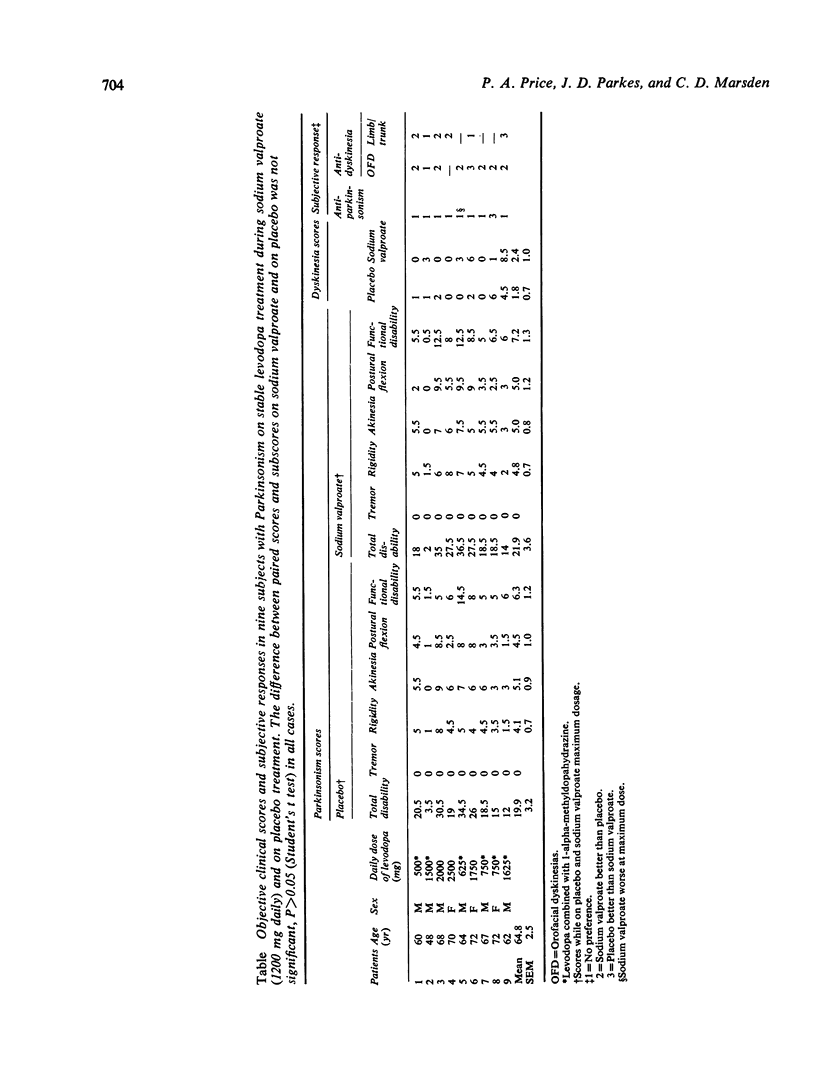
Abstract
The effect of sodium valproate 1200 mg daily on the disability of Parkinsonism and on levodopa-induced dyskinesia was assessed in a double-blind crossover trial with matched placebo in 12 patients with Parkinson's disease. No objective change in the severity of Parkinsonism or dyskinesias was noted. However, six out of nine patients who completed the trial noted a slight to moderate improvement in their dyskinesias with no change in their Parkinsonism. Excess salivation improved in four subjects on sodium valproate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anlezark G., Horton R. W., Meldrium B. S., Sawaya C. B. Anticonvulsant action of ethanolamine-O-sulphate and di-n-propylacetate and the metabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in mice with audiogenic seizures. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Feb 15;25(4):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90343-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbeau A. Letter: G.A.B.A. and Huntington's chorea. Lancet. 1973 Dec 29;2(7844):1499–1500. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92765-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cools A. R., Van Rossum J. M. Excitation-mediating and inhibition-mediating dopamine-receptors: a new concept towards a better understanding of electrophysiological, biochemical, pharmacological, functional and clinical data. Psychopharmacologia. 1976 Feb 2;45(3):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00421135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Agnati L., Johansson O., Perez de la Mora M. Evidence for an inhibitory gabergic control of the meso-limbic dopamine neurons: possibility of improving treatment of schizophrenia by combined treatment with neuroleptics and gabergic drugs. Med Biol. 1975 Jun;53(3):177–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., McGeer P. L., Fibiger H. C., McGeer E. G. On the source of GABA-containing terminals in the substantia nigra. Electron microscopic autoradiographic and biochemical studies. Brain Res. 1973 May 17;54:103–114. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. H., Moore K. E. Mesolimbic dopaminergic neurones in the rotational model of nigrostriatal function. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):695–696. doi: 10.1038/263695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. S., Bak I. J., Hassler R., Okada Y. Role of -aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the extrapyramidal motor system. 2. Some evidence for the existence of a type of GABA-rich strio-nigral neurons. Exp Brain Res. 1971;14(1):95–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00234913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnoila M., Viukari M., Kietala O. Effect of sodium valproate on tardive dyskinesia. Br J Psychiatry. 1976 Aug;129:114–119. doi: 10.1192/bjp.129.2.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. G., Hornykiewicz O. L-glutamic acid decarboxylase in Parkinson's disease: effect of L-dopa therapy. Nature. 1973 Jun 29;243(5409):521–523. doi: 10.1038/243521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Parkes J. D., Rees J. E. A year's comparison of treatment of patients with parkinson's disease with levodopa combined with carbidopa versus treatment with levodopa alone. Lancet. 1973 Dec 29;2(7844):1459–1462. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92729-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G., Fibiger H. C. Glutamic-acid decarboxylase and choline acetylase in Huntington's chorea and Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 1973 Sep 15;2(7829):622–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes J. D., Bedard P., Marsden C. D. Letter: Chorea and torsion in parkinsonism. Lancet. 1976 Jul 17;2(7977):155–155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92894-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pycock C. J., Horton R. W. Possible GABA-mediated control of dopamine-dependent behavioural effects from the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1976 Sep 17;49(2):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00427286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pycock C., Horton R. W., Marsden C. D. The behavioural effects of manipulating GABA function in the globus pallidus. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 5;116(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90916-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts E. Gamma-aminobutyric acid and nervous system function--a perspective. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Oct 1;23(19):2637–2649. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarsy D., Pycock C., Meldrum B., Marsden C. D. Rotational behavior induced in rats by intranigral picrotoxin. Brain Res. 1975 May 16;89(1):160–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


