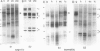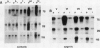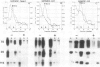Abstract
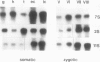
Cell-free translational and northern blot analyses were used to examine the distribution of storage protein messages in the cytoplasmic polysomal and mRNA-protein complex (mRNP) fractions during development of somatic and zygotic embryos of alfalfa (Medicago sativa cv Rangelander RL-34). No special array of messages was identified in the mRNP fraction; however, some messages were selectively enriched in either the polysome or mRNP fractions, and their distribution pattern varied quantitatively during development of the embryos. During the earliest stages of somatic embryo development, storage protein messages already were present, but there was no detectable accumulation of the proteins. Selective enrichment of messages for the 11S, 7S, and 2S storage proteins occurred in the mRNP fraction during the globular, heart, and torpedo stages of somatic embryogenesis, but the distribution pattern was shifted toward the polysomal fraction at the beginning of cotyledon development. Thus, there was translational repression of storage protein synthesis at the early stage of somatic embryo development that was relieved later. During the cotyledonary development stages in the somatic and zygotic embryos, storage protein synthesis and distribution of the messages were similar in that these specific messages were predominantly in the polysomal fraction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bag J. Cytoplasmic mRNA-protein complexes of chicken muscle cells and their role in protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewley J. D., Marcus A. Gene expression in seed development and germination. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;38:165–193. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60711-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamborg O. L., Miller R. A., Ojima K. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Apr;50(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krochko J. E., Pramanik S. K., Bewley J. D. Contrasting Storage Protein Synthesis and Messenger RNA Accumulation during Development of Zygotic and Somatic Embryos of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Physiol. 1992 May;99(1):46–53. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Tierney M. L., Meinke D. W., Hosángadi P., Veith M., Beachy R. N. Developmental Regulation of beta-Conglycinin in Soybean Axes and Cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1987 May;84(1):35–41. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preobrazhensky A. A., Spirin A. S. Informosomes and their protein components: the present state of knowledge. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1978;21:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal M., Depigny D., Cooke R., Delseny M. Characterization of a Radish Nuclear Gene Expressed during Late Seed Maturation. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):829–836. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Groner Y. Post-transcriptional and translational controls of gene expression in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:1079–1126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.005243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Hunt T., Ruderman J. V. Selective translation of mRNA controls the pattern of protein synthesis during early development of the surf clam, Spisula solidissima. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90635-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttuck-Eidens D. M., Beachy R. N. Degradation of beta-Conglycinin in Early Stages of Soybean Embryogenesis. Plant Physiol. 1985 Aug;78(4):895–898. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.4.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein E. Subribosomal ribonucleoprotein particles of developing wheat embryo. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):951–958. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling L., Drews G. N., Goldberg R. B. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of soybean seed protein mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2123–2127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]