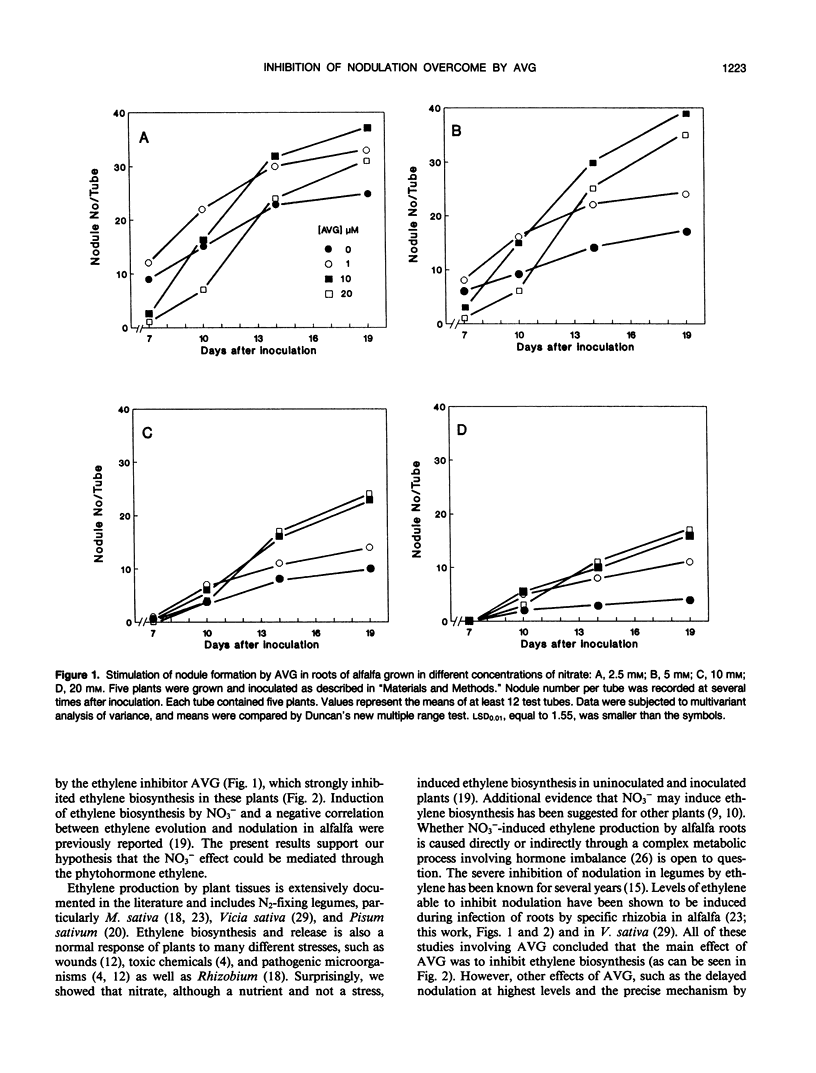
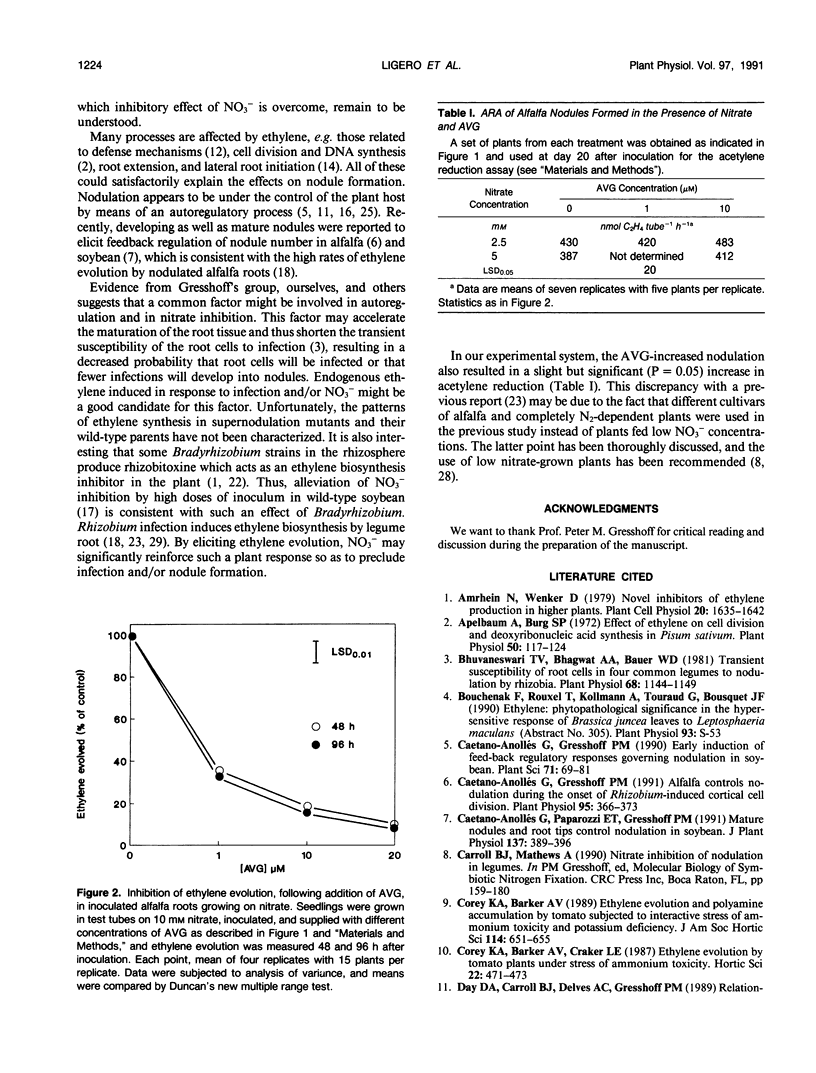
Abstract
Previously, we reported (a) a positive correlation between the nitrate concentrations in growth medium and ethylene evolved from uninoculated and inoculated alfalfa (Medicago sativa) roots and (b) a negative correlation between ethylene evolution and nodulation. Here, we report that the inhibitory effect of NO3− on nodulation of alfalfa can be eliminated by the ethylene inhibitor aminoethoxyvinylglycine (AVG). This effect was probably related to the strong inhibition (90%) of ethylene biosynthesis caused by AVG in these inoculated and NO3−-treated roots. These results support our hypothesis that the inhibitory effect of NO3− is mediated through the phytohormone ethylene. A possible role of endogenous ethylene in the autoregulation of nodulation also is discussed. AVG at 10 micromolar significantly (P < 0.05) increased total nitrogenase activity (acetylene reduction) in 2.5 and 5 millimolar NO3−-fed plants probably as a result of the very high stimulation of nodulation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apelbaum A., Burg S. P. Effect of Ethylene on Cell Division and Deoxyribonucleic Acid Synthesis in Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jul;50(1):117–124. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bhagwat A. A., Bauer W. D. Transient susceptibility of root cells in four common legumes to nodulation by rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caetano-Anollés G., Gresshoff P. M. Alfalfa Controls Nodulation during the Onset of Rhizobium-induced Cortical Cell Division. Plant Physiol. 1991 Feb;95(2):366–373. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. J. Regulation of root development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol. 1984;35:223–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pp.35.060184.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gremaud M. F., Harper J. E. Selection and initial characterization of partially nitrate tolerant nodulation mutants of soybean. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):169–173. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik N. S., Calvert H. E., Bauer W. D. Nitrate induced regulation of nodule formation in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):266–271. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Lieberman M., Kunishi A. Inhibition of ethylene production by rhizobitoxine. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jul;48(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Crist-Estes D. K. Nodule formation is stimulated by the ethylene inhibitor aminoethoxyvinylglycine. Plant Physiol. 1989 Oct;91(2):690–693. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.2.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce M., Bauer W. D. A rapid regulatory response governing nodulation in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):286–290. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


