Abstract
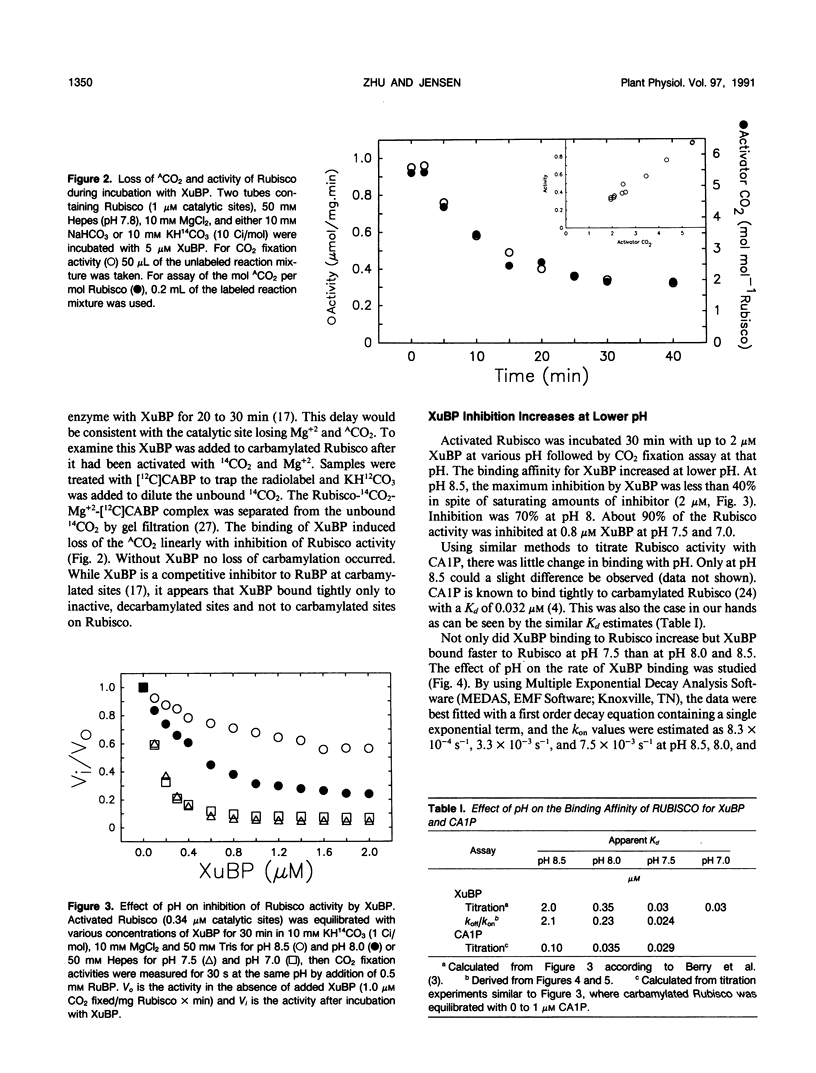
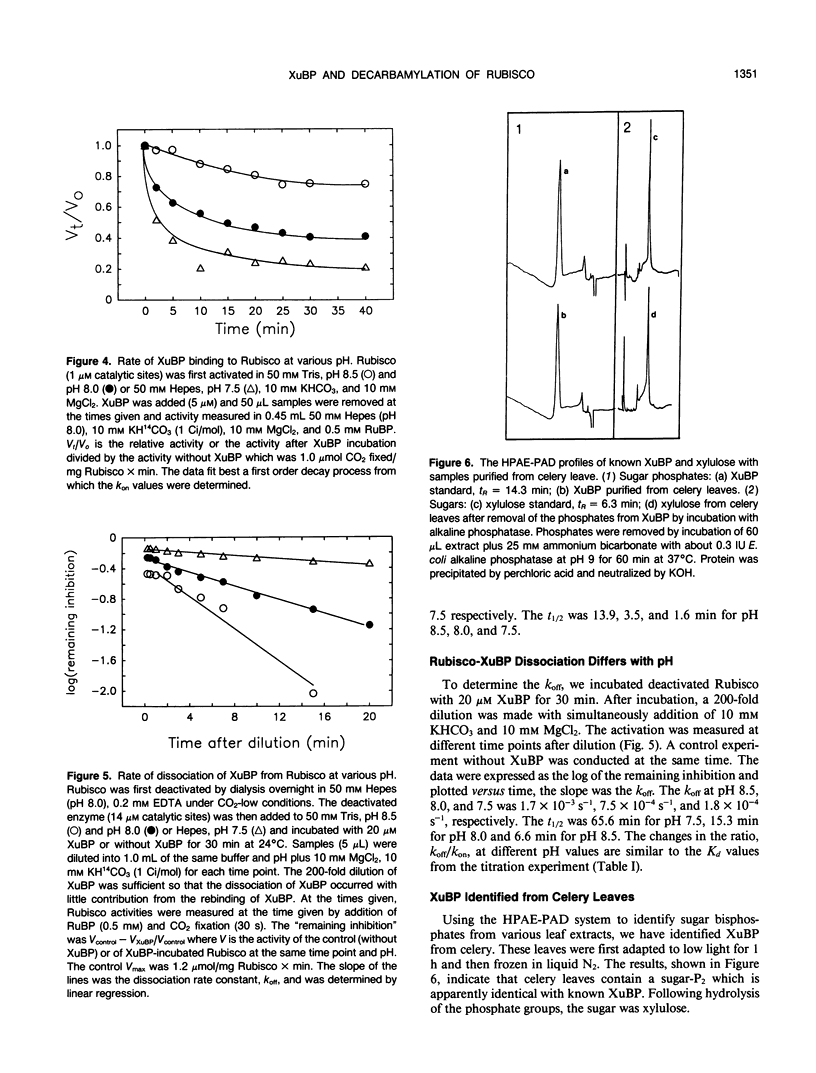
Xylulose 1,5-bisphosphate (XuBP) is synthesized from ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) at carbamylated catalytic sites on ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) with significant amounts of XuBP being formed at pH less than 8.0. XuBP has been separated by high performance liquid chromatography and identified by pulsed amperometry from compounds bound to Rubisco during catalysis with the purified enzyme and from celery (Apium graveolens var Utah) leaf extracts. XuBP does not bind tightly to carbamylated sites, but does bind tightly to decarbamylated sites. Upon incubation of fully activated Rubisco with 5 micromolar XuBP, loss of activator CO2 occurred before XuBP bound to the enzyme catalytic sites, even in the presence of excess CO2 and Mg2+. Binding of XuBP to decarbamylated Rubisco sites was highly pH dependent. At pH 7.0 and 7.5 with 10 millimolar MgCl2 and 10 millimolar KHCO3, the apparent dissociation constant for XuBP, Kd, was 0.03 micromolar, whereas at pH 8.0 and 8.5, the apparent Kd was 0.35 and 2.0 micromolar, respectively. This increase in Kd with pH was a result of a decrease in the association rate constant and an increase in the dissociation rate constant of XuBP bound to decarbamylated sites on Rubisco. The Kd of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate binding to carbamylated sites was only slightly pH dependent.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BYRNE W. L., LARDY H. A. Pentose phosphates formed by muscle aldolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Aug;14(4):495–501. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger M. R., Andrews T. J., Canvin D. T., Lorimer G. H. Interactions of hydrogen peroxide with ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7870–7875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahr J. T., Jensen R. G. Activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in intact chloroplasts by CO2 and light. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 15;185(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry J. A., Lorimer G. H., Pierce J., Seemann J. R., Meek J., Freas S. Isolation, identification, and synthesis of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate, a diurnal regulator of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):734–738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A., Portis A. R. Protein-bound ribulose bisphosphate correlates with deactivation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in leaves. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):244–249. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardon Z. G., Mott K. A. Evidence that Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate (RuBP) Binds to Inactive Sites of RuBP Carboxylase in Vivo and an Estimate of the Rate Constant for Dissociation. Plant Physiol. 1989 Apr;89(4):1253–1257. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.4.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. L., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. A Kinetic Characterization of Slow Inactivation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase during Catalysis. Plant Physiol. 1990 Aug;93(4):1376–1382. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.4.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. L., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. Slow Inactivation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase during Catalysis Is Caused by Accumulation of a Slow, Tight-Binding Inhibitor at the Catalytic Site. Plant Physiol. 