Abstract
Practical relevance:
The health of the cat mirrors a complex interaction between its environment (nurture) and its genetics (nature). To date, over 70 genetic mutations (variants) have been defined in the cat; many involve diseases, structural anomalies, coat color and texture, including numerous that are clinically relevant. This trend will continue as more of the feline genome is deciphered. Genetic testing, and eventually whole-genome sequencing, should become routine diagnostic tools in feline healthcare within the foreseeable future.
Global importance:
Cat breeds have dispersed around the world. Thus, feline medicine clinicians should be aware of breeds common to their region and common mutations found within those regional populations. Random-bred populations of domestic cats can also have defined genetic characteristics and mutations, which are equally worthy of understanding by feline medicine clinicians.
Outline:
This article reviews the chronology and evolution of genetic and genomic tools pertinent to feline medicine. Possible strategies for mapping genetic traits and defects, and how these impact on feline health, are also discussed. The focus is on three historical periods: (1) research conducted before the availability of the cat genome; (2) research performed immediately after the availability of sequences of the cat genome; and (3) current research that goes beyond one cat genome and utilizes the genome sequences of many cats.
Evidence base:
The data presented are extracted from peer-reviewed publications pertaining to mutation identification, and relevant articles concerning heritable traits and/or diseases. The authors draw upon their personal experience and expertise in feline genetics.
The domesticated cat of today
Cats are a common household inhabitant and represent an important part of many human lives. According to survey data, approximately 86 million cats are owned within the United States 1 and 2.4 million in Australia.2,3 The majority of owned cats are randomly bred domestic crossbreeds, while only a small proportion constitutes pedigree ‘fancy’ breeds (10–15% in the United States, 4 perhaps 25% in Australia 5 ). Feral cat populations are ubiquitous around the world; wherever humans are found (and also in many places where they are not found!) a feral cat population is likely to be present. In Australia, the feral feline population is said to outnumber the owned cat population by about 3 to 1, and sometimes members of this population will interbreed with owned domestic crossbreed and pedigree cats.
Feral and owned cats are collectively referred to as ‘domestic cats’. The scientific name for the domestic cat is Felis silvestris catus, 6 a subspecies belonging to one of the 38 species in Felidae (the cat family). 7 This subspecies was likely domesticated from a wildcat progenitor, Felis silvestris lybica, by means of altering its ecology. 8 Around 10,000 years ago, with the emergence of agriculture, humans transitioned from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle into settlements. Availability of grain and other food in and around human settlements caused rodent populations to substantially increase in size, and attracted the progenitor wildcat population. Over time, and probably aided by selection for a temperament suitable for cohabitation with human populations, the progenitor population grew isolated from its wild counterparts and evolved into the domesticated cat of today. The pools of domesticated cats surrounding human settlements around the world subsequently served as the source for the establishment of individual cat breeds.
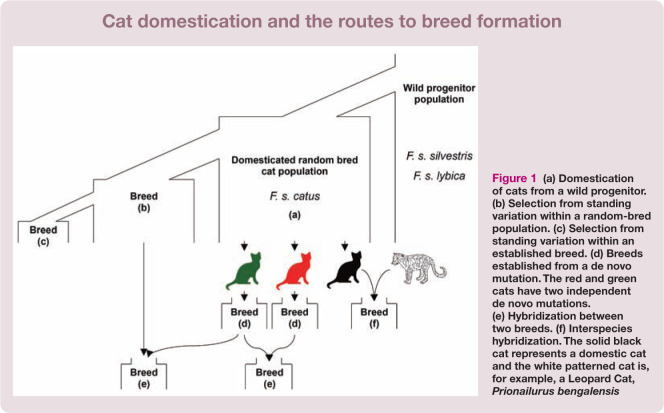
Intentional human development of cat breeds followed several routes, summarized in Figure 1. The processes of cat breed development are distinct from those implemented in other companion animal species. 9 Modern domestic cats comprise some 40–55 designated breeds, 10 yet owned random-bred and unowned or semi-owned feral cats (eg, street cats and cats living independently in rural areas) represent the overwhelming majority of cats in the world.11 –13 While feral cats are diverse in all respects (coat colour, coat length, size, morphotype – ie, the morphological variation within a species population), breeds were established through the artificial selection of specific physical or behavioral characteristics. 12
Figure 1.
