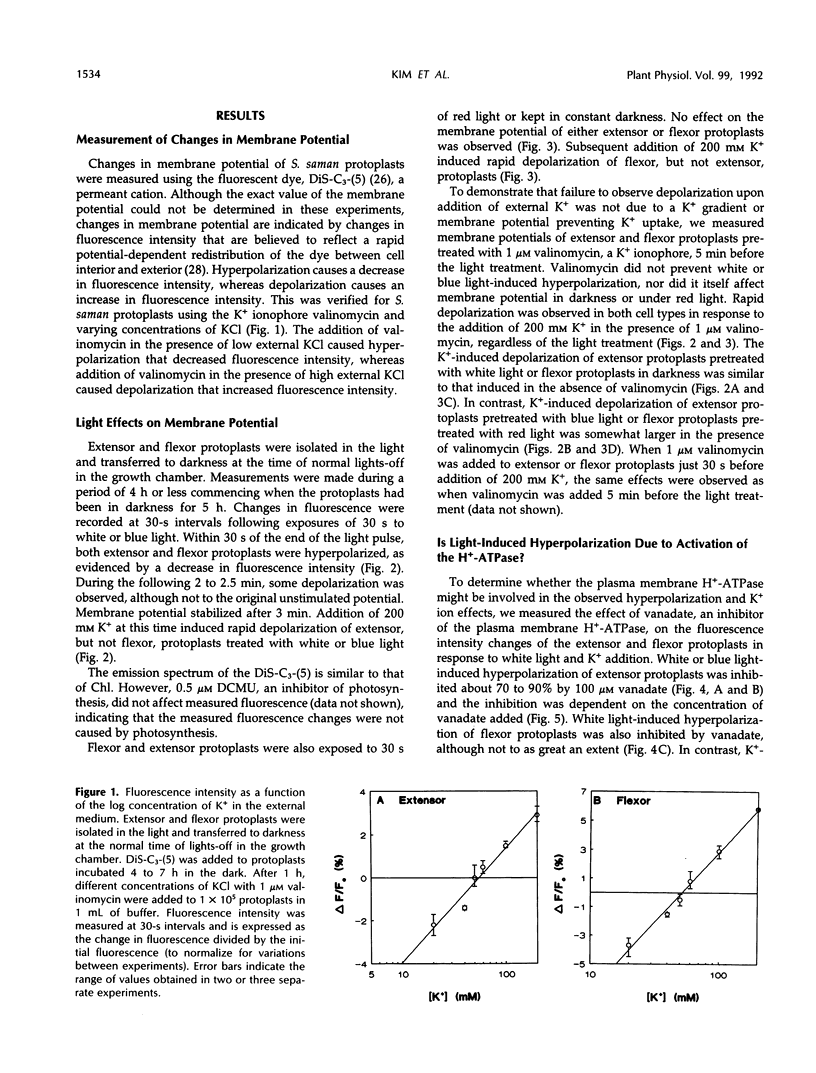
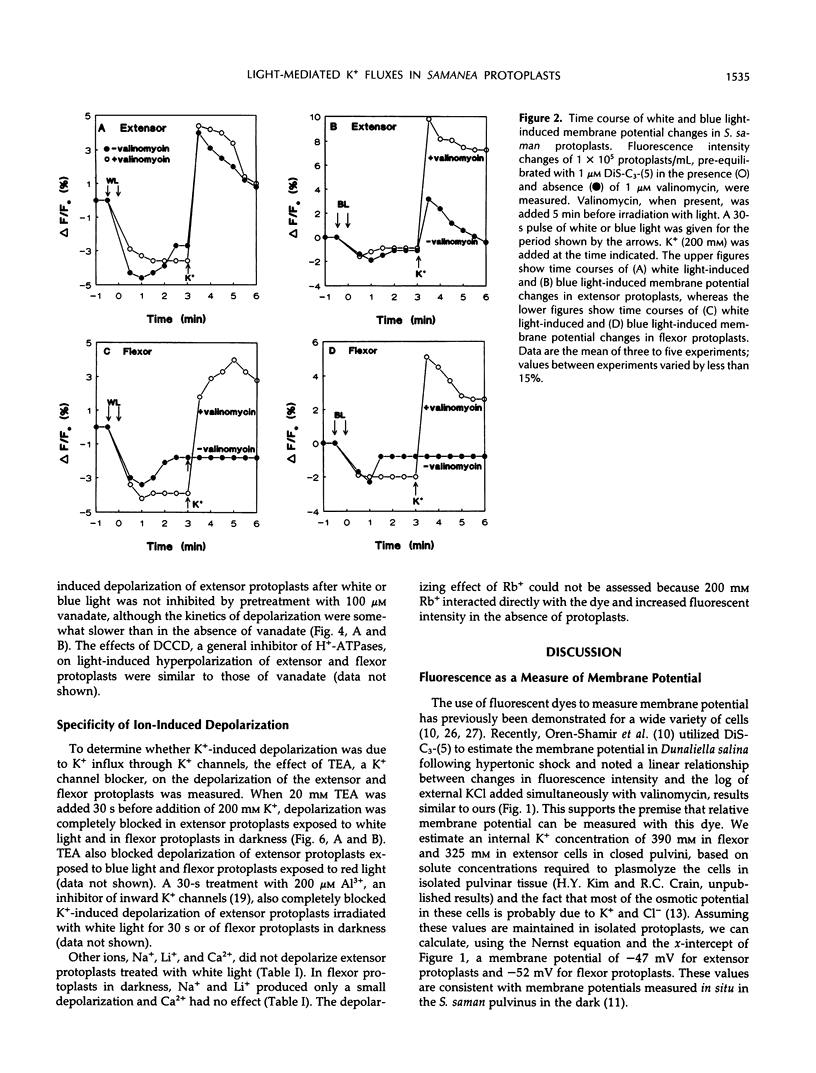
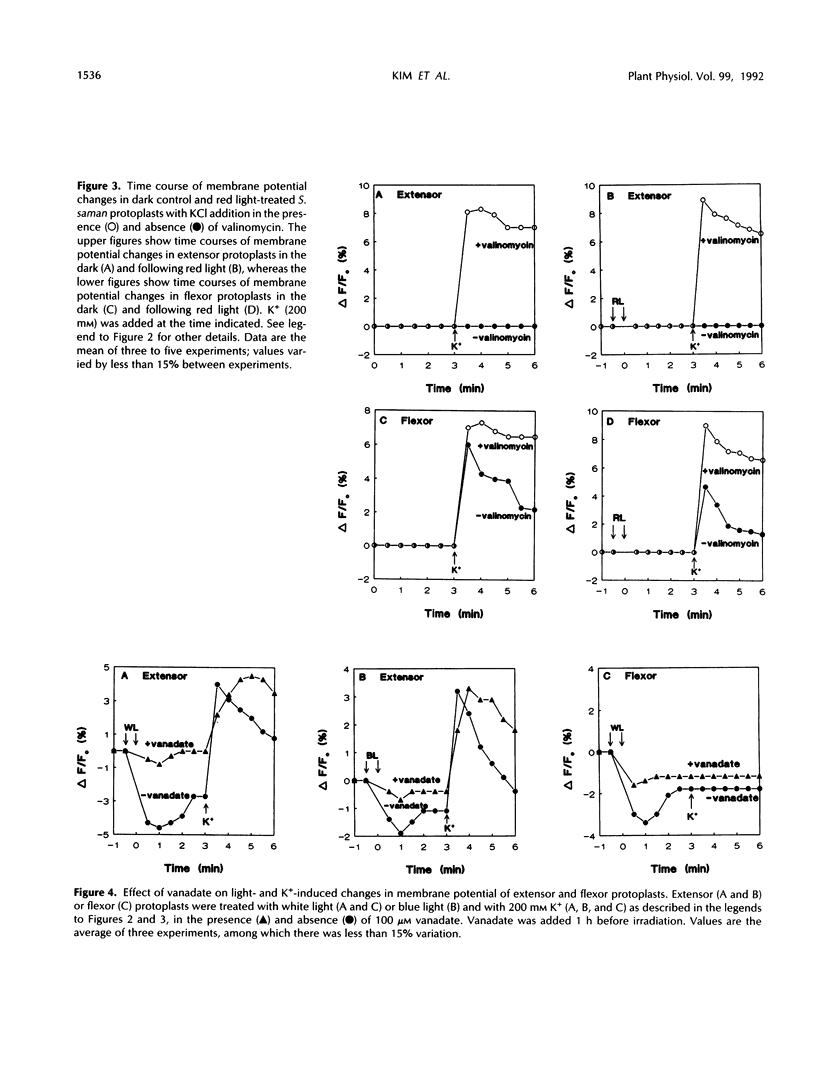
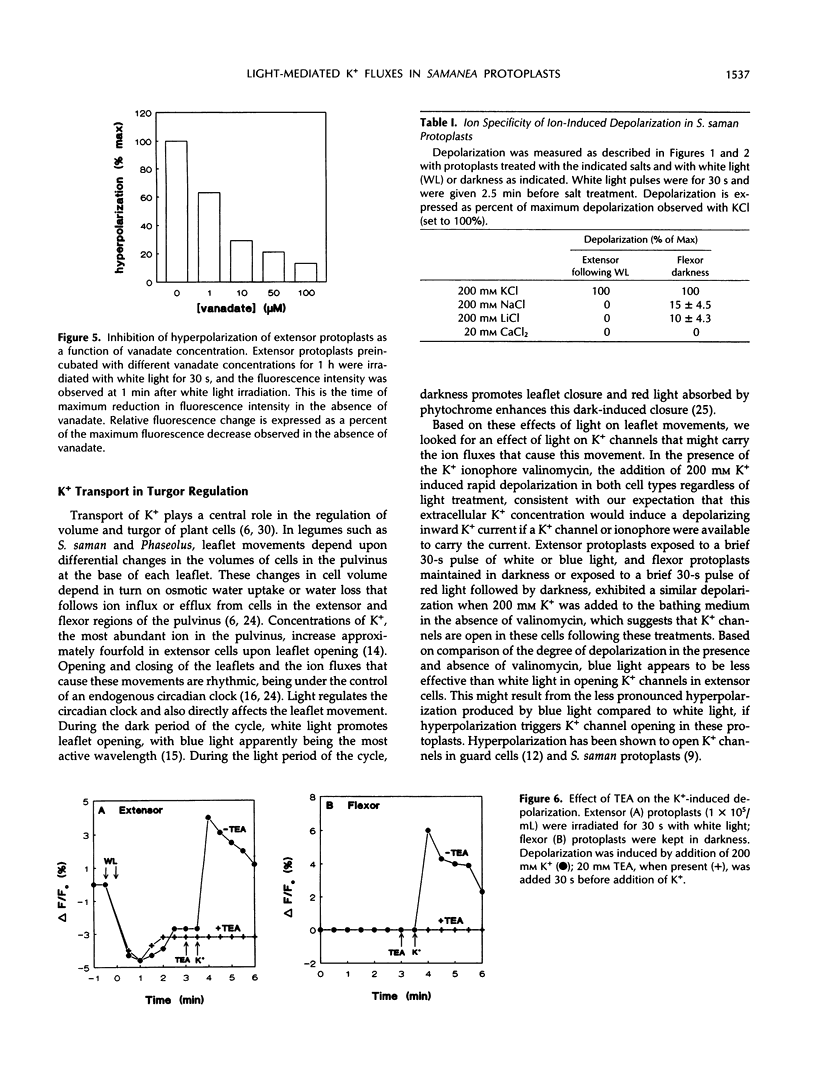
Abstract
Rhythmic light-sensitive movements of the leaflets of Samanea saman depend upon ion fluxes across the plasma membrane of extensor and flexor cells in opposing regions of the leaf-movement organ (pulvinus). We have isolated protoplasts from the extensor and flexor regions of S. saman pulvini and have examined the effects of brief 30-second exposures to white, blue, or red light on the relative membrane potential using the fluorescent dye, 3,3′-dipropylthiadicarbocyanine iodide. White and blue light induced transient membrane hyperpolarization of both extensor and flexor protoplasts; red light had no effect. Following white or blue light-induced hyperpolarization, the addition of 200 millimolar K+ resulted in a rapid depolarization of extensor, but not of flexor protoplasts. In contrast, addition of K+ following red light or in darkness resulted in a rapid depolarization of flexor, but not of extensor protoplasts. In both flexor and extensor protoplasts, depolarization was completely inhibited by tetraethylammonium, implicating channel-mediated movement of K+ ions. These results suggest that K+ channels are closed in extensor plasma membranes and open in flexor plasma membranes in darkness and that white and blue light, but not red light, close the channels in flexor plasma membranes and open them in extensor plasma membranes. Vanadate treatment inhibited hyperpolarization in response to blue or white light, but did not affect K+ -induced depolarization. This suggests that white or blue light-induced hyperpolarization results from activation of the H+ -ATPase, but this hyperpolarization is not the sole factor controlling the opening of K+ channels.