Abstract
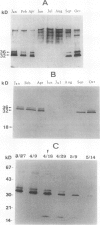
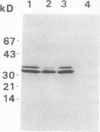
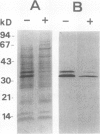
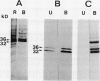
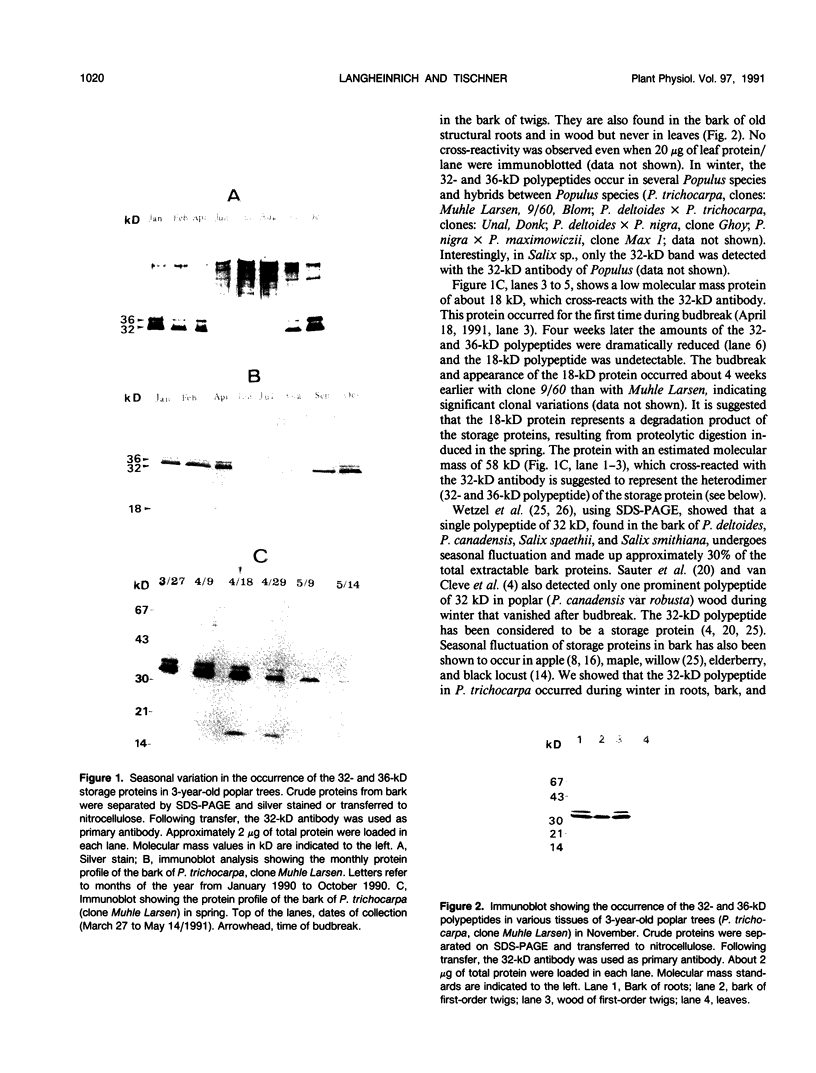
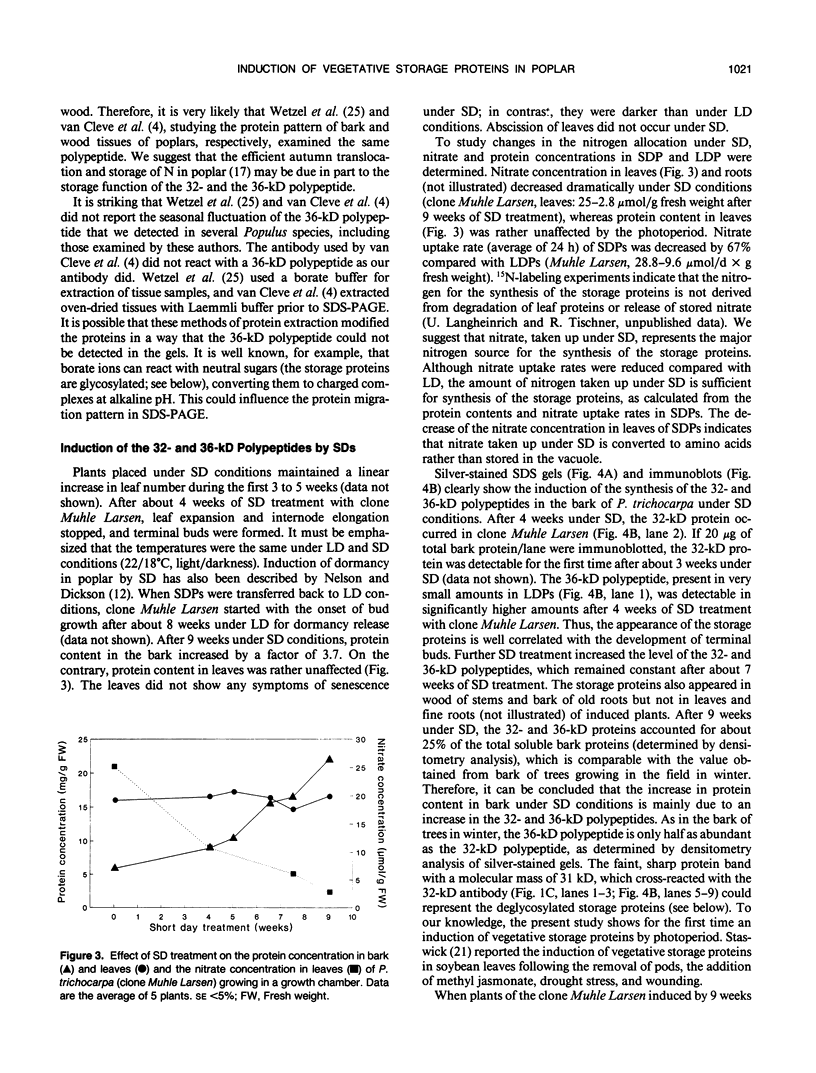
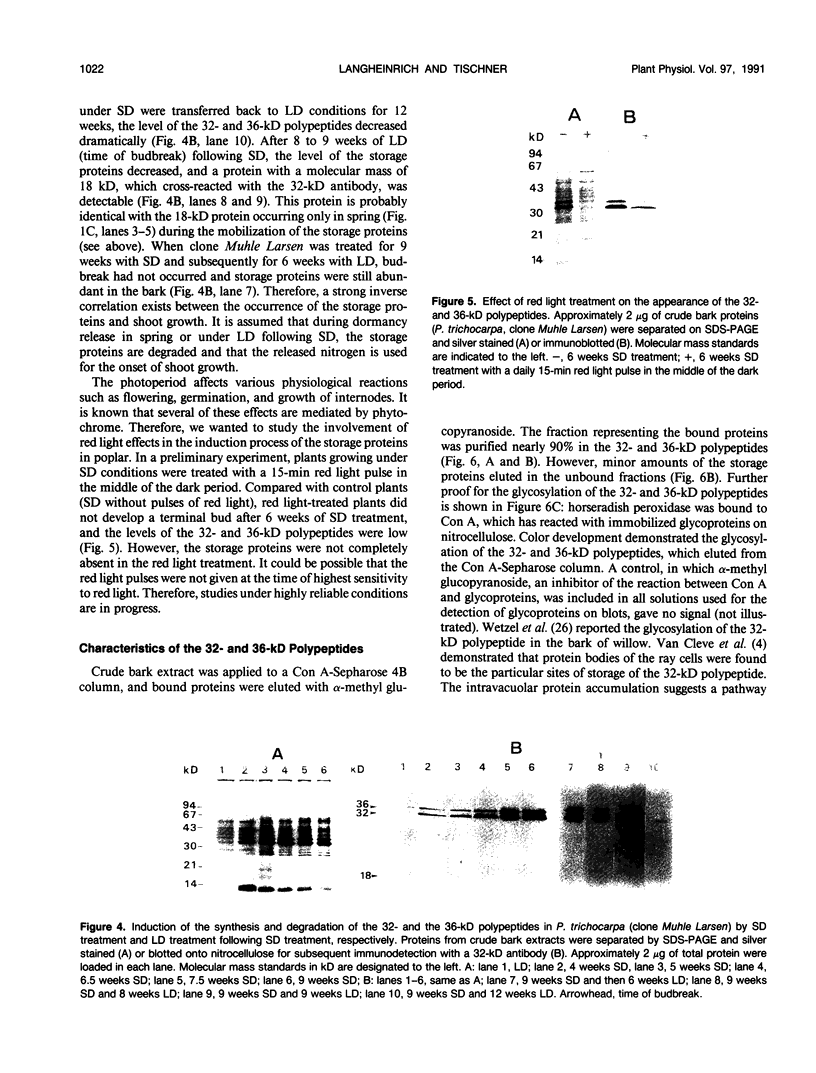
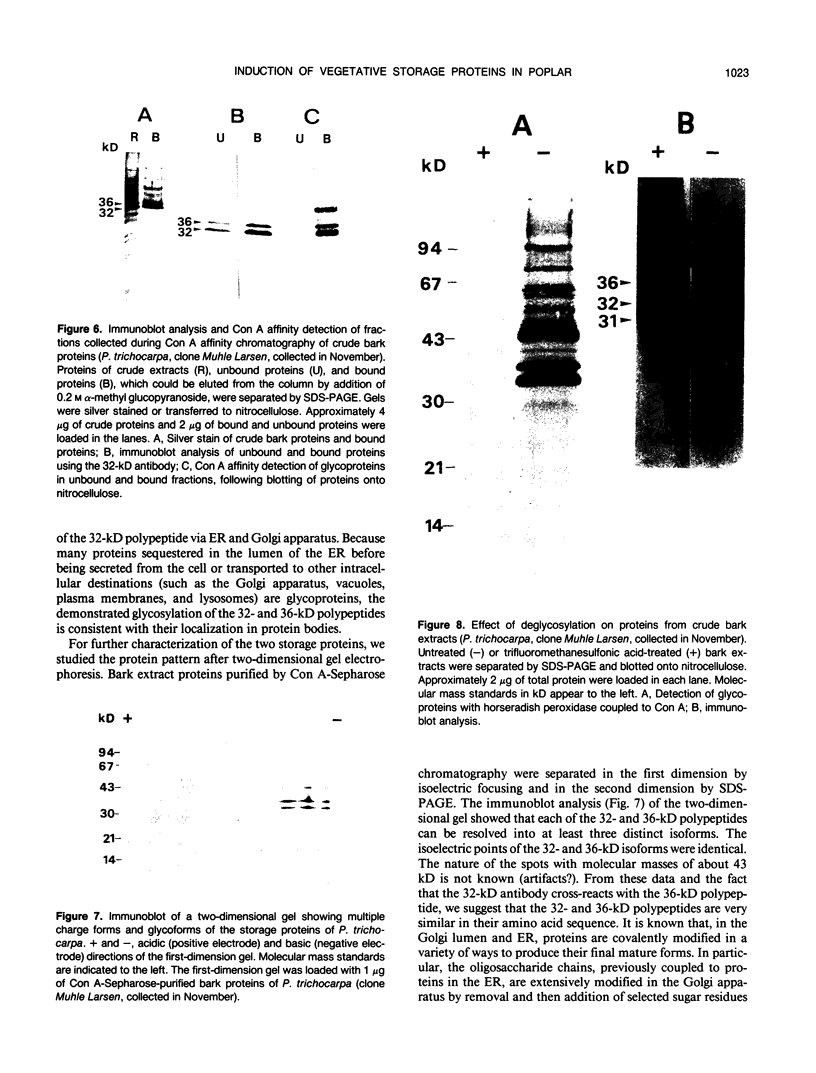
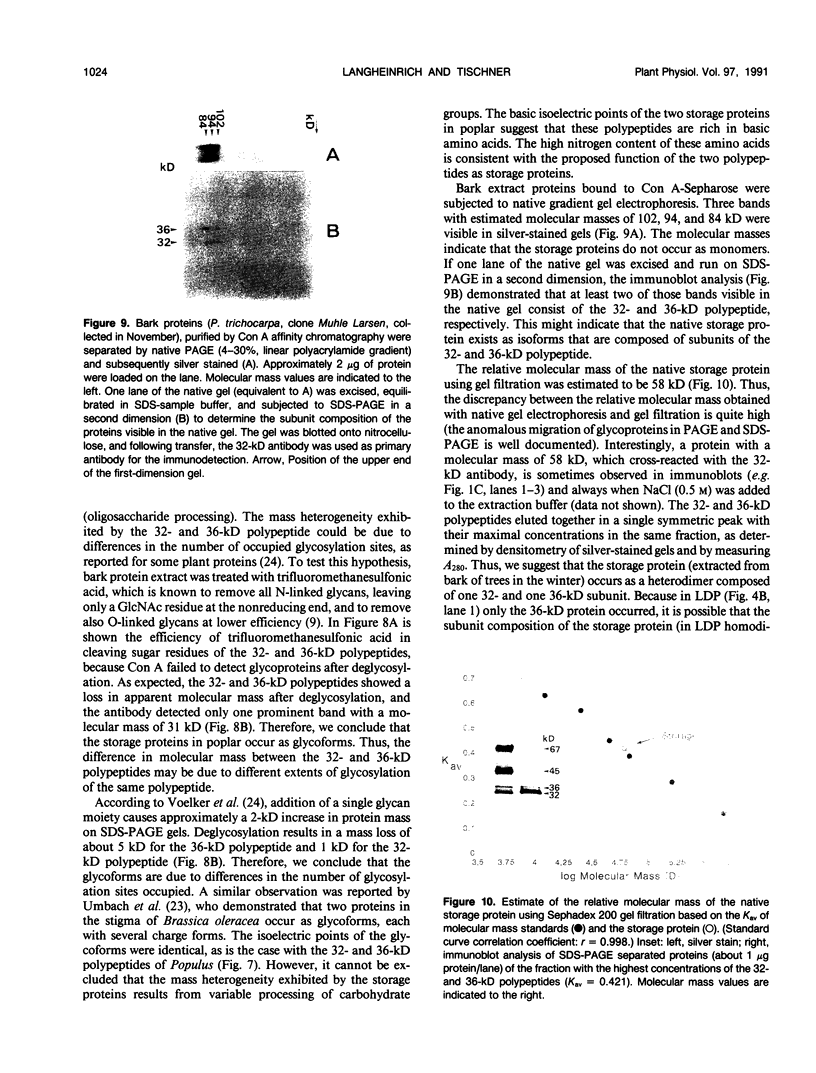
Bark, wood, and root tissues of several Populus species contain a 32- and a 36-kilodalton polypeptide which undergo seasonal fluctuations and are considered to be storage proteins. These two proteins are abundant in winter and not detectable in summer as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunodetection. An antibody raised against the 32-kilodalton storage protein of Populus trichocarpa (T. & G.) cross-reacts with the 36-kilodalton protein of this species. The synthesis of the 32- and 36-kilodalton proteins can be induced in micropropagated plants by short-day conditions in the growth chamber. These proteins are highly abundant in structural roots, bark, and wood and combined represent >25% of the total soluble proteins in these tissues. Nitrate concentration in the leaves and nitrate uptake rate decreased dramatically when LD plants were transferred to short-day conditions; the protein content in leaves was unaffected. A decrease of the 32- and 36-kilodalton