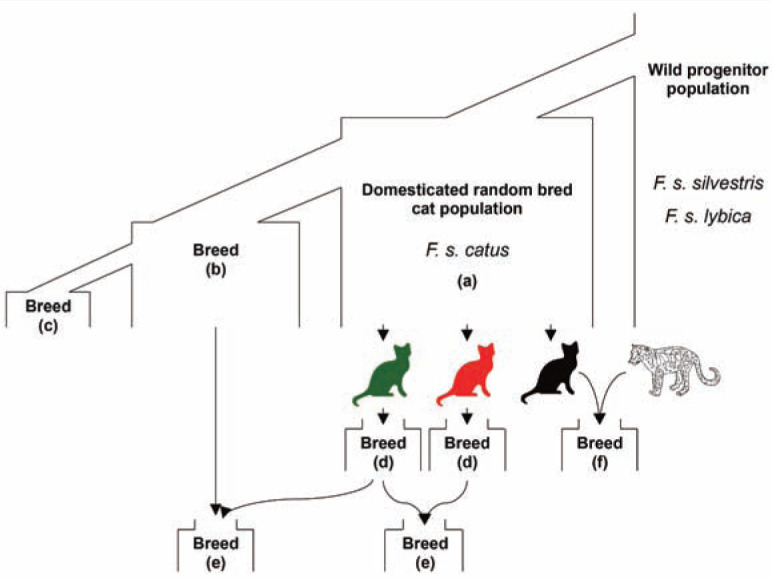
(a) Domestication of cats from a wild progenitor. (b) Selection from standing variation within a random-bred population. (c) Selection from standing variation within an established breed. (d) Breeds established from a de novo mutation. The red and green cats have two independent de novo mutations. (e) Hybridization between two breeds. (f) Interspecies hybridization. The solid black cat represents a domestic cat and the white patterned cat is, for example, a Leopard Cat, Prionailurus bengalensis
Several historical features of feline pedigree development are relevant to the current discussion (see box below).
Figure 2.
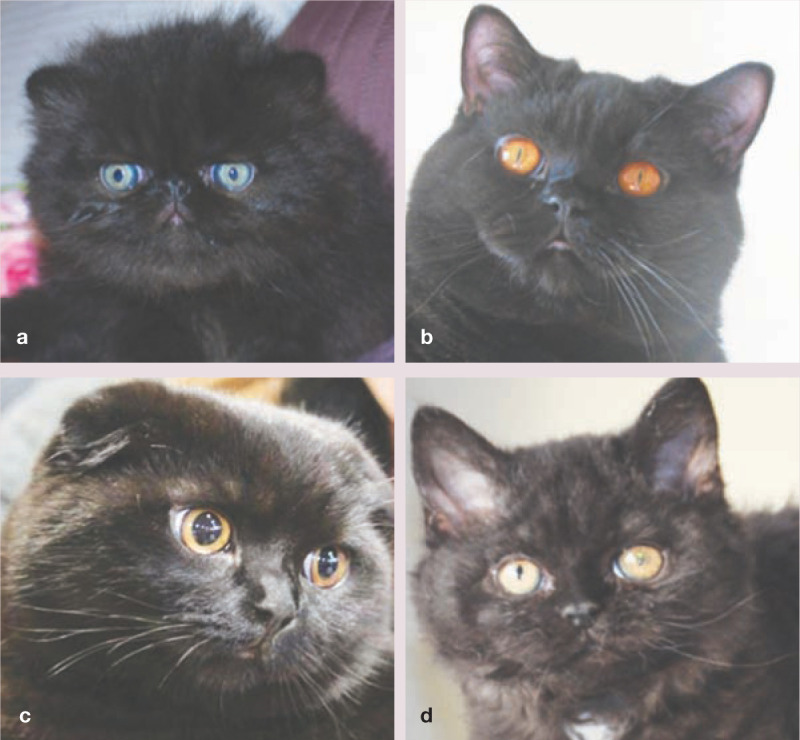

The Persian (a) is the foundation breed of the Persian family members (British Shorthair, Scottish Fold, Selkirk Rex). Previous genetic studies confirmed that the family contains members genetically very similar to the foundation breed. Often cat breeds are characterized by one single esthetic trait; in this case the British Shorthair is characterized by the normal coat length (b), the Scottish Fold by the folded ears (c) and the Selkirk Rex by the curly hair (d). All these breeds share the brachycephalic structure of the head
General recommendations for the study of feline genetic diseases
For a study of genetic disease in cats to be fruitful, the following recommendations should be considered:
Genetic diseases should be characterized by veterinarians, ideally feline specialists with an interest in genetic diseases, or organ system specialists A comprehensive description of a genetic disease highly influences the collection of appropriate clinical specimens and the genetic tools to be utilized in a given study. Advancements in veterinary medicine, and especially diagnostic imaging, have enabled the precise characterization of anatomical and physiological phenotypes of feline disease and reduced the possibility of incorrect assignment of phenotype, which would impact on subsequent genetic analyses. The characterization of inherited disease is often easier when there is a comparable genetic disease in humans, other domestic animals, rodents or other model organisms. In such circumstances, the time required to identify a causative genetic mutation can often be reduced.
Samples should be collected from diverse populations and breeds This is essential to conduct appropriate genetic tests and provide sufficient control samples for any analysis. Sample collection needs to be an ongoing process because it is important to maintain surveillance of the genetic variation within a population.
Appropriate cats should be recruited Select appropriate cases (cats suspected of carrying a genetic disease) and controls (normal cats) that share as similar genetic ancestry as possible.
