Abstract
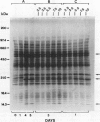
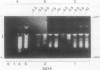
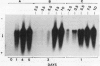
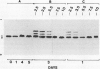
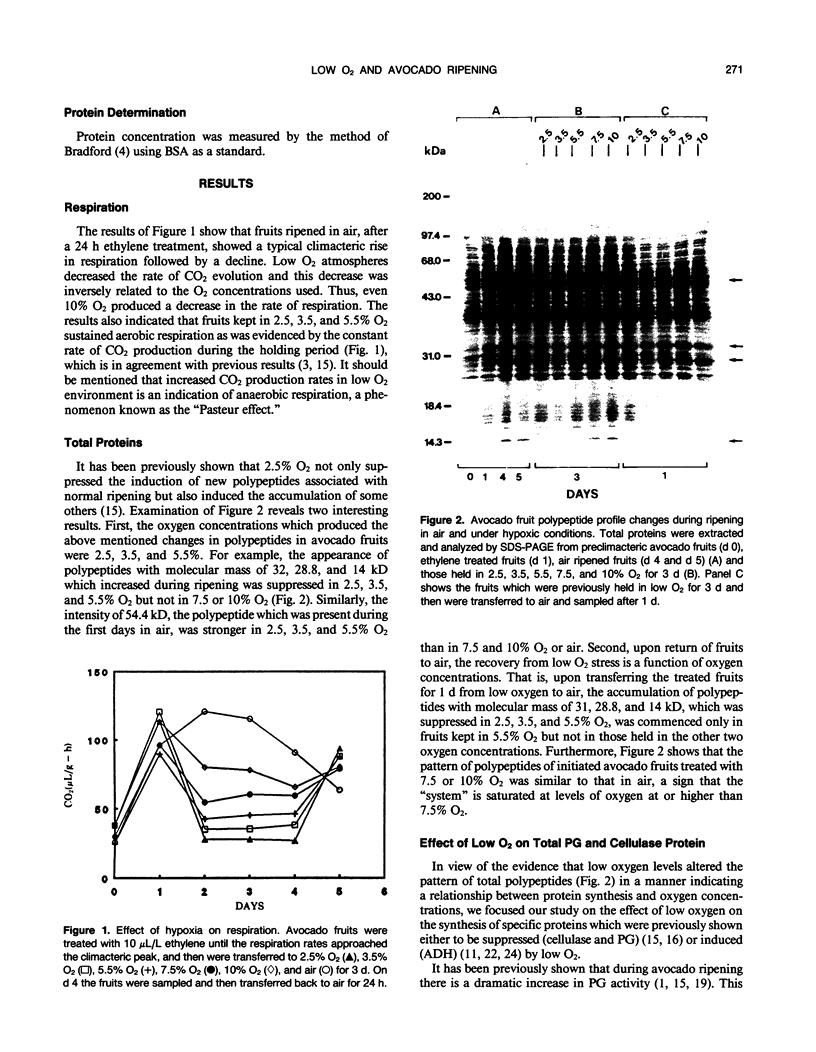
Expression of polygalacturonase and cellulase, two hydrolytic enzymes of avocado (Persea americana, cv Hass) fruit which are synthesized de novo during ripening, and alcohol dehydrogenase, a known anaerobic protein, were studied under different O2 regimes. Low O2 concentrations (2.5-5.5%) diminished the accumulation of polygalacturonase and cellulase proteins and the expression of their isoenzymes. This pattern of change in cellulase protein was also reflected in the steady-state amount of its mRNA. In contrast, 7.5 and 10% O2 did not alter the changes observed in fruits ripened in air. On the other hand, alcohol dehydrogenase was induced in 2.5, 3.5, and 5.5% O2 but not in 7.5 or 10% O2. The recovery from the hypoxic stress upon returning the fruits back to air for 24 hours, was also a function of O2 tensions under which the fruits were kept. Thus, the synthesis of polygalacturonase and cellulase was directly related to O2 levels, while the activity of the isoenzymes of alcohol dehydrogenase was inversely related to O2 levels. The results indicate that hypoxia exerts both negative and positive effects on the expression of certain genes and that these effects are initiated at the same levels of O2.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awad M., Young R. E. Postharvest Variation in Cellulase, Polygalacturonase, and Pectinmethylesterase in Avocado (Persea americana Mill, cv. Fuerte) Fruits in Relation to Respiration and Ethylene Production. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):306–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertheau Y., Madgidi-Hervan E., Kotoujansky A., Nguyen-The C., Andro T., Coleno A. Detection of depolymerase isoenzymes after electrophoresis or electrofocusing, or in titration curves. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jun;139(2):383–389. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg S. P., Burg E. A. Molecular requirements for the biological activity of ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jan;42(1):144–152. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W., Cook L., Vayda M. E. Hypoxic stress inhibits multiple aspects of the potato tuber wound response. Plant Physiol. 1990 May;93(1):264–270. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della-Penna D., Christoffersen R. E., Bennett A. B. Biotinylated proteins as molecular weight standards on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):329–332. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. S., Gerlach W. L., Walker J. C., Lavin M., Peacock W. J. Anaerobically regulated aldolase gene of maize. A chimaeric origin? J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90556-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hake S., Kelley P. M., Taylor W. C., Freeling M. Coordinate induction of alcohol dehydrogenase 1, aldolase, and other anaerobic RNAs in maize. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5050–5054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery D., Smith C., Goodenough P., Prosser I., Grierson D. Ethylene-independent and ethylene-dependent biochemical changes in ripening tomatoes. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):32–38. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanellis A. K., Solomos T., Mattoo A. K. Hydrolytic Enzyme Activities and Protein Pattern of Avocado Fruit Ripened in Air and in Low Oxygen, with and without Ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1989 May;90(1):259–266. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesis E., Fuchs Y., Zauberman G. Cellulase activity and fruit softening in avocado. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):416–419. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E. F., Dannelly H. K., Malloy P. J., Reeves H. C. Rapid isoelectric focusing in a vertical polyacrylamide minigel system. Anal Biochem. 1987 Dec;167(2):290–294. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. A., Wong D. M., Sachs M. M. The anaerobic response of soybean. Plant Physiol. 1990 Feb;92(2):401–407. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Freeling M., Okimoto R. The anaerobic proteins of maize. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker M. L., Laties G. G. Interrelationship of Gene Expression, Polysome Prevalence, and Respiration during Ripening of Ethylene and/or Cyanide-Treated Avocado Fruit. Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):307–315. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C., Howard E. A., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. DNA sequences required for anaerobic expression of the maize alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6624–6628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]