Abstract
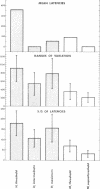
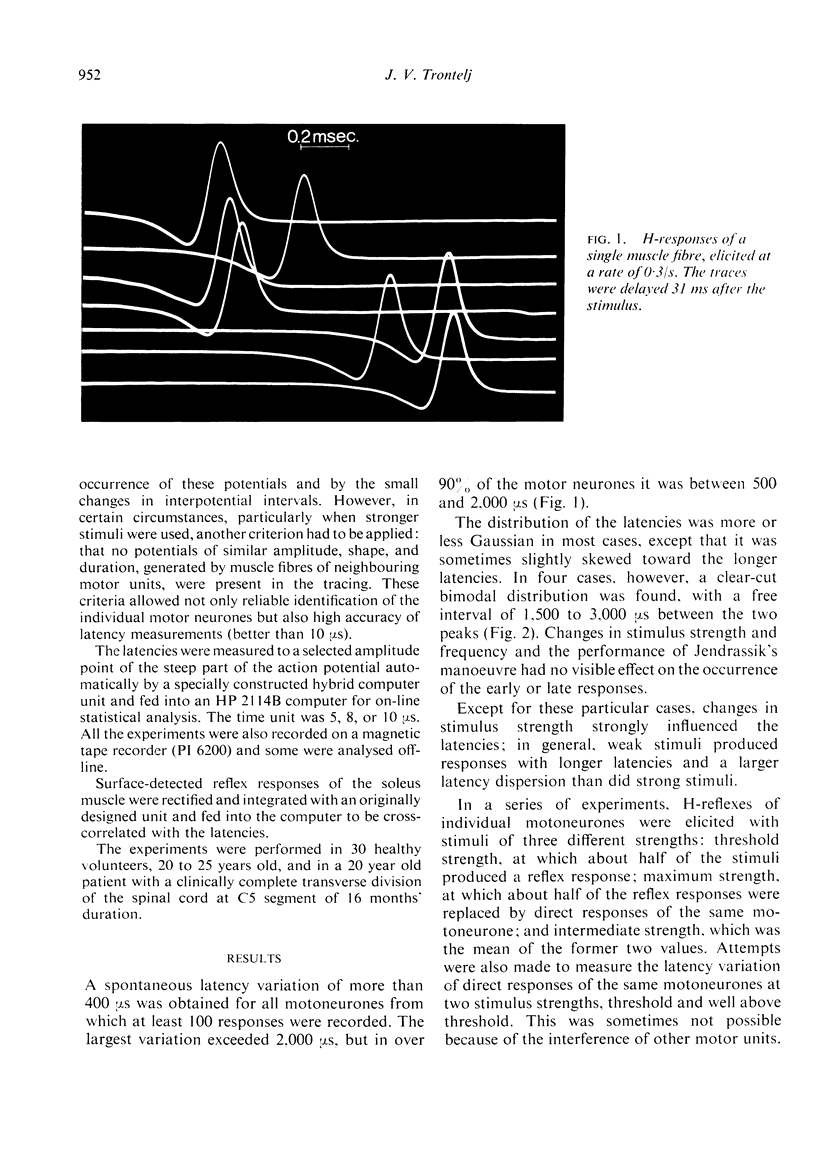
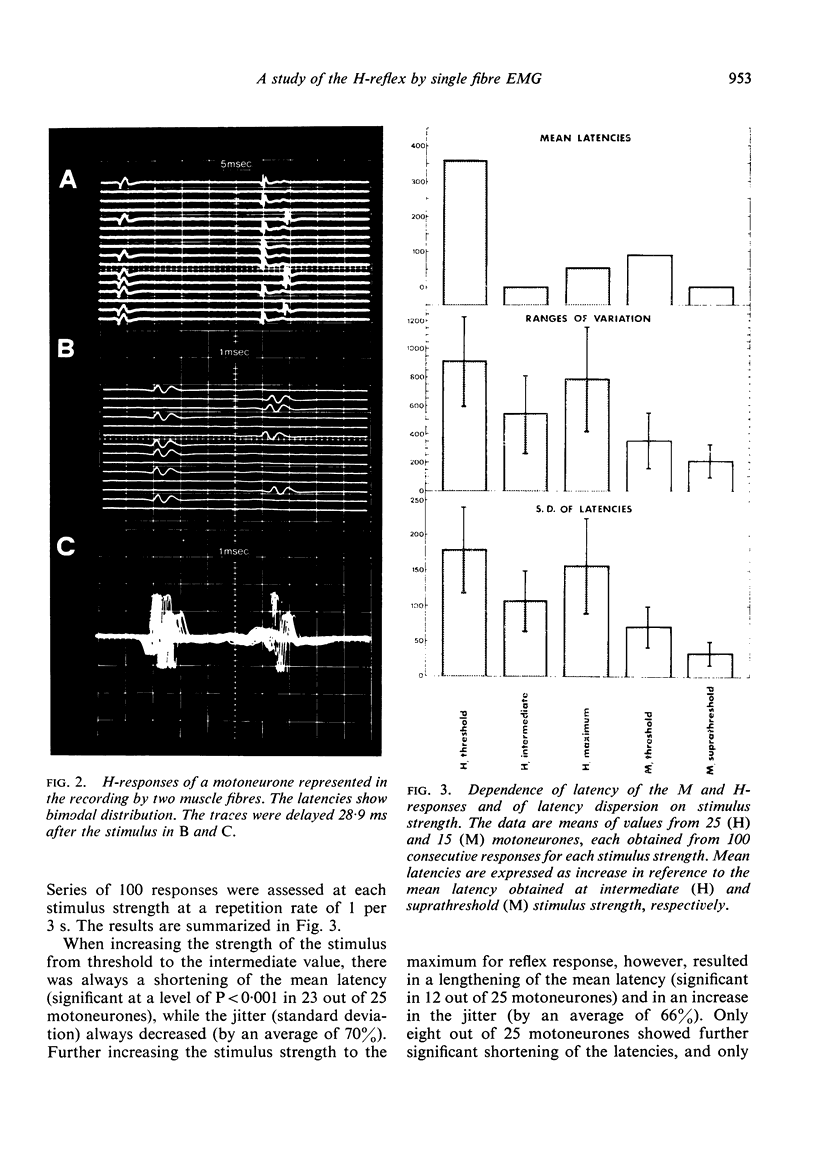