Genetic testing should be implemented based on a summation of all available information (disease phenotype, pedigree analysis, mode of inheritance, etc) A trait, caused by a single gene mutation, can be inherited in a dominant, recessive or sex-linked manner. Sexually reproducing animals have two copies of most genes. The two copies, called alleles, can be the same or slightly different. The allele that differs from the highly represented (normal or wild type) allele might represent the ‘mutation’ that is associated with a phenotypic change in the animal. For a recessive trait to be expressed, two copies of the same mutant allele are necessary (such as for hypokalemia or hairless traits in cats). A dominant trait requires only one copy of the mutant allele in order to be expressed phenotypically (such as feline PKD or Selkirk Rex curly coat). An X-linked trait (a form of sex-linked mode of inheritance), as the name suggests, is linked to and segregates with the X chromosome. Males inherit a single X chromosome from the dam while females inherit two copies, one from the dam and one from the sire. The expression of an X-linked phenotype within a male is achieved regardless of the mode of inheritance, whereas females receive two copies of the X chromosome and the expression of the phenotype depends on the nature of the mutation (recessive or dominant). A classical example of X-linked inheritance is orange colouration. 26
Opportunities for comparative research should be pursued Potentially a cat model of human disease might be developed by studying feline disease mutations while simultaneously developing strategies to remove the disease mutation from the feline breeding population.


Table 1.
Overview of the main genomic approaches used for identifying a mutation
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate gene sequencing | Fast. Cheap(er) | Needs previous study in which the gene function and phenotype are well described |
| Linkage analysis | Identifies large region of association in the absence of a known candidate gene | Needs multigenerational pedigree and results in large regions of association. Once a region is identified, a candidate gene within the associated interval needs to be identified and sequenced |
| Genome-wide association | Quick analysis. Region of association for disease ranges from 500 kilobases (kb) to 10 million bases (mb) | Expensive. Needs appropriate sampling and sufficient numbers of cases and controls. Requires a long time to collect enough samples for the study. Fine mapping might be necessary followed by candidate gene sequencing |
| Genome-wide sequencing | Identifies the causative mutation | Extremely expensive. Needs data storage space, bioinformatics skills, and enough controls to exclude non-causative mutations |
Prior to the cat genome era
Key highlights of this era of genetics research were the development of genetic tools for the domestic cat and an improved understanding of the cat genome as a result of the human genome project.
Early studies of mitotic chromosomes of the domestic cat, initiated in the 1970s, revealed a karyotype consisting of 18 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and the XY sex chromosome pair.27,28 The feline karyotype and early gene mapping studies indicated that the cat has a genome organization more similar to that of humans than to that of the mouse or dog.
Thereafter, and for nearly three decades, genetic and genomic resources for cats have been in production, progressing from (1) somatic cell hybrid panels, 29 through (2) inter- and intra-species linkage maps,26,30,31 and (3) radiation hybrid panels,32,33 to (4) integration of these early technologies with the genome sequence.
Somatic cell hybrid panels
A somatic cell hybrid is the result of fusion of cell lines of a cat and a rodent. This fusion leads to integration of the chromosomes of the cat, or parts thereof, into the nucleus and chromosomes of the rodent cell line. Analysis of the chromosomes in each cell line can reveal which specific cat chromosomes or parts of chromosomes entered the rodent’s nucleus. Cell lines can be assayed for the presence or absence of specific proteins, thereby indicating whether the gene resides on the cat chromosome.
In 1997, this mapping approach provided feline geneticists with the first genetic map of the cat, comprising 105 loci. 34 Loci (plural of ‘locus’) are any specific locations within the genome. In the case of the genetic map, this term is used to refer to locations of variability between individual cats, which can be used as markers for genetic analyses. This approach facilitated the mapping of haemoglobin beta (HBB) to cat chromosome D1 and tyrosinase (TYR) to chromosome D4. 35
Linkage analysis
Genetic recombination-based maps of the feline genome offer an improvement in resolution over somatic cell hybrid maps, with the additional benefits of estimating gene order and distance between genes on a chromosome. This technique is probably the oldest method developed for genetic analyses.
The method utilizes the information in a pedigree coupled with the genotypes of selected variable markers across the genome. The markers of choice for linkage analyses are DNA microsatellites (short tandem repeats – STRs), which exhibit a high degree of variability between individuals. For this method to be implemented, a genetic recombination map needs to be developed. This map establishes the relative locations of the variable markers and assigns them to chromosomes. This is achieved first by the identification of markers, followed by careful analysis of the markers’ inheritance pattern in an extended pedigree. Markers that reside on different chromosomes will be inherited independently (segregation and independent assortment), while the inheritance of markers located on the same chromosome will depend on the likelihood of recombination events. Markers that are further apart from one another are likely to experience more recombination than markers that are close to each other. The resulting map contains markers on each chromosome with a known genetic inter-distance. The same markers can be employed for studying genetic diseases via linkage analysis.
To study a particular feline disease or phenotype using linkage analysis, members of a large extended pedigree need to be genotyped for the genetic map markers previously characterized. The pedigree provides the necessary information regarding the inheritance of the phenotype and relationships among individuals. The genotyping results will prove or refute the coinheritance of marker(s) with the phenotype under study. The genetic distance between the phenotype-causing gene and closest marker(s) can be estimated. The detection of a region of linkage is followed by a candidate gene approach to sequence regions of likely involvement.
