Abstract
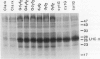
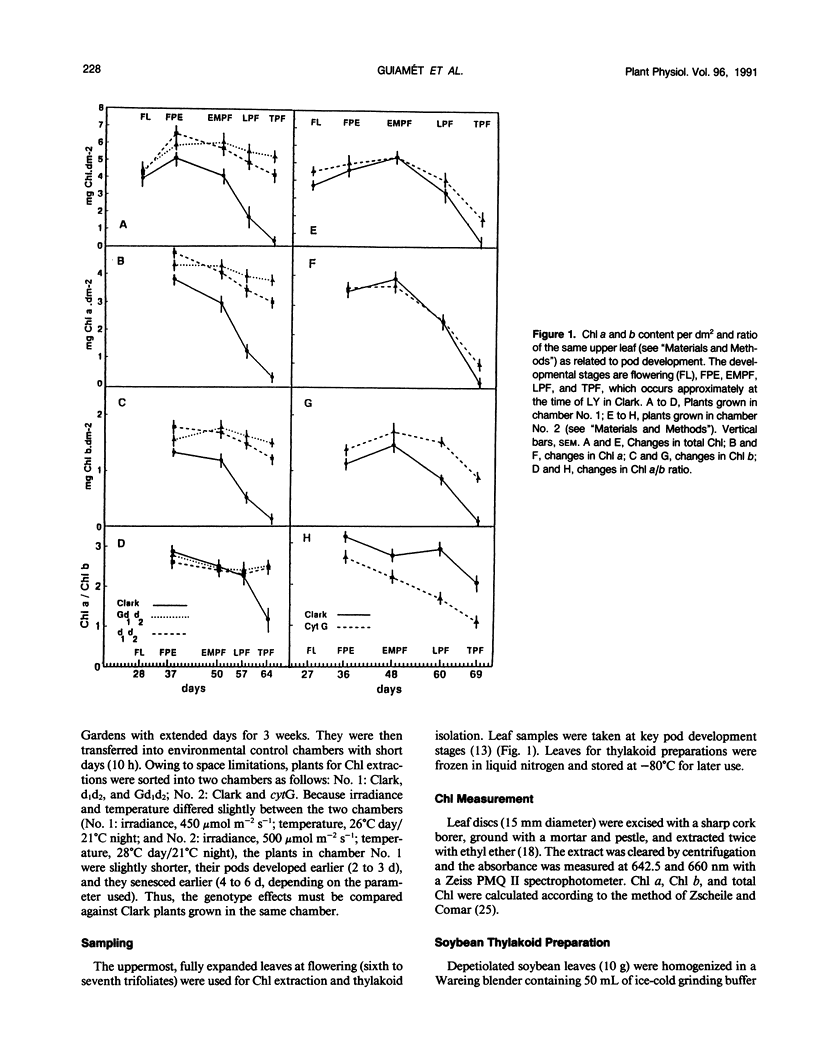
Soybean plants (Glycine max [L.] Merr. cv Clark) carrying nuclear and cytoplasmic “stay-green” mutations, which affect senescence, were examined. Normally, the levels of chlorophyll (Chl) a and b decline during seedfill and the Chl a/b ratio decreases during late pod development in cv Clark. Plants homozygous for both the d1 and d2 recessive alleles, at two different nuclear loci, respectively, retained most (64%) of their Chl a and b and exhibited no change in their Chl a/b ratio. Combination of G (a dominant nuclear allele in a third locus causing only the seed coat to stay green during senescence) with d1d2 further inhibited the loss of Chl in the leaf. Whereas the thylakoid proteins seem to be degraded in normal Clark leaves during late pod development, they were not substantially diminished in d1d2 and Gd1d2 leaves. In plants carrying a cytoplasmic mutation, cytG, Chl declined in parallel with normal cv Clark; however, the cytG leaves had a much higher level of Chl b, and somewhat more Chl a, remaining at abscission, enough to color the leaves green. In cytG, most thylakoid proteins were degraded, but the Chl a/b-binding polypeptides of the light-harvesting complex in photosystem II (LHCII), and their associated Chl a and b molecules, were not. Thus, the combination of d1 and d2 causes broad preservation of the thylakoid proteins, whereas cytG appears to selectively preserve LHCII. The cytG mutation may be useful in elucidating the sequence of events involved in the degradation of LHCII proteins and their associated pigments during senescence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gottesman S., Squires C., Pichersky E., Carrington M., Hobbs M., Mattick J. S., Dalrymple B., Kuramitsu H., Shiroza T., Foster T. Conservation of the regulatory subunit for the Clp ATP-dependent protease in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3513–3517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornber J. P., Highkin H. R. Composition of the photosynthetic apparatus of normal barley leaves and a mutant lacking chlorophyll b. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):109–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]