Abstract
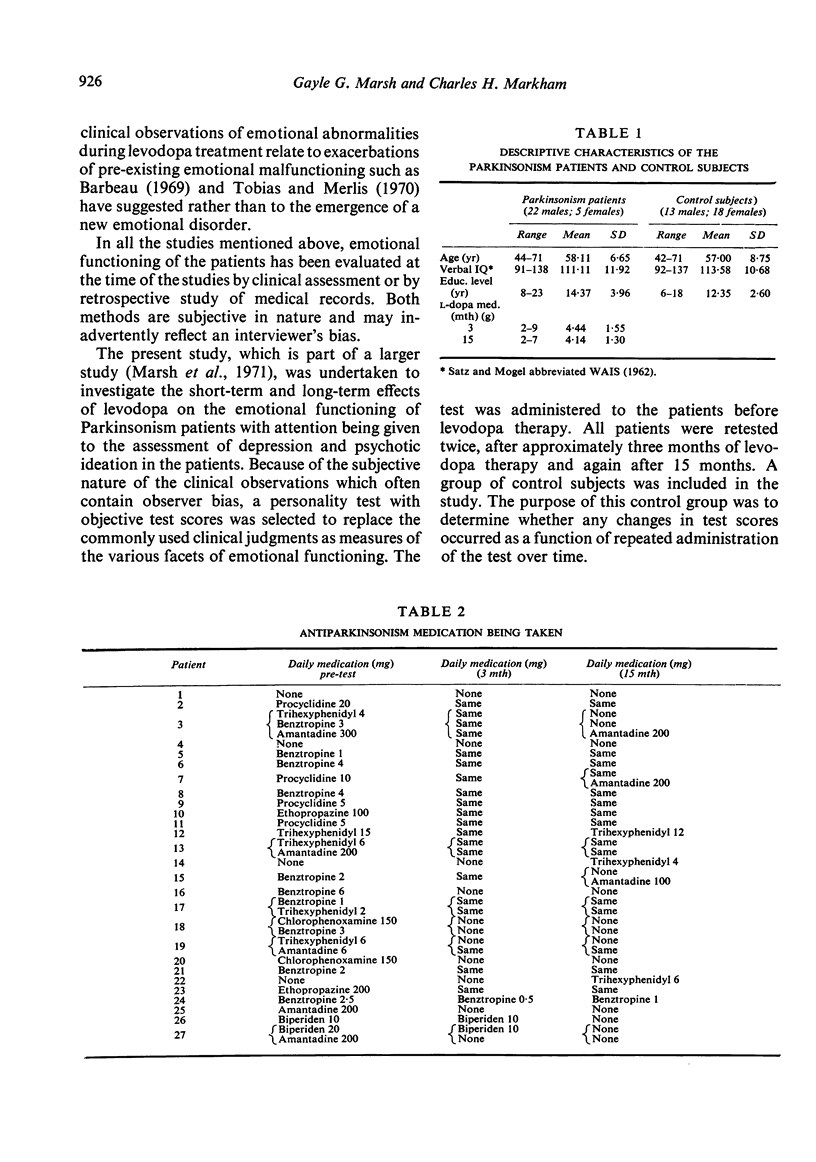
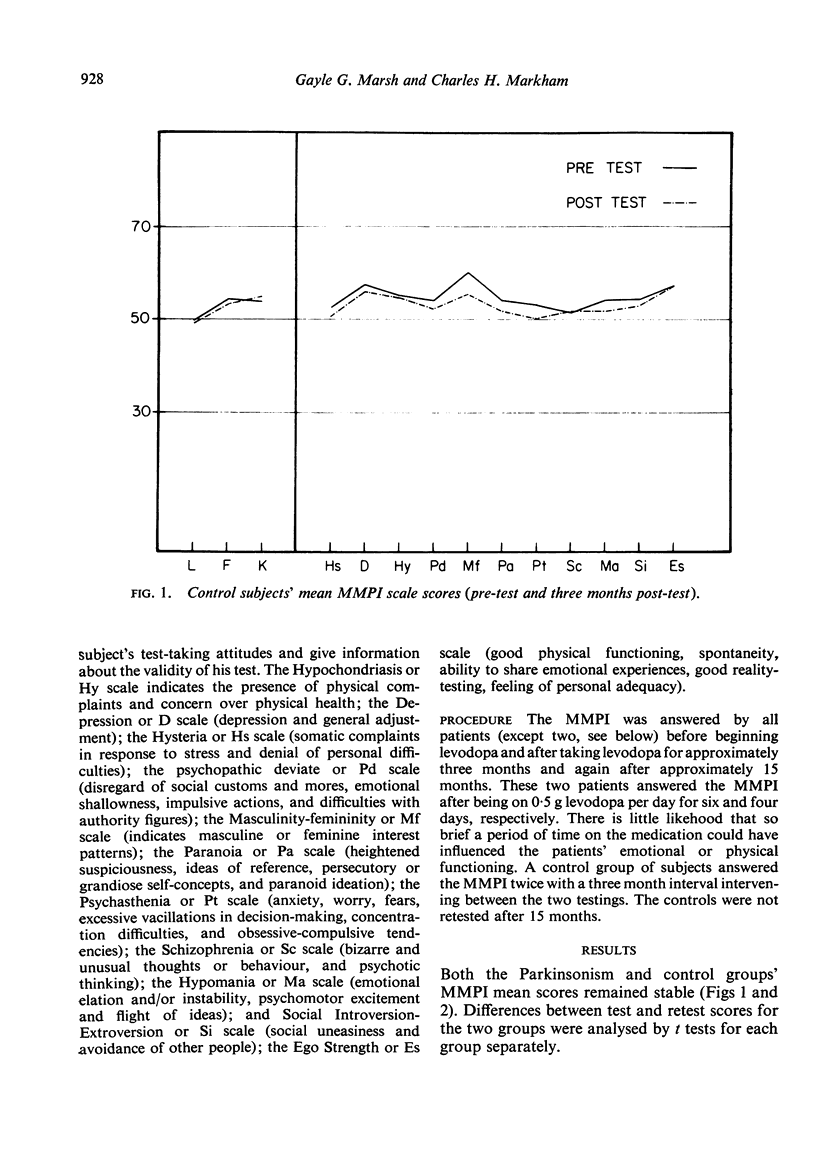
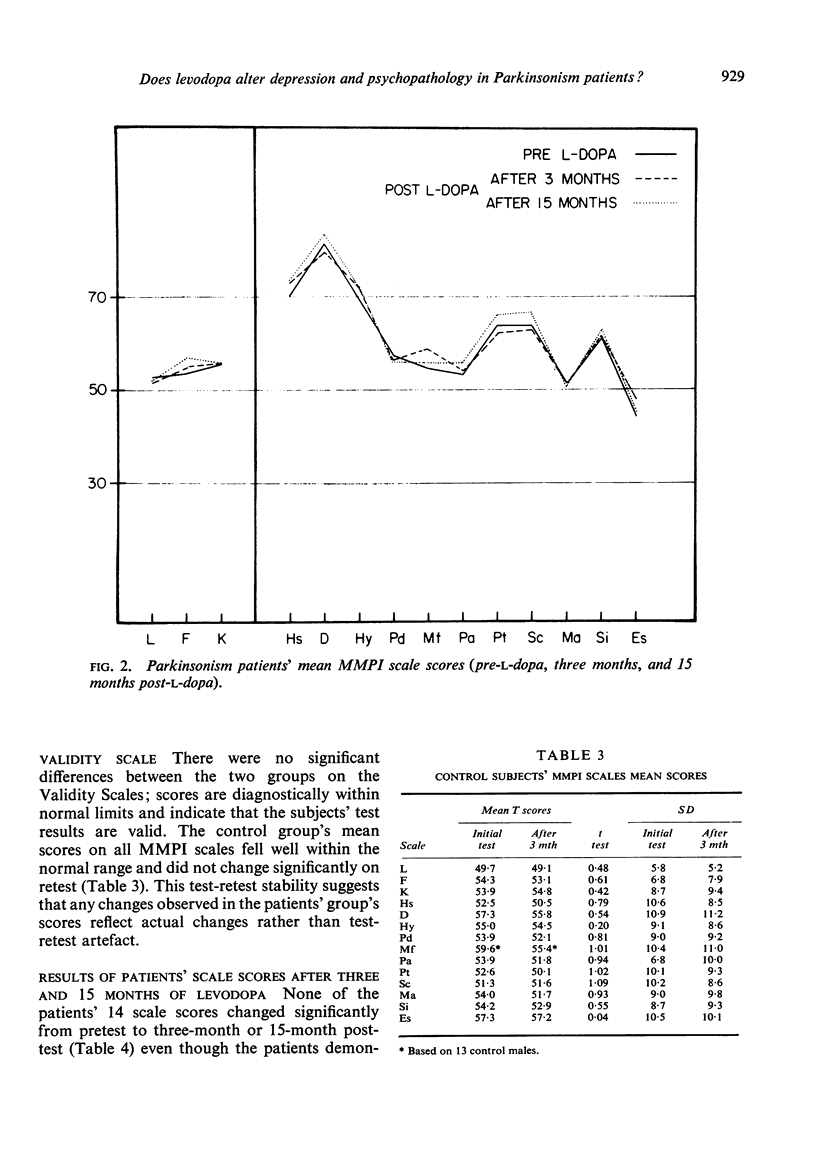
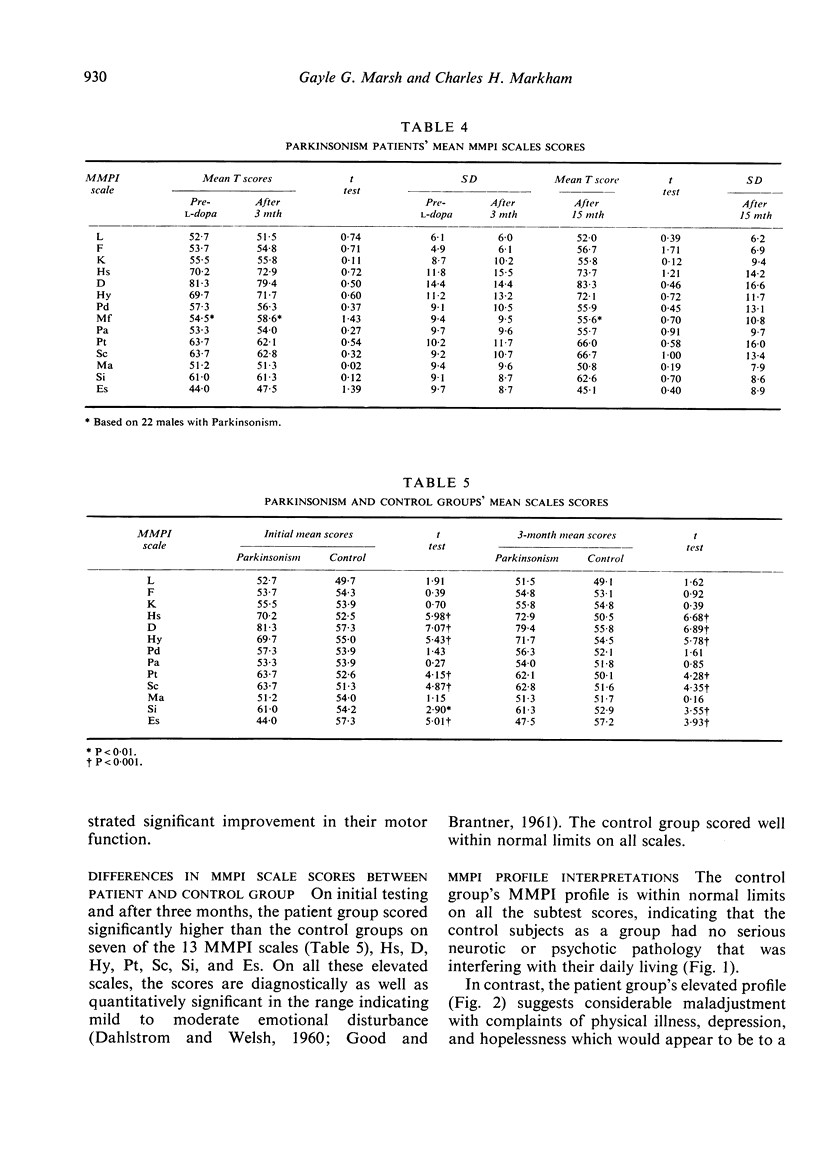
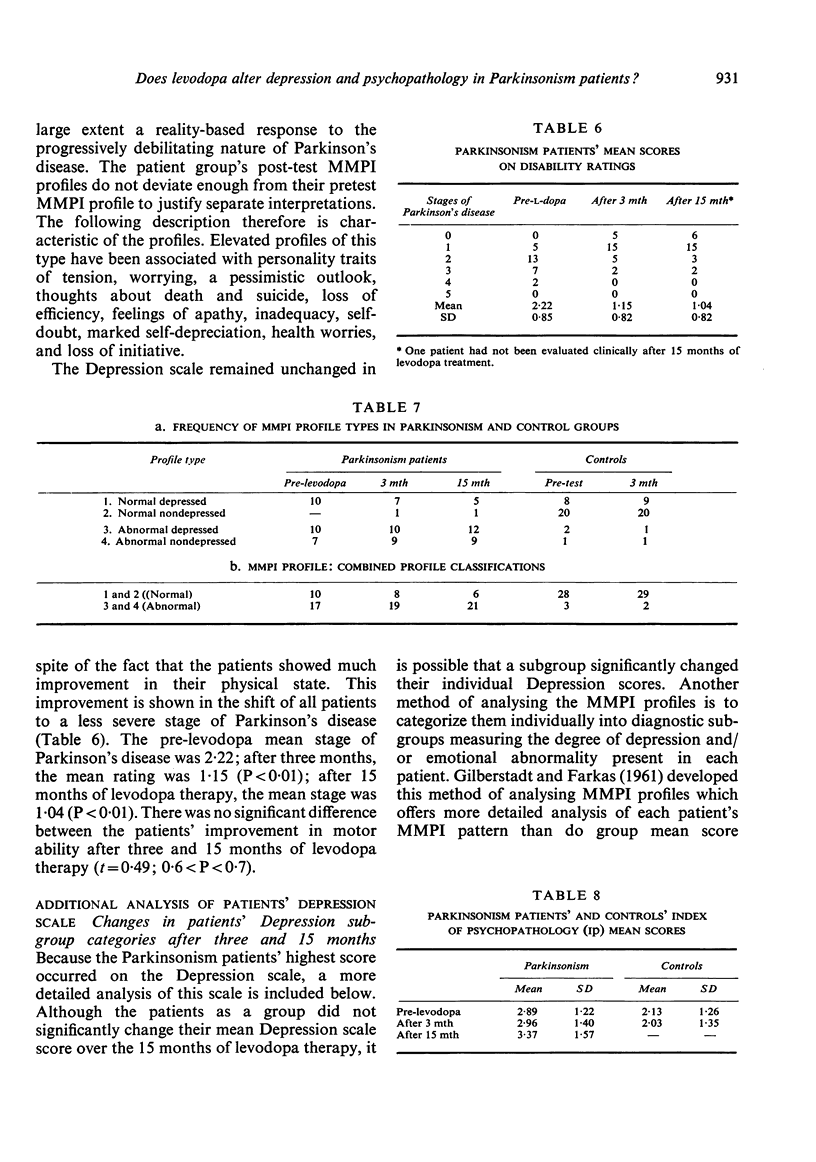
Twenty-seven Parkinsonism patients and 31 controls, matched for age and verbal IQ, were tested on an objectively scored personality test (Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory) at the beginning of the patients' levodopa therapy and three months later. Patients, but not the controls, were retested after 15 months of levodopa treatment. The patients, all of whom were intact intellectually, obtained MMPI scores indicating moderate depression before beginning levodopa treatment. There was no test evidence to indicate that levodopa significantly increased or decreased the amount of depression in the patients after three or 15 months of levodopa. The patient group, however, significantly increased their Index of Psychopathology (Ip) score after 15 months of levodopa but not after three months.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calne D. B., Stern G. M., Laurence D. R., Sharkey J., Armitage P. L-dopa in postencephalitic parkinsonism. Lancet. 1969 Apr 12;1(7598):744–746. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91751-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherington M. Parkinsonism, L-dopa and mental depression. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1970 Jul;18(7):513–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1970.tb02784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Papavasiliou P. S., Gellene R. Modification of Parkinsonism--chronic treatment with L-dopa. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 13;280(7):337–345. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902132800701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damásio A. R., Antunes J. L., Macedo C. L-dopa, parkinsonism, and depression. Lancet. 1970 Sep 19;2(7673):611–612. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damãsio A. R., Lobo-Antunes J., Macedo C. Psychiatric aspects in Parkinsonism treated with L-dopa. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Oct;34(5):502–507. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.5.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvoisin R. C., Katz R. Reversal of central anticholinergic syndrome in man by physostigmine. JAMA. 1968 Nov 25;206(9):1963–1965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERSTADT H., FARKAS E. Another look at MMPI profile types in multiple sclerosis. J Consult Psychol. 1961 Oct;25:440–444. doi: 10.1037/h0039473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins R. B., Groh R. H. Mental symptoms in Parkinsonian patients treated with L-dopa. Lancet. 1970 Jul 25;2(7665):177–179. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins R. B., Groh R. H. Psychic effects in patients treated with levodopa. JAMA. 1970 Jun 29;212(13):2265–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klawans H. L., Jr, Garvin J. S. Treatment of parkinsonism with L-dopa (study of 105 patients). Dis Nerv Syst. 1969 Nov;30(11):737–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh G. G., Markham C. M., Ansel R. Levodopa's awakening effect on patients with Parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Jun;34(3):209–218. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawdsley C. Treatment of Parkinsonism with Laevo-dopa. Br Med J. 1970 Feb 7;1(5692):331–337. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5692.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell F., Lee J. E., Swift T., Sweet R. D., Ogsbury J. S., Kessler J. T. Treatment of Parkinson's syndrome with L dihydroxyphenylalanine (levodopa). Ann Intern Med. 1970 Jan;72(1):29–35. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier M. J., French L. A. Changes in MMPI scale scores and an index of psychopathology following unilateral temporal lobectomy for epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1965 Sep;6(3):263–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1965.tb03794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SATZ P., MOGEL S. An abbreviation of the WAIS for clinical use. J Clin Psychol. 1962 Jan;18:77–79. doi: 10.1002/1097-4679(196201)18:1<77::aid-jclp2270180124>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAB R. S., ENGLAND A. C. Parkinson's disease. J Chronic Dis. 1958 Oct;8(4):488–509. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(58)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINES L. K., SILVER R. J. An index of psychopathology (Ip) derived from clinicians' judgments of MMPI profiles. J Clin Psychol. 1963 Jul;19:324–326. doi: 10.1002/1097-4679(196307)19:3<324::aid-jclp2270190323>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks O. W., Messeloff C., Schartz W., Goldfarb A., Kohl M. Effects of L-dopa in patients with dementia. Lancet. 1970 Jun 6;1(7658):1231–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91820-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias J. A., Merlis S. Levodopa and schizophrenia. JAMA. 1970 Mar 16;211(11):1857–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treciokas L. J., Ansel R. D., Markham C. H. One to two year treatment of Parkinson's disease with levodopa. Calif Med. 1971 May;114(5):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagshul A. M., Daroff R. B. Depression during L-dopa treatment. Lancet. 1969 Sep 13;2(7620):592–592. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton J. W. Depressive symptoms in Parkinson patients referred for thalamotomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Aug;30(4):368–370. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.4.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahr M. D., Duvoisin R. C., Hoehn M. M., Schear M. J., Barrett R. E. L-Dopa (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylanine)--its clinical effects in parkinsonism. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1968;93:56–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahr M. D., Duvoisin R. C., Schear M. J., Barrett R. E., Hoehn M. M. Treatment of parkinsonism with levodopa. Arch Neurol. 1969 Oct;21(4):343–354. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480160015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