In 1999, the first version of the feline interspecies hybrid-based linkage map contained approximately 250 microsatellite markers, 30 and used a pedigree where domestic cats were crossed with the Leopard Cat (P bengalensis) to create a Bengal breed pedigree. This map, in 2004, assisted the targeted gene approach that led to the discovery of the mutation responsible for autosomal dominant PKD. 22 Other large feline pedigrees were used to map more variable genetic markers (microsatellites). 36 This supported pedigree-based genetic studies for simple Mendelian traits in cats, such as Tabby, 37 Spotting 31 and Orange. 26
However, as a genomic tool, there are some major limitations. For example, linkage analyses require large extended pedigrees with precise phenotypic assignment to obtain meaningful results (64 cats to find the Tabby locus, 114 to find the Spotting locus and 134 to find Orange). Such extensive pedigrees are not available for most genetic diseases and maintaining a colony of cats segregating for a disease is a very expensive task; indeed, it can be hard enough to convince breeders to repeat a key mating to confirm a trait as heritable. Furthermore, markers used in linkage studies need to be variable among the individuals of the pedigree. Lastly, in some cases the genomic region identified by the linkage analysis is large and harbours a lot of candidate genes.
Radiation hybrid maps
Radiation hybrid maps provide finer mapping of markers, with a resolution of one marker per 40 kb for the latest panel created in 2012. 38 A better map enables the precise localization of traits under investigation to a specific chromosomal region.
Early feline genetic studies
Feline genetic studies in this era focused on the localization of disease-producing alleles to a specific genomic region using the available tools. Attempts to discover inherited disease mutations were conducted using a candidate gene approach.
The candidate gene approach varies based on the availability of genetic resources and the observed disease phenotype. When a feline genetic disease is characterized phenotypically and found to share pathophysiological similarities to a previously characterized inherited disease of humans, the human gene serves as a candidate gene. Due to the lack of a cat genome (at that time), conserved sequences in a candidate gene across a number of mammalian species were used to design primers (small nucleotide sequences used to amplify DNA). Primers designed in conserved sequences are used to study the candidate gene in affected cats. Such an approach resulted in the identification of a number of disease-producing mutations in cats.15,18,22,39 –43
Despite these successes, the risks involved in such an approach should not be underestimated. A disease phenotype may be similar in different species as a result of mutations in different genes within a single biochemical pathway; hence the wrong candidate gene may be chosen for study. An example of such a situation is the entity of white spotting, where mutations in different genes (such as MITF, PAX3, SOX10 or KIT) can be associated with similar fur coloration.44 –48 The candidate gene approach can frequently be laborious, time consuming and expensive, due to the limited success rate of obtaining cat sequences using primers designed in conserved regions of genes from other species. In addition, sometimes the ‘model’ human disease is actually not equivalent to the feline disease, as was the case for hypokalaemic polymyopathy in the Burmese breed; this was thought to be similar to human hypokalaemic periodic paralysis (a channelopathy affecting the muscle cell membrane), when in fact the problem was a defective enzyme (WNK4 kinase) in the kidney tubules (see later).

The feline genome project
The availability of a cat genome enabled the field of feline genetics to flourish. Researchers no longer needed to look for conserved sequences of great similarity across other mammalian species to design experiments. Instead, they could focus on the specific sequences of the cat reference genome.
In 2007, the first cat genome was obtained by sequencing the genome of an inbred female Abyssinian cat. 49 This genome sequence represented approximately 60% of the euchromatic genome (uncondensed part of the genome); euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome (expressed genes). Despite the low coverage (1.9x), the first assembled cat genome provided the feline genomics community with a valuable resource. Additional sequencing of several cat breeds covered approximately 80% of the cat genome.50,51 In addition to the reference cat (Abyssinian), several other cats were used in this sequencing phase. The sequencing of different cat breeds, feral cats and wild cats enabled the identification of genetic variation (namely single nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs]) across the genome. Millions of SNPs were identified in each cat population and a considerable number were suitable for genetic analyses for various populations. Consequently, in 2012, an Illumina 63K dense SNP array, containing approximately 63,000 SNP variations across the cat genome, was constructed for commercial use by researchers.
This genetic tool paved the way for new studies into cat genetic diseases.
