Abstract
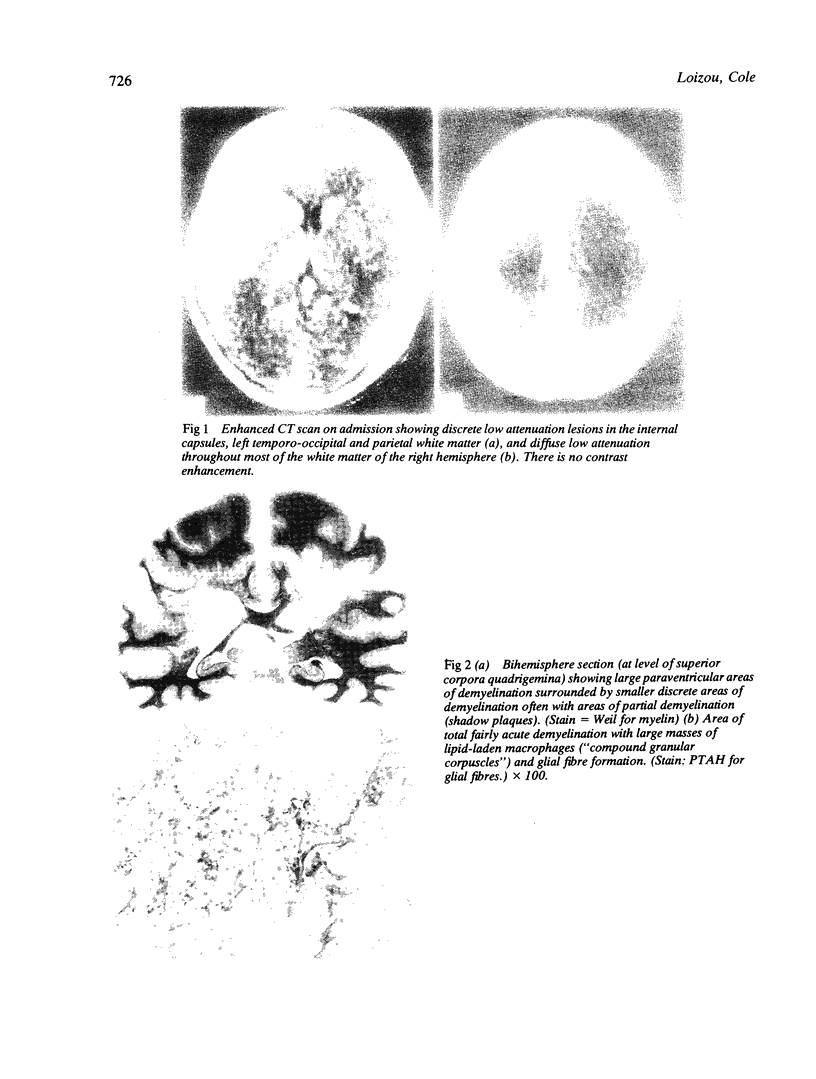
A 30-year-old woman died eleven weeks after the onset of an acute illness during which she developed quadriplegia, dysphasia, incontinence, confusion, emotional lability and gaze palsies. The CT scan demonstrated large white matter low attenuation lesions with no mass effect and minimal contrast enhancement. At necropsy the lesions were shown to be those of massive cerebral demyelination.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aita J. F., Bennett D. R., Anderson R. E., Ziter F. Cranial CT appearance of acute multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1978 Mar;28(3):251–255. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.3.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aita J. F. Multiple sclerosis and cranial lesions. Arch Neurol. 1980 Nov;37(11):738–738. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500600086025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cala L. A., Mastaglia F. L., Black J. L. Computerized tomography of brain and optic nerve in multiple sclerosis. Observations in 100 patients, including serial studies in 16. J Neurol Sci. 1978 May;36(3):411–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M., Davis K. R., Newhouse J., Pfister R. C. Expanded high iodine dose in computed cranial tomography: a preliminary report. Radiology. 1979 May;131(2):373–380. doi: 10.1148/131.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gado M. H., Phelps M. E., Coleman R. E. An extravascular component of contrast enhancement in cranial computed tomography. Part I. The tissue-blood ratio of contrast enhancement. Radiology. 1975 Dec;117(3 Pt 1):589–593. doi: 10.1148/117.3.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gado M. H., Phelps M. E., Coleman R. E. An extravascular component of contrast enhancement in cranial computed tomography. Part II. Contrast enhancement and the blood-tissue barrier. Radiology. 1975 Dec;117(3 Pt 1):595–597. doi: 10.1148/117.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyldensted C. Computer tomography of the cerebrum in multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology. 1976 Oct 27;12(1):33–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00344224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B., Carroll B. A., Pedley T. A. Computerized cranial tomography in cerebral diseases of white matter. Neurology. 1978 Jun;28(6):534–544. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.6.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebow S., Anderson D. C., Mastri A., Larson D. Acute multiple sclerosis with contrast-enhancing plaques. Arch Neurol. 1978 Jul;35(7):435–439. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500310037007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marano G. D., Goodwin C. A., Ko J. P. Atypical contrast enhancement of computerized tomography of demyelinating disease. Arch Neurol. 1980 Aug;37(8):523–524. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500570071013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendes J. L. Contrast dose in CT scanning. Arch Neurol. 1981 Jan;38(1):67–68. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510010093029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears E. S., Tindall R. S., Zarnow H. Active multiple sclerosis. Enhanced computerized tomographic imaging of lesions and the effect of corticosteroids. Arch Neurol. 1978 Jul;35(7):426–434. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500310028006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Ball M. J., Paty D. W., Banna M. Computer tomography in disseminated sclerosis. Can J Neurol Sci. 1976 Aug;3(3):211–216. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100025750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Velden M., Bots G. T., Endtz L. J. Cranial CT in multiple sclerosis showing a mass effect. Surg Neurol. 1979 Oct;12(4):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]