1990 Aug;93(4):1390–1397. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.4.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. L., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. Slow Inactivation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase during Catalysis Is Not Due to Decarbamylation of the Catalytic Site. Plant Physiol. 1990 Aug;93(4):1383–1389. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt W. H., Werdan K., Milovancev M., Geller G. Alkalization of the chloroplast stroma caused by light-dependent proton flux into the thylakoid space. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 31;314(2):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobza J., Seemann J. R. Mechanisms for light-dependent regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity and photosynthesis in intact leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3815–3819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurry S. D., Gee R., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from spinach, tomato, or tobacco leaves. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):515–521. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurry S. D., Tolbert N. E. Inhibition of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase by xylulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8344–8346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott K. A., Berry J. A. Effects of pH on Activity and Activation of Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase at Air Level CO(2). Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):77–82. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paech C., Pierce J., McCurry S. D., Tolbert N. E. Inhibition of ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate epimerization and degradation products. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91506-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J., Tolbert N. E., Barker R. Interaction of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase with transition-state analogues. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):934–942. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Salvucci M. E., Ogren W. L. Activation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase at Physiological CO(2) and Ribulosebisphosphate Concentrations by Rubisco Activase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):967–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Berry J. A., Freas S. M., Krump M. A. Regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo by a light-modulated inhibitor of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Hatch A. L., Stumpf D. K., Jensen R. G. Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate and activation of the carboxylase in the chloroplast. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):252–255. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Jensen R. G. HPLC separation and indirect ultraviolet detection of phosphorylated sugars. Plant Physiol. 1988 Feb;86(2):615–618. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu G., Jensen R. G. Fallover of Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Activity : Decarbamylation of Catalytic Sites Depends on pH. Plant Physiol. 1991 Dec;97(4):1354–1358. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.4.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu G., Jensen R. G. Status of the substrate binding sites of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase as determined with 2-C-carboxyarabinitol 1,5-bisphosphate. Plant Physiol. 1990 May;93(1):244–249. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