Genome-wide association studies
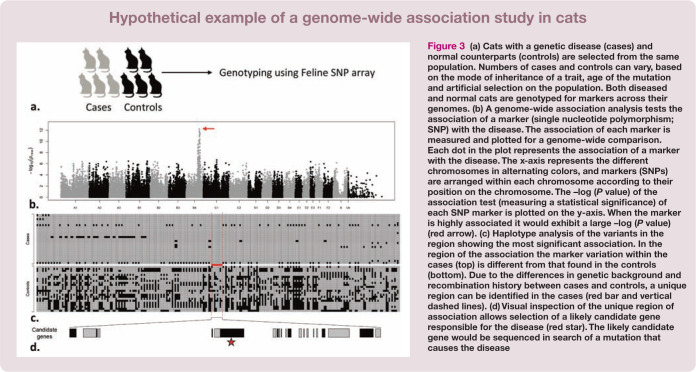
The availability of a dense SNP array provided the needed resource for the implementation of population-based analyses instead of the rather limited pedigree-based analyses. The SNP array can provide a general overview of entire genomes from hundreds of cats in a single experiment, which subsequently allows genome-wide association studies (GWASs) for cat diseases (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
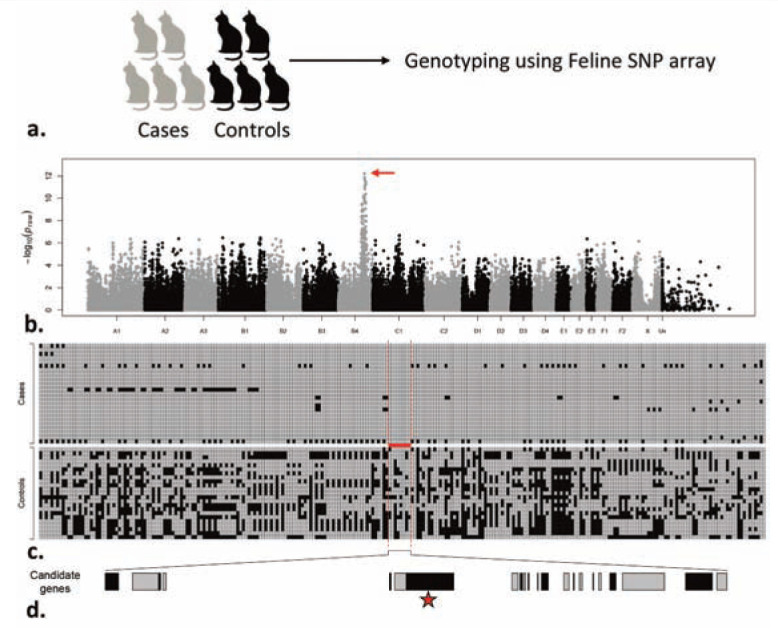
(a) Cats with a genetic disease (cases) and normal counterparts (controls) are selected from the same population. Numbers of cases and controls can vary, based on the mode of inheritance of a trait, age of the mutation and artificial selection on the population. Both diseased and normal cats are genotyped for markers across their genomes. (b) A genome-wide association analysis tests the association of a marker (single nucleotide polymorphism; SNP) with the disease. The association of each marker is measured and plotted for a genome-wide comparison. Each dot in the plot represents the association of a marker with the disease. The x-axis represents the different chromosomes in alternating colors, and markers (SNPs) are arranged within each chromosome according to their position on the chromosome. The –log (P value) of the association test (measuring a statistical significance) of each SNP marker is plotted on the y-axis. When the marker is highly associated it would exhibit a large –log (P value) (red arrow). (c) Haplotype analysis of the variants in the region showing the most significant association. In the region of the association the marker variation within the cases (top) is different from that found in the controls (bottom). Due to the differences in genetic background and recombination history between cases and controls, a unique region can be identified in the cases (red bar and vertical dashed lines). (d) Visual inspection of the unique region of association allows selection of a likely candidate gene responsible for the disease (red star). The likely candidate gene would be sequenced in search of a mutation that causes the disease
The conceptual framework of a GWAS approach is based on the notion that a disease mutation arises on a specific genetic background. Through time, and due to random mating between diseased and normal individuals, the unique genetic background of the diseased individuals becomes similar to normal individuals, except for the region surrounding the mutation site. Variations near the disease-causing mutation would, therefore, be non-randomly associated with the disease-causing mutation due to lack of recombination between them (markers are in linkage disequilibrium with the mutation site). Thus, by comparing diseased cats (cases) with normal ones (controls), individuals harboring a disease mutation would demonstrate statistically unique genetic markers only near the mutation site and nowhere else in the genome. When associated markers are detected, a refined chromosomal region is thereby identified, permitting a candidate gene search using the reference cat genome sequence.
The marker density of the first generation cat Illumina 63K SNP array was relatively low. Despite this limitation, many successful studies were reported, with different numbers of cases and controls, depending on the mode of inheritance and the trait under study (Table 2). A significantly lower number of cases and controls are needed compared with the linkage analysis approach. The inherited condition hypokalemic polymyopathy of Burmese and Tonkinese cats was tackled using a GWAS approach and a mutation in WNK4 was identified. Similarly, the genetic basis for the Japanese Bobtail 52 and Scottish Fold cat (B Gandolfi, B Haase and L Lyons, unpublished data) was found. The progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) of Persian cats was localized to a small genomic region using the array. 53
Table 2.
Overview of successful genome-wide association studies
| Trait | Breed | Mode of inheritance | Number of cases | Number of controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypokalemic polymyopathy | Burmese | Recessive | 35 | 25 |
| Rex hair | Selkirk Rex | Dominant | 9 | 29 |
| Curly hair | Cornish Rex | Recessive | 12 | NA* |
| Folded ears | Scottish Fold | Dominant | 44 | 55 |
| Orofacial pain | Burmese | Multigenic (?) | 27 | 60 |
| Blood type | Ragdoll | Recessive (?) | 38 | 23 |
| FIP | Birman | Multigenic (?) | 38 | 161 |
Mutation identified using array data and population genetics methods. NA = not applicable, FIP = feline infectious peritonitis
Beyond the genetics of inherited diseases, the SNP array was instrumental in the identification of the mutation associated with various phenotypes in cats, including the mutation causing curly hair texture in Selkirk Rex 14 and Cornish Rex cats. 16

Without doubt, the GWAS approach has enabled researchers to overcome the limitations and constraints of using pedigree-based methods such as linkage analysis. However, there are a number of factors that influence the success of GWAS in cats. To name a few:
The number of samples needed for a successful analysis is dependent on the selective pressure imposed on the trait under study Fewer cases are required for a trait under positive selection in the population, such as hair color (B Gandolfi, unpublished data) or texture,14,16 while more samples are required for the localization and identification of a disease locus, 21 which is generally under negative selection pressure.