polypeptides occurs after transferring induced plants back to LD conditions. Both polypeptides are glycosylated and can be efficiently purified by affinity chromatography using concanavalin A-Sepharose 4B. The 32- and the 36-kilodalton polypeptides have identical basic isoelectric points and both consist of at least three isoforms. The storage proteins show a loss in apparent molecular mass after deglycosylation with trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. It is concluded that the 32- and 36-kilodalton polypeptides are glycoforms differing only in the extent of glycosylation. The relative molecular mass of the native storage protein was estimated to be 58 kilodalton, using gel filtration. From the molecular mass and the elution pattern it is supposed that the storage protein occurs as a heterodimer composed of one 32- and one 36-kilodalton subunit. Preliminary data suggest the involvement of the phytochrome system in the induction process of the 32- and 36-kilodalton polypeptides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieleski R. L., Turner N. A. Separation and estimation of amino acids in crude plant extracts by thin-layer electrophoresis and chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1966 Nov;17(2):278–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. G. A direct method for the visualization of glutathione S-transferase activity in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jun;123(1):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90635-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett W. F., Dunn M. F. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae Pathovars in Infected Leaves of Susceptible Hosts. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):5–9. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heukeshoven J., Dernick R. Improved silver staining procedure for fast staining in PhastSystem Development Unit. I. Staining of sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Electrophoresis. 1988 Jan;9(1):28–32. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs E., Clad A. Electroelution of fixed and stained membrane proteins from preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels into a membrane trap. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 1;154(2):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp D. R., Atkinson J. P., Shreffler D. C. Genetic variation in glycosylation of the fourth component of murine complement. Association with hemolytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7330–7335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen K. A. Proteins transferred to nitrocellulose for use as immunogens. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jun;147(2):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nsimba-Lubaki M., Peumans W. J. Seasonal Fluctuations of Lectins in Barks of Elderberry (Sambucus nigra) and Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia). Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):747–751. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pregitzer Kurt S., Dickmann Donald I., Hendrick Ron, Nguyen Phu V. Whole-tree carbon and nitrogen partitioning in young hybrid poplars. Tree Physiol. 1990 Dec;7(1_2_3_4):79–93. doi: 10.1093/treephys/7.1-2-3-4.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staswick P. E. Novel Regulation of Vegetative Storage Protein Genes. Plant Cell. 1990 Jan;2(1):1–6. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbach A. L., Lalonde B. A., Kandasamy M. K., Nasrallah J. B., Nasrallah M. E. Immunodetection of protein glycoforms encoded by two independent genes of the self-incompatibility multigene family of brassica. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):739–747. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelker T. A., Herman E. M., Chrispeels M. J. In vitro mutated phytohemagglutinin genes expressed in tobacco seeds: role of glycans in protein targeting and stability. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):95–104. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]