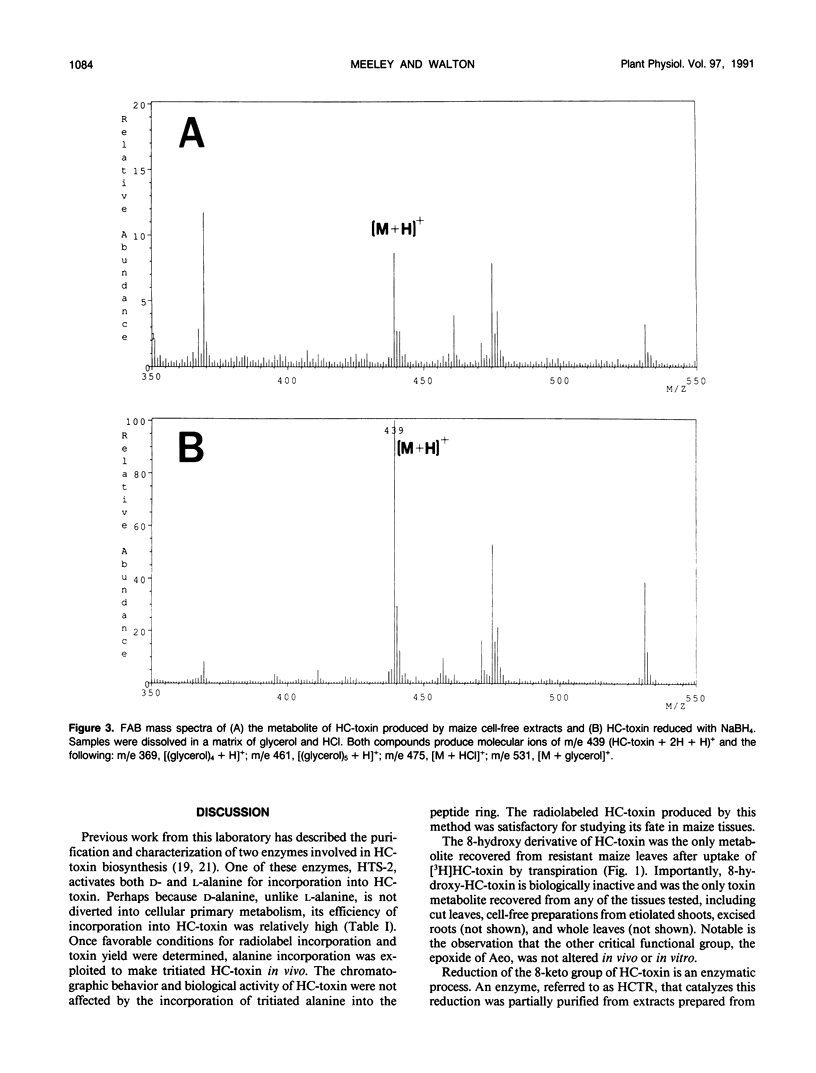
Abstract
Resistance to the fungal plant pathogen Cochliobolus carbonum race 1 and to its host-selective toxin, HC-toxin, is determined by Hm, a single dominant gene in the host plant maize, (Zea mays L). Radiolabeled HC-toxin of specific activity 70 milliCuries per millimole, prepared by feeding tritiated d,l-alanine to the fungus, was used to study its fate in maize leaf tissues. HC-toxin was converted by resistant leaf segments to a single compound, identified by mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance as the 8-hydroxy derivative of HC-toxin formed by reduction of the 8-keto group of 2-amino-9, 10-epoxy-8-oxo-decanoic acid, one of the amino acids in HC-toxin. Reduction of HC-toxin occurred in cell-free preparations from etiolated (Hm/hm) maize shoots, and the activity was sensitive to heat and proteolytic digestion, dependent on NADPH, and inhibited by p-hydroxymercuribenzoate and disulfiram. The enzyme (from the Hm/hm genotype) was partially purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation and diethylaminoethyl-ion exchange chromatography. By gel filtration chromatography, the enzyme had a molecular weight of 42,000. NADH was approximately 30% as effective as NADPH as a hydride donor, and flavin-containing cofactors had no effect on activity. When HC-toxin was introduced to maize leaf segments through the transpiration stream, leaf segments from both resistant and susceptible maize inactivated toxin equally well over a time-course of 9 hours. Although these data suggest no relationship between toxin metabolism and host selectivity, we discuss findings in apparent conflict with the current data and describe why the relationship between enzymatic reduction of HC-toxin and Hm remains unresolved.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Closse A., Huguenin R. Isolierung und Strukturaufklärung von Chlamydocin. Helv Chim Acta. 1974 Apr 27;57(3):533–545. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19740570306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D., Stich K., Britsch L., Grisebach H. Purification and characterization of (+)dihydroflavonol (3-hydroxyflavanone) 4-reductase from flowers of Dahlia variabilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jul;264(1):40–47. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90567-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammock L. G., Hammock B. D., Casida J. E. Detection and analysis of epoxides with 4-(p-Nitrobenzyl)-pyridine. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1974 Dec;12(6):759–764. doi: 10.1007/BF01685927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata N., Inazu N., Takeo S., Satoh T. Carbonyl reductases from rat testis and vas deferens. Purification, properties and localization. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 5;193(1):75–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Rich D. H., Walton J. D. The structure and conformation of HC-toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90319-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. B., Scheffer R. P. Isolation and Biological Activities of Four Selective Toxins from Helminthosporium carbonum. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):187–191. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimabukuro R. H., Frear D. S., Swanson H. R., Walsh W. C. Glutathione conjugation. An enzymatic basis for atrazine resistance in corn. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jan;47(1):10–14. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. D., Earle E. D., Gibson B. W. Purification and structure of the host-specific toxin from Helminthosporium carbonum race 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):785–794. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. D. Two enzymes involved in biosynthesis of the host-selective phytotoxin HC-toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8444–8447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe L. S., Rostworowski K., Pellerin L., Sherwin A. Metabolism of prostaglandin D2 by human cerebral cortex into 9 alpha, 11 beta-prostaglandin F2 by an active NADPH-dependent 11-ketoreductase. J Neurochem. 1989 Jul;53(1):64–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]