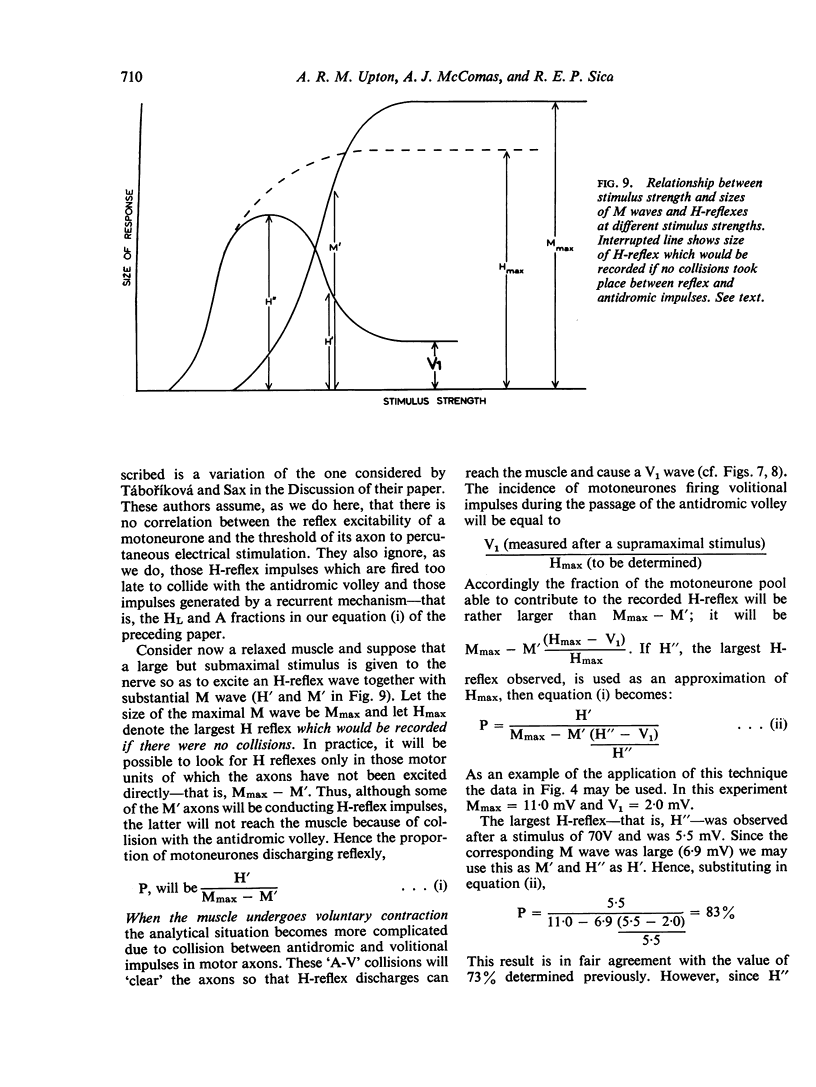
Abstract
A study has been made of the effect of voluntary contraction on the `late' responses which can be recorded in muscles after indirect stimulation. Two late responses have been described of which the first was shown to consist mainly of a potentiated H-reflex. The potentiation of this wave was greatest in the abductor pollicis brevis muscle and depended largely on `direct' descending pathways to motoneurones. In addition, a later evoked muscle response appeared during effort; the nature of this wave was uncertain. Simple formulae have been devised to express the excitability of motoneurones to inputs from muscle nerves during effort.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., SEARS T. A. THE ROLE OF INHIBITION IN THE PHASING OF SPONTANEOUS THALAMO-CORTICAL DISCHARGE. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;173:459–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel R. W., Eppler W., Iannone A. Silent period produced by unloading of muscle during voluntary contraction. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):864–870. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIGLAND B., LIPPOLD O. C. Motor unit activity in the voluntary contraction of human muscle. J Physiol. 1954 Aug 27;125(2):322–335. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter D., Engberg I., Lundberg A. Primary afferent depolarization evoked from the brain stem and the cerebellum. Arch Ital Biol. 1966 Mar;104(1):73–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamann H. P. Activity of single motor units during isometric tension. Neurology. 1970 Mar;20(3):254–260. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DASGUPTA A., SIMPSON J. A. Relation between firing frequency of motor units and muscle tension in the human. Electromyography. 1962 Mar-Jun;2:117–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERNANDT B. E., SHIMAMURA M. Mechanisms of interlimb reflexes in cat. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Nov;24:665–676. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb G. L., Agarwal G. C., Stark L. Interactions between voluntary and postural mechanisms of thehuman motor system. J Neurophysiol. 1970 May;33(3):365–381. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGBARTH K. E. Post-tetanic potentiation of myotatic reflexes in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 Feb;25:1–10. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES C. M. Intraveneus regional analgesia. A useful method of producing analgesia of thelimbs. Lancet. 1963 Feb 2;1(7275):245–247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90954-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., McDOUGAL D. B., Jr Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. I. Identification of certain reflexes in the electromyogram and the conduction velocity of peripheral nerve fibers. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950 May;86(5):265–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., PORTER W. E., PARK A. M., TEASDALL R. D. Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. IV. The two-neurone reflex and identification of certain action potentials from spinal roots and cord. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1951 Jun;88(6):499–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. The silent period in a muscle of the human hand. J Physiol. 1951 Jun;114(1-2):183–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):553–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. F., Feldman R. G. Observations on the nature of the F wave in man. Neurology. 1967 Feb;17(2):147–156. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Sica R. E., Upton A. R. Excitability of human motoneurones during effort. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):145P–146P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Wray S. H. An experimental study of the F wave in the baboon. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Jun;29(3):196–200. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.3.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica R. E., McComas A. J., Upton A. R. Impaired potentiation of H-reflexes in patients with upper motoneurone lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Dec;34(6):712–717. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.6.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEASDALL R. D., PARK A. M., LANGUTH H. W., MAGLADERY J. W. Electrophysiological studies of reflex activity in patients with lesions of the nervous system. II. Disclosure of normally suppressed monosynaptic reflex discharge of spinal motoneurones by lesions of lower brain-stem and spinal cord. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1952 Oct;91(4):245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS J. E., LAMBERT E. H. Ulnar nerve conduction velocity and H-reflex in infants and children. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Jan;15:1–9. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne J. Central responses to electrical activation of the peripheral nerves supplying the intrinsic hand muscles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1965 Dec;28(6):482–495. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.28.6.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara N., Ohye C. Polysynaptic activation of extensor motorneurones from group Ia fibres in the cat spinal cord. Experientia. 1964 Nov 15;20(11):628–629. doi: 10.1007/BF02144828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Táboríková H., Sax D. S. Motoneurone pool and the H-reflex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Aug;31(4):354–361. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.4.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEAVER R. A., LANDAU W. M., HIGGINS J. F. FUSIMOTOR FUNCTION. II. EVIDENCE OF FUSIMOTOR DEPRESSION IN HUMAN SPINAL SHOCK. Arch Neurol. 1963 Aug;9:127–132. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1963.00460080037004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