The mode of inheritance of the trait under investigation (dominant, recessive, sex-linked, multigenic) influences the number of samples needed Fewer cases are required for a recessive trait, 16 while far more are needed for a dominant trait 14 or a multigenic trait with a relative risk. 54
Breeding strategies practiced within the population (inbreeding, outbreeding) are likely to affect the number of samples required Fewer cases are required if inbreeding of individuals is commonly practiced, while substantially more cases are needed for outbred or randomly bred populations. The recent success in the identification of several deleterious traits within the Burmese breed (such as hypokalemic polymyopathy, orofacial pain and a craniofacial malformation) is associated with the level of inbreeding within the breed. In fact, as previously mentioned, fewer individuals are needed if there is a common genetic background within a breed (high linkage disequilibrium). Moreover, the use of cases from one study can serve as controls for another disease/trait study within the same breed, reducing the cost of the study and the number of samples to be collected.
A very well defined and homogeneous phenotype/disease within the population of cases will help exclude confounding factors from the study and support the selection of appropriate controls For instance, in the study of early-onset blindness in Persian cats, the appropriate cases are cats with similar age of onset and disease progression. Appropriate controls are cats from the same breed, sighted and well beyond the age of onset of the disease. 51
The few studies published to date have shown that the density of the current array is, for some studies, insufficient to localize a disease to a sufficiently small region of the genome for candidate gene analysis. Furthermore, the genetic variation in the current SNP array was selected and designed based on comparatively few cat populations, which makes it more suitable for some breeds/populations than others. Current and future advances in DNA sequencing technologies would likely overcome these obstacles.
Beyond a single cat genome
The sequencing of the cat genome has provided the feline genomics community with two valuable resources.
The current cat genome, assembled in 2010 and released to the public in 2011, is a better assembled genome, where many previously unassembled sequences are now correctly placed, and it contains polymorphisms and genetic variants that differ between cat populations. The availability of a genome has allowed impressive and rapid progress in feline genetics, from single gene trait to complex trait analysis. The localization of a trait locus using an association study requires the segregation of the locus in a population or a pedigree, and is often successful in traits within a breed or across breeds.
However, many cat diseases appear randomly in single cats, and cannot be studied using the strategies mentioned above.55,56 Indeed, in the majority of instances, the cats have already been neutered, and their dam, sire and siblings may be impossible to locate; this precludes producing additional affected cats through classical repeat matings, inbreeding and test mating scenarios. The best approach to characterize such sporadic genetic disease is applying a whole-genome sequencing strategy. Whole-genome sequencing requires high quality DNA extracted from tissue samples. The whole-genome sequence of a diseased cat can be directly compared with that of a normal cat (preferably the parents and siblings) to identify the mutation directly using modern bioinformatics tools.
The advantage of whole-genome sequencing is that it can directly identify disease-causing mutations without performing candidate gene analyses or gene-specific sequencing. The chief disadvantages are the current high cost of sequencing and the lack of a robust database of healthy cat genome sequences. Additionally, whole-genome sequencing generates an enormous amount of data (terabytes) that requires specialized bioinformatics knowledge and resources. Currently, several ‘trios’ (an affected individual and parents) that segregate for disease traits (such as progressive retinal atrophy in the Bengal and Persian breeds) are being sequenced, and hopefully the subsequent genomic analyses will identify the polymorphisms that can be investigated further to identify the disease-causing mutation. This powerful approach will be rapidly implemented in the future, as the cost of the sequencing technology reduces. Undoubtedly, whole-genome sequencing will soon be performed for every interesting genetic case that the veterinary practitioner sees, leading to the discovery of new genetic mutations.
Key Points
The available genetic resources for cats are no longer a limiting factor for studies of inherited diseases. The only limiting factor is the acquisition of sufficient case and control specimens, and the funds to support such studies.
Primary care veterinarians in general small animal practice, feline clinicians and organ system specialists need to join forces with each other and with basic scientists to collect appropriate research materials (patients) to permit a study.
An interesting example is hypokalemic polymyopathy in the Burmese breed. The first DNA was collected and archived from an affected cat in the 1990s. After 20 years, sufficient cases and controls were available and finally used to characterize the causative mutation in 2012.
Whole-genome sequencing can largely overcome the limitations of low numbers of patients.
A well-characterized disease by veterinarians and sample collection remain key to any successful study of feline genetic diseases.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr Richard Malik for the helpful discussions and editorial assistance, and Alessandra Piersanti, Maria Palmieri, Monica Venturato and Magdalena Zdrodowska for providing access to their cats for photos.