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell N. A., Satter R. L., Garber R. C. Apoplastic transport of ions in the motor organ of Samanea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2981–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L., Warner R., Yanagisawa M., Lechene C., Guidotti G. Vanadate is a potent (Na,K)-ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7421–7423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorton H. L., Satter R. L. Extensor and flexor protoplasts from samanea pulvini : I. Isolation and initial characterization. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):680–684. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich R., Busch H., Raschke K. Ca2+ and nucleotide dependent regulation of voltage dependent anion channels in the plasma membrane of guard cells. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3889–3892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren-Shamir M., Pick U., Avron M. Plasma membrane potential of the alga dunaliella, and its relation to osmoregulation. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):403–408. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen R., Satter R. L. Rhythmic and phytochrome-regulated changes in transmembrane potential in samanea pulvini. Nature. 1975 May 29;255(5507):408–410. doi: 10.1038/255408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satter R. L., Geballe G. T., Applewhite P. B., Galston A. W. Potassium flux and leaf movement in Samanea saman. I. Rhythmic movement. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Oct;64(4):413–430. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satter R. L., Guggino S. E., Lonergan T. A., Galston A. W. The effects of blue and far red light on rhythmic leaflet movements in samanea and albizzia. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):965–968. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I. K+ transport properties of K+ channels in the plasma membrane of Vicia faba guard cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Nov;92(5):667–683. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Raschke K., Neher E. Voltage dependence of K channels in guard-cell protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4108–4112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short T. W., Briggs W. R. Characterization of a Rapid, Blue Light-Mediated Change in Detectable Phosphorylation of a Plasma Membrane Protein from Etiolated Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jan;92(1):179–185. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. S. Dye indicators of membrane potential. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:47–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. S. The use of cyanine dyes for the determination of membrane potentials in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:689–695. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H., Tolles R. L. Mechanism of potential-dependent light absorption changes of lipid bilayer membranes in the presence of cyanine and oxonol dyes. J Membr Biol. 1977 May 6;33(1-2):109–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01869513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warpeha K. M., Hamm H. E., Rasenick M. M., Kaufman L. S. A blue-light-activated GTP-binding protein in the plasma membranes of etiolated peas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8925–8929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


