Abstract
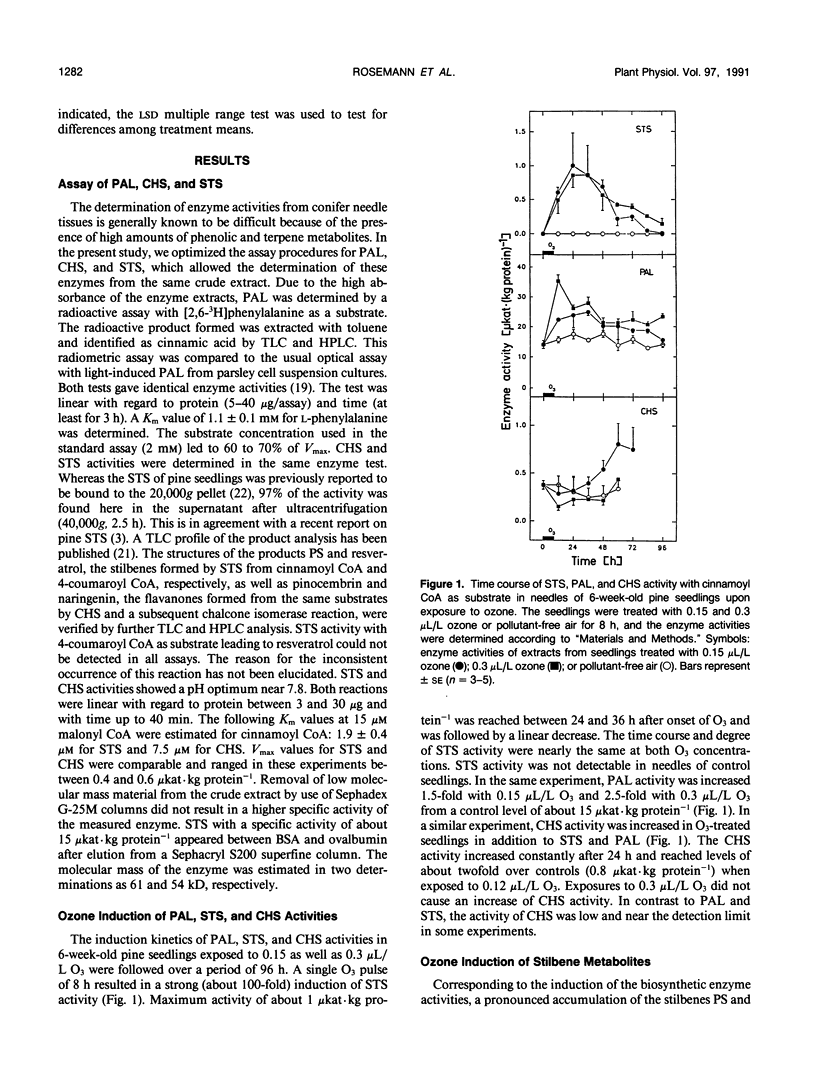
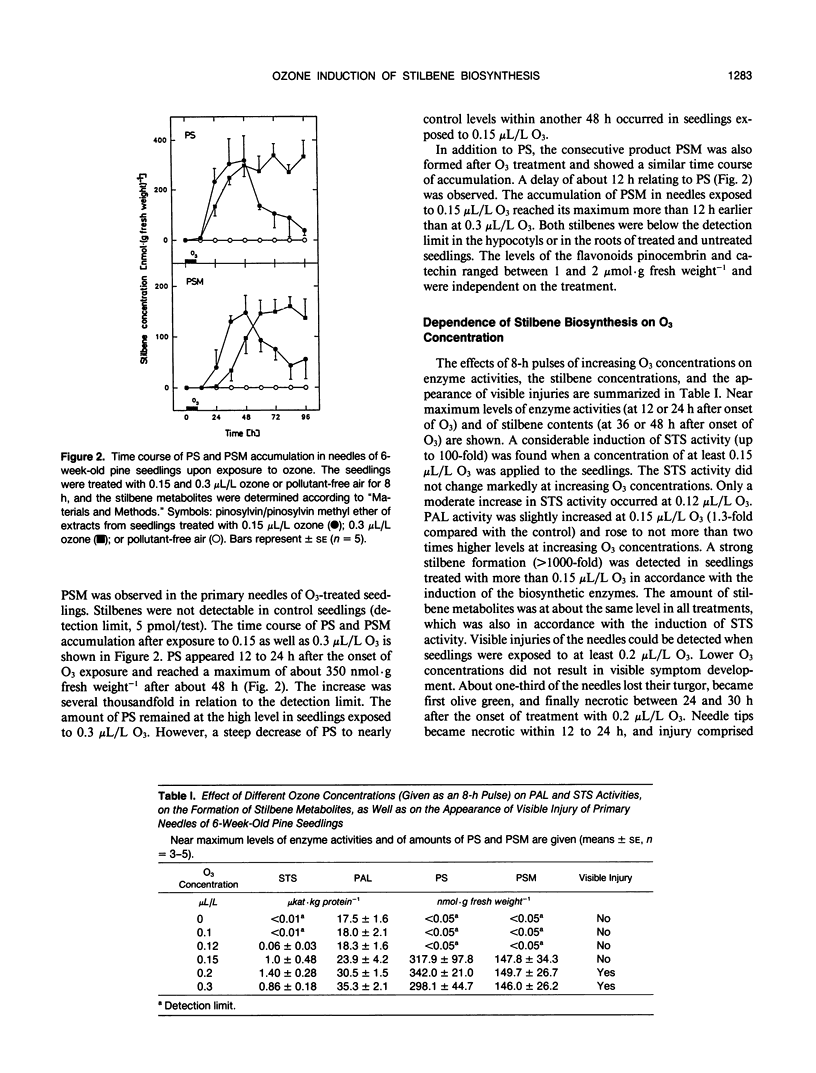
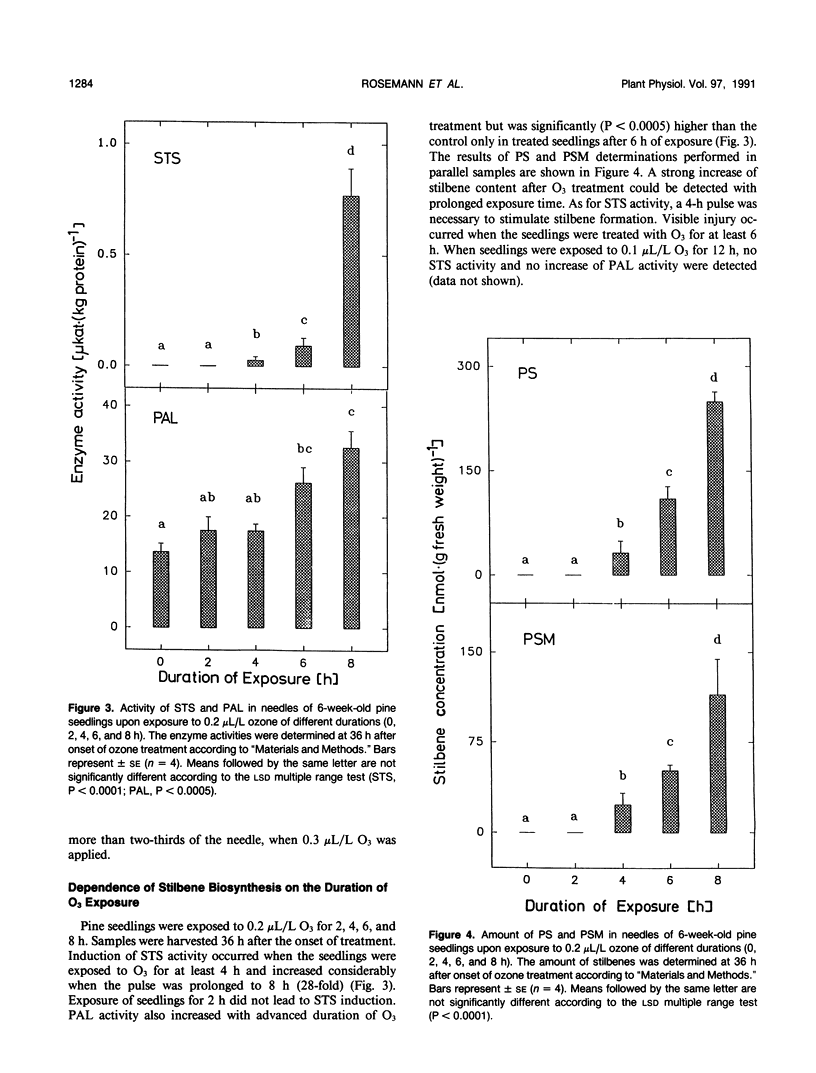
Formation of the stilbenes pinosylvin and pinosylvin 3-methyl ether, as well as the activity of the biosynthetic enzyme stilbene synthase (pinosylvin-forming), were induced several hundred- to thousandfold in primary needles of 6-week-old pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) seedlings upon exposure to a single pulse of ozone of at least 0.15 microliters per liter. The seedlings required 4 hours of exposure as a minimum for the induction of stilbene biosynthesis when exposed to 0.2 microliters per liter ozone. Both stilbene synthase activity and stilbene accumulation increased with the duration of ozone treatment. The activity of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and the activity of chalcone synthase, a key enzyme of the flavonoid pathway that uses the same substrates as stilbene synthase, were also stimulated about twofold by ozone. Stilbene biosynthesis appears to represent the first example of a dose-dependent biochemical response to ozone in a conifer species and may serve as a useful biomarker to study stress impacts on pine trees.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bors W., Heller W., Michel C., Saran M. Flavonoids as antioxidants: determination of radical-scavenging efficiencies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:343–355. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86128-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller W., Rosemann D., Osswald W. F., Benz B., Schönwitz R., Lohwasser K., Kloos M., Sandermann H., Jr Biochemical response of Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) towards 14-month exposure to ozone and acid mist: part I--Effects on polyphenol and monoterpene metabolism. Environ Pollut. 1990;64(3-4):353–366. doi: 10.1016/0269-7491(90)90057-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Taylor O. C. Ozone injury in soybeans: isoflavonoid accumulation is related to necrosis. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):731–733. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langebartels C., Kerner K., Leonardi S., Schraudner M., Trost M., Heller W., Sandermann H. Biochemical plant responses to ozone : I. Differential induction of polyamine and ethylene biosynthesis in tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1991 Mar;95(3):882–889. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.3.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perloff L. J., Rowlands D. T., Jr, Barker C. F. The antigenicity of venous allografts. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1976;22:234–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. L., Castillo F. J., Heath R. L. Alteration of Extracellular Enzymes in Pinto Bean Leaves upon Exposure to Air Pollutants, Ozone and Sulfur Dioxide. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):159–164. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeppner A., Kindl H. Stilbene synthase (pinosylvine synthase) and its induction by ultraviolet light. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80561-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöppner A., Kindl H. Purification and properties of a stilbene synthase from induced cell suspension cultures of peanut. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6806–6811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöckigt J., Zenk M. H. Chemical syntheses and properties of hydroxycinnamoyl-coenzyme A derivatives. Z Naturforsch C. 1975 May-Jun;30(3):352–358. doi: 10.1515/znc-1975-5-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


