Abstract
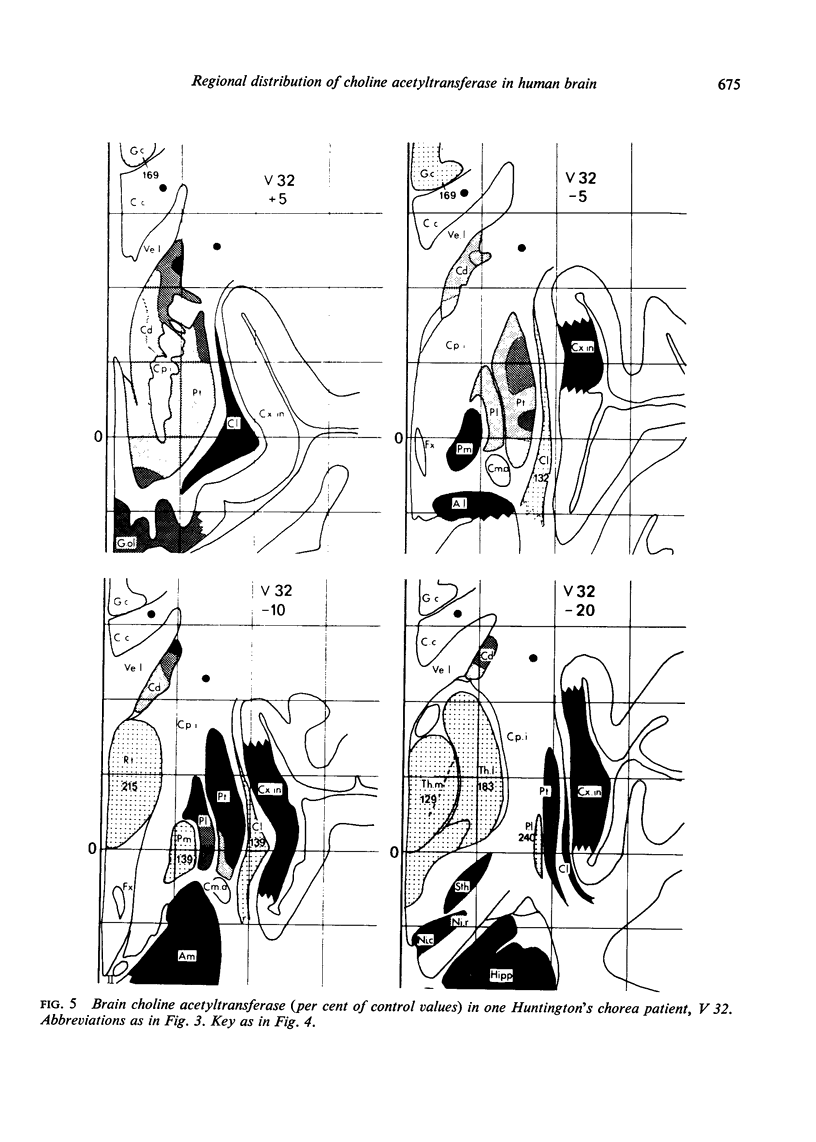
A stereotaxic method of tissue sampling has been developed permitting detailed studies of the distribution of choline acetyltransferase (CAT) in brains from controls and from patients suffering from Huntington's chorea. The characteristic pattern of CAT distribution within extra-pyramidal structures is described. In Huntington's chorea, CAT is unevenly reduced in several brain regions particularly in the rostromedial part of the caudate nucleus. The results indicate a preferential degeneration of neostriatal cholinergic neurones in Huntington's chorea.