Footnotes
Funding: The authors received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors for the preparation of this review article.
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Contributor Information
Barbara Gandolfi, Department of Veterinary Medicine and Surgery, College of Veterinary Medicine, W106 Vet Med Building, 1600 E Rollins St, University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO 65211, USA.
Hasan Alhaddad, College of Science, Department of Biological Sciences, Kuwait University, Safat, 13060, Kuwait.
References
- 1. American Pet Product Association. 2011–2012 National Pet Owners Survey. http://www.americanpetproducts.org/pubs_survey.asp, 2012.
- 2. Australian Companion Animal Council. Contribution of the pet care industry to the Australian economy. http://www.acac.org.au/pdf/ACAC%20Report%200810_sm.pdf (2010).
- 3. Baldock FC, Alexander L, More SJ. Estimated and predicted changes in the cat population of Australian households from 1979 to 2005. Aust Vet J 2003; 81: 289–292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Louwerens M, London CA, Pedersen NC, et al. Feline lymphoma in the post-feline leukemia virus era. J Vet Intern Med 2005; 19: 329–335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Toribio JA, Norris JM, White JD, et al. Demographics and husbandry of pet cats living in Sydney, Australia: results of cross-sectional survey of pet ownership. J Feline Med Surg 2009; 11: 449–461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Gentry AS, Clutton-Brock J, Groves CP. The naming of wild animal species and their domestic derivates. J Archeol Sci 2004; 31: 645–651. [Google Scholar]
- 7. Nowak RM. Walker’s carnivores of the world. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 8. Driscoll CA, Macdonald DW, O’Brien SJ. From wild animals to domestic pets, an evolutionary view of domestication. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America; 2009; 106 Suppl 1: 9971–9978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Wayne RK. Consequences of domestication: morphological diversity of the dog. In: Ruvinsky A, Sampson J. (eds). The genetics of the dog. New York: CABI, 2001, pp 43–61. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Morris D. Cat breeds of the world. New York: Penguin Books, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 11. American Pet Products Association. National pet owners survey. Greenwich, CT, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 12. Lipinski MJ, Froenicke L, Baysac KC, et al. The ascent of cat breeds: genetic evaluations of breeds and worldwide random-bred populations. Genomics 2008; 91: 12–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Kurushima JD, Lipinski MJ, Gandolfi B, et al. Variation of cats under domestication: genetic assignment of domestic cats to breeds and worldwide random-bred populations. Anim Genet 2013; 44: 311–324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Gandolfi B, Alhaddad H, Joslin SE, et al. A splice variant in KRT71 is associated with curly coat phenotype of Selkirk Rex cats. Sci Rep 2013; 3: 2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Gandolfi B, Outerbridge CA, Beresford LG, et al. The naked truth: Sphynx and Devon Rex cat breed mutations in KRT71. Mamm Genome 2010; 21: 509–515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Gandolfi B, Alhaddad H, Affolter VK, et al. To the root of the curl: a signature of a recent selective sweep identifies a mutation that defines the Cornish Rex cat breed. PloS One 2013; 8: e67105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Drogemuller C, Rufenacht S, Wichert B, et al. Mutations within the FGF5 gene are associated with hair length in cats. Anim Genet 2007; 38: 218–221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Lyons LA, Imes DL, Rah HC, et al. Tyrosinase mutations associated with Siamese and Burmese patterns in the domestic cat (Felis catus). Anim Genet 2005; 36: 119–126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Robinson R. The Canadian hairless or Sphinx cat. J Hered 1973; 64: 47–49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Filler S, Alhaddad H, Gandolfi B, et al. Selkirk Rex: morphological and genetic characterization of a new cat breed. J Hered 2012; 103: 727–733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Gandolfi B, Gruffydd-Jones TJ, Malik R, et al. First WNK4-hypokalemia animal model identified by genome-wide association in Burmese cats. PloS One 2012; 7: e53173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Lyons LA, Biller DS, Erdman CA, et al. Feline polycystic kidney disease mutation identified in PKD1. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004; 15: 2548–2555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Penny Illustated Paper, The Cat Show, The Naturalist, 1871, p 511.
