Abstract
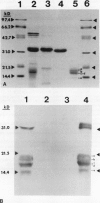
There are claims that phytohemagglutinin (PHA), the lectin of common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris, is toxic when fed to the cowpea weevil, Callosobruchus maculatus, and that PHA serves as the chemical defense against this seed-feeding bruchid beetle (DH Janzen, HB Juster, IE Liener [1976] Science 192: 795-796; AMR Gatehouse, FM Dewey, J Dove, KA Fenton, A Pusztai [1984] J Sci Food Agric 35: 373-380). However, our studies indicate that neither PHA nor its isolectins have detrimental effects when fed to the cowpea weevil. To explain these contradictory results we characterized the commercial lectin source used by A. M. R. Gatehouse, F. M. Dewey, J. Dove, K. A. Fenton, A. Pusztai (1984, J Sci Food Agric 35: 373-380). We demonstrate here that the toxic effects of PHA to cowpea weevil are due to an α-amylase inhibitor contaminant in the commercial preparation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barondes S. H. Bifunctional properties of lectins: lectins redefined. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Dec;13(12):480–482. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzen D. H., Juster H. B., Liener I. E. Insecticidal action of the phytohemagglutinin in black beans on a bruchid beetle. Science. 1976 May 21;192(4241):795–796. doi: 10.1126/science.1265481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. J., Lauda C. M. Purification and properties of phaseolamin, an inhibitor of alpha-amylase, from the kidney bean, Phaseolus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8030–8037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno J., Altabella T., Chrispeels M. J. Characterization of alpha-Amylase-Inhibitor, a Lectin-Like Protein in the Seeds of Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1990 Mar;92(3):703–709. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno J., Chrispeels M. J. A lectin gene encodes the alpha-amylase inhibitor of the common bean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborni T. C., Alexander D. C., Sun S. S., Cardona C., Bliss F. A. Insecticidal activity and lectin homology of arcelin seed protein. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):207–210. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4849.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryrie I. J., Gallagher A. The yeast mitochondrial ATPase complex. Subunit composition and evidence for a latent protease contaminant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 11;545(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]