Full text
PDF

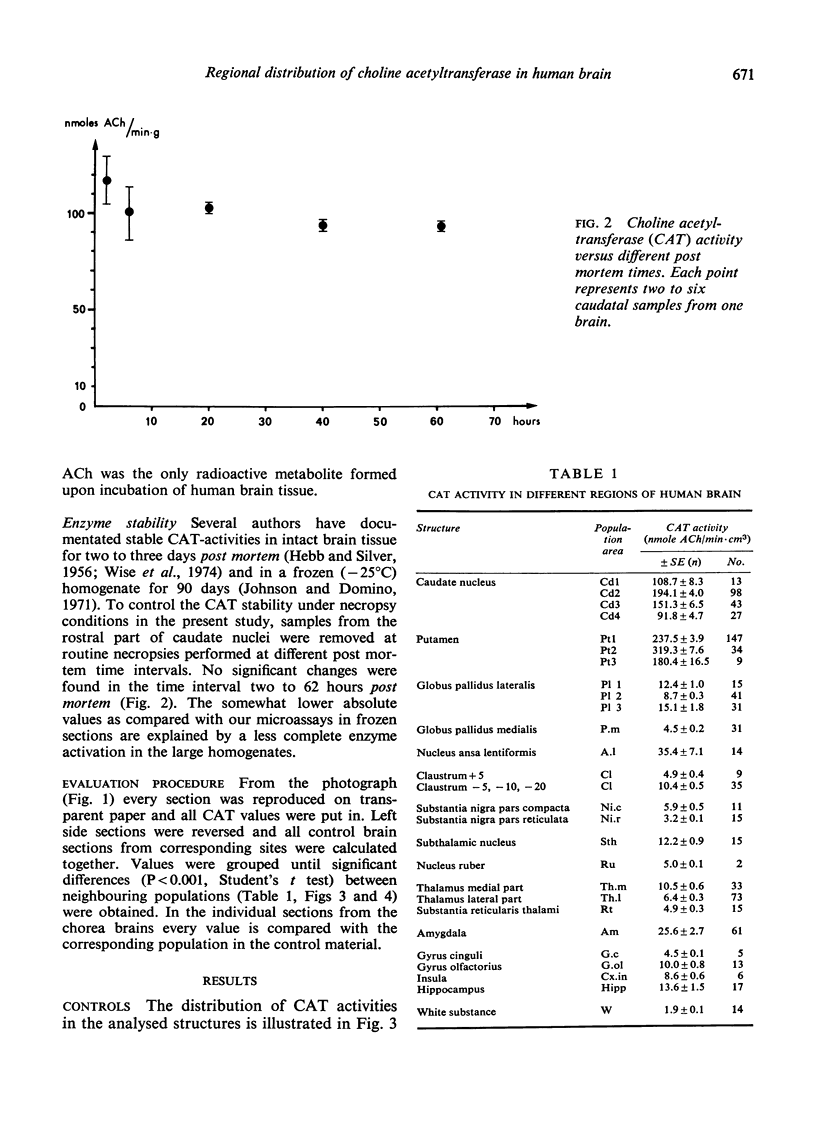


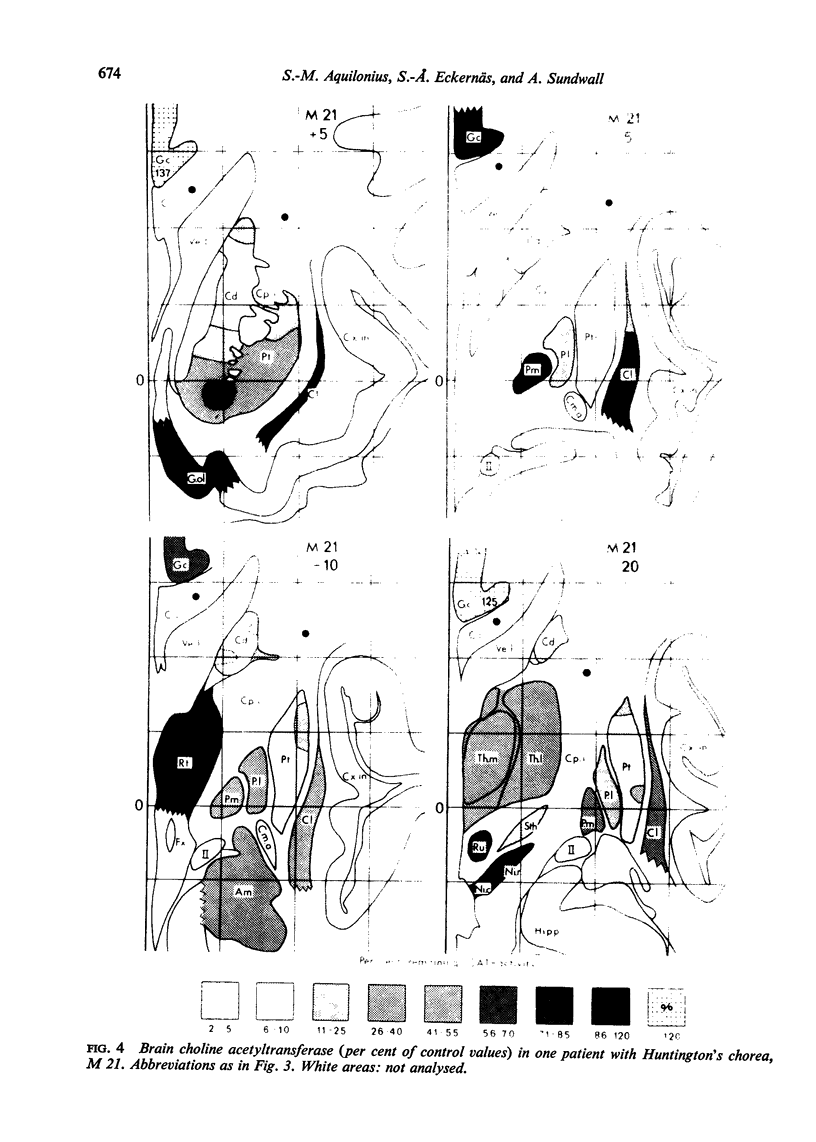

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aquilonius S. M., Nyström B., Schuberth J., Sundwall A. Cerebrospinal fluid choline in extrapyramidal disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Oct;35(5):720–725. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.5.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aquilonius S. M., Sjöström R. Cholinergic and dopaminergic mechanisms in Huntington's chorea. Life Sci I. 1971 Apr 1;10(7):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
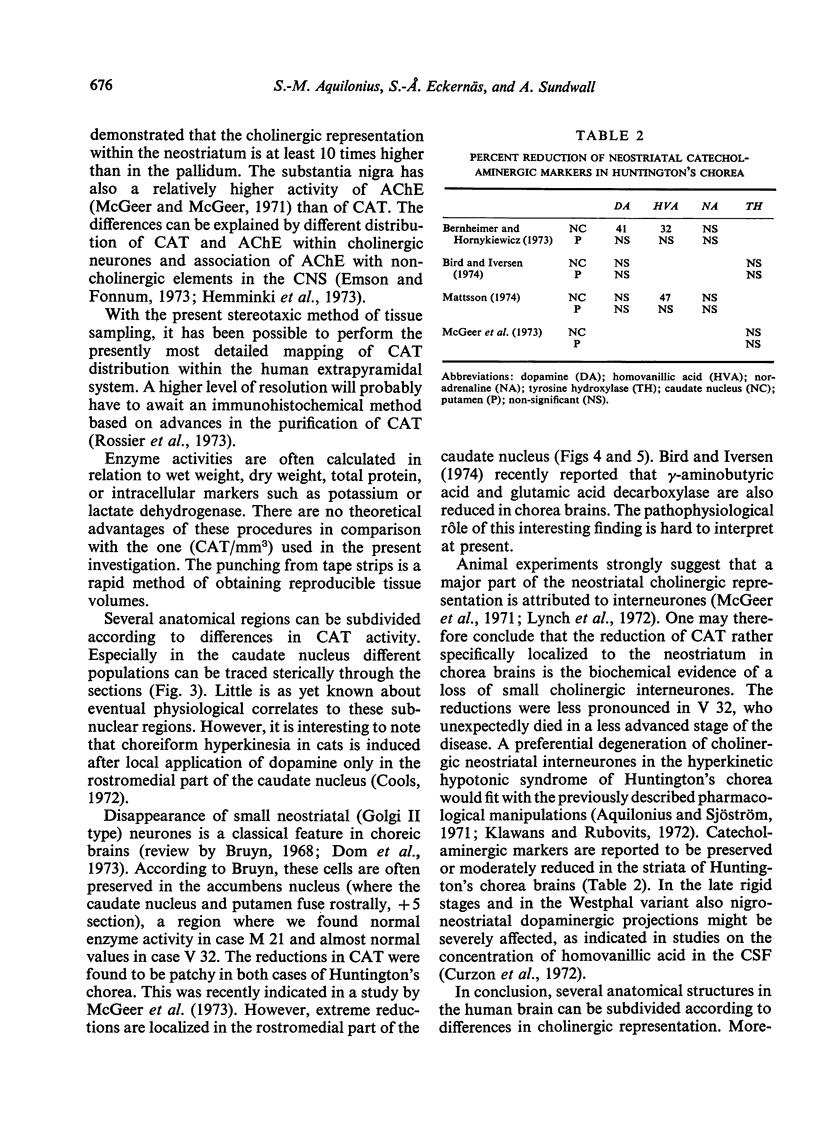
- Bird E. D., Iversen L. L. Huntington's chorea. Post-mortem measurement of glutamic acid decarboxylase, choline acetyltransferase and dopamine in basal ganglia. Brain. 1974 Sep;97(3):457–472. doi: 10.1093/brain/97.1.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cools A. R. Athetoid and choreiform hyperkinesias produced by caudate application of dopamine in cats. Psychopharmacologia. 1972;25(3):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00422504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Gumpert J., Sharpe D. Amine metabolites in the cerbrospinal fluid in Huntington's chorea. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Aug;35(4):514–519. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.4.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Radiochemical micro assays for the determination of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):465–472. doi: 10.1042/bj1150465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Recent developments in biochemical investigations of cholinergic transmission. Brain Res. 1973 Nov 23;62(2):497–507. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90714-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover V., Green D. P. A simple quick microassay for choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1972 Oct;19(10):2465–2466. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB C. O., SILVER A. Choline acetylase in the central nervous system of man and some other mammals. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):718–728. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Hemminki E., Giacobini E. Activity of enzymes related to neurotransmission in neuronal and glial fractions. Int J Neurosci. 1973 Feb;5(2):87–90. doi: 10.3109/00207457309149458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Friede R. L. A comparative histochemical mapping of the distribution of acetylcholinesterase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-diaphorase activities in the human brain. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1967;10:231–275. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S., Domino E. F. Cholinergic enzymatic activity of cerebrospinal fluid of patients with various neurologic diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Dec;35(2):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klawans H. L., Jr, Rubovits R. Central cholinergic-anticholinergic antagonism in Huntington's chorea. Neurology. 1972 Feb;22(2):107–116. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G. S., Lucas P. A., Deadwyler S. A. The demonstration of acetylcholinesterase containing neurones within the caudate nucleus of the rat. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 27;45(2):617–621. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90494-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G. Cholinergic enzyme systems in Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1971 Sep;25(3):265–268. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00490030091011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G., Fibiger H. C. Choline acetylase and glutamic acid decarboxylase in Huntington's chorea. A preliminary study. Neurology. 1973 Sep;23(9):912–917. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.9.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G., Fibiger H. C., Wickson V. Neostriatal choline acetylase and cholinesterase following selective brain lesions. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 10;35(1):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90625-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinne U. K., Riekkinen P., Sonninen V., Laaksonen H. Brain acetylcholinesterase in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 1973;49(2):215–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1973.tb01293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Bauman A., Benda P. Antibodies to rat brain choline acetyltransferase: species and organ specificity. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 1;36(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80333-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver A. Cholinesterases of the central nervous system with special reference to the cerebellum. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1967;10:57–109. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise C. D., Baden M. M., Stein L. Post-mortem measurement of enzymes in human brain: evidence of a central noradrenergic deficit in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 1974;11:185–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(74)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]