- 24. Alhaddad H, Khan R, Grahn RA, et al. Extent of linkage disequilibrium in the domestic cat, Felis silvestris catus, and its breeds. PloS One 2013; 8: e53537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Driscoll CA, Clutton-Brock J, Kitchener AC, et al. The taming of the cat. Genetic and archaeological findings hint that wildcats became housecats earlier – and in a different place – than previously thought. Sci Am 2009; 300: 68–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Grahn RA, Lemesch BM, Millon LV, et al. Localizing the X-linked orange colour phenotype using feline resource families. Anim Genet 2005; 36: 67–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Wurster-Hill DH, Centerwall WR. The interrelationships of chromosome banding patterns in canids, mustelids, hyena, and felids. Cytogenet Cell Genet 1982; 34: 178–192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Wurster-Hill DH, Gray CW. Giemsa banding patterns in the chromosomes of twelve species of cats (Felidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 1973; 12: 388–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. O’Brien SJ, Nash WG. Genetic mapping in mammals: chromosome map of domestic cat. Science 1982; 216: 257–265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Menotti-Raymond M, David VA, Lyons LA, et al. A genetic linkage map of microsatellites in the domestic cat (Felis catus). Genomics 1999; 57: 9–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Cooper MP, Fretwell N, Bailey SJ, et al. White spotting in the domestic cat (Felis catus) maps near KIT on feline chromosome B1. Anim Genet 2006; 37: 163–165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Sun S, Murphy WJ, Menotti-Raymond M, et al. Integration of the feline radiation hybrid and linkage maps. Mamm Genome 2001; 12: 436–441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Menotti-Raymond M, David VA, Roelke ME, et al. Second-generation integrated genetic linkage/ radiation hybrid maps of the domestic cat (Felis catus). J Hered 2003; 94: 95–106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. O’Brien SJ, Cevario SJ, Martenson JS, et al. Comparative gene mapping in the domestic cat (Felis catus). J Hered 1997; 88: 408–414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. O’Brien SJ, Haskins ME, Winkler CA, et al. Chromosomal mapping of beta-globin and albino loci in the domestic cat. A conserved mammalian chromosome group. J Hered 1986; 77: 374–378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Menotti-Raymond M, David VA, Schaffer AA, et al. An autosomal genetic linkage map of the domestic cat, Felis silvestris catus. Genomics 2009; 93: 305–313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Lyons LA, Bailey SJ, Baysac KC, et al. The Tabby cat locus maps to feline chromosome B1. Anim Genet 2006; 37: 383–386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Bach LH, Gandolfi B, Grahn JC, et al. A high-resolution 15,000(Rad) radiation hybrid panel for the domestic cat. Cytogenet Genome Res 2012; 137: 7–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Buckingham KJ, McMillin MJ, Brassil MM, et al. Multiple mutant T alleles cause haploinsufficiency of Brachyury and short tails in Manx cats. Mamm Genome 2013; 24: 400–408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Grahn RA, Ellis MR, Grahn JC, et al. A novel CYP27B1 mutation causes a feline vitamin D-dependent rickets type IA. J Feline Med Surg 2012; 14: 587–590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Bighignoli B, Niini T, Grahn RA, et al. Cytidine monophospho-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase (CMAH) mutations associated with the domestic cat AB blood group. BMC Genet 2007; 8: 27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Lyons LA, Foe IT, Rah HC, et al. Chocolate coated cats: TYRP1 mutations for brown color in domestic cats. Mamm Genome 2005; 16: 356–366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Gandolfi B, Daniel RJ, O’Brien DP, et al. A novel mutation in CLCN1 associated with feline myotonia congenita. PLoS One 2014; 9: e109926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Hauswirth R, Haase B, Blatter M, et al. Mutations in MITF and PAX3 cause ‘splashed white’ and other white spotting phenotypes in horses. PLoS Genet 2012; 8: e1002653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Brooks SA, Bailey E. Exon skipping in the KIT gene causes a Sabino spotting pattern in horses. Mamm Genome 2005; 16: 893–902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Fontanesi L, Tazzoli M, Russo V, et al. Genetic heterogeneity at the bovine KIT gene in cattle breeds carrying different putative alleles at the spotting locus. Anim Genet 2010; 41: 295–303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Rothschild MF, Van Cleave PS, Glenn KL, et al. Association of MITF with white spotting in Beagle crosses and Newfoundland dogs. Anim Genet 2006; 37: 606–607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Philipp U, Lupp B, Momke S, et al. A MITF mutation associated with a dominant white phenotype and bilateral deafness in German Fleckvieh cattle. PloS One 2011; 6: e28857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Pontius JU, Mullikin JC, Smith DR, et al. Initial sequence and comparative analysis of the cat genome. Genome Res 2007; 17: 1675–1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Mullikin JC, Hansen NF, Shen L, et al. Light whole genome sequence for SNP discovery across domestic cat breeds. BMC Genomics 2010; 11: 406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Montague MJ, Li G, Gandolfi B, et al. Comparative analysis of the domestic cat genome reveals genetic signatures underlying feline biology and domestication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 17230–17235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Pollard RE, Koehne AL, Peterson CB, et al. Japanese Bobtail: vertebral morphology and genetic characterization of an established cat breed. J Feline Med Surg. Epub ahead of print 8 December 2014. DOI: 10.1177/1098612X14558147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Alhaddad H, Gandolfi B, Grahn RA, et al. Genome-wide association and linkage analyses localize a progressive retinal atrophy locus in Persian cats. Mamm Genome 2014; 25: 354–362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Golovko L, Lyons LA, Liu H, et al. Genetic susceptibility to feline infectious peritonitis in Birman cats. Virus Res 2013; 175: 58–63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Worthing KA, Wigney DI, Dhand NK, et al. Risk factors for feline infectious peritonitis in Australian cats. J Feline Med Surg 2012; 14: 405–412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Phillips AM, Fawcett AC, Allan GS, et al. Vitamin D-dependent non-type 1, non-type 2 rickets in a 3-month-old Cornish Rex kitten. J Feline Med Surg 2011; 13: 526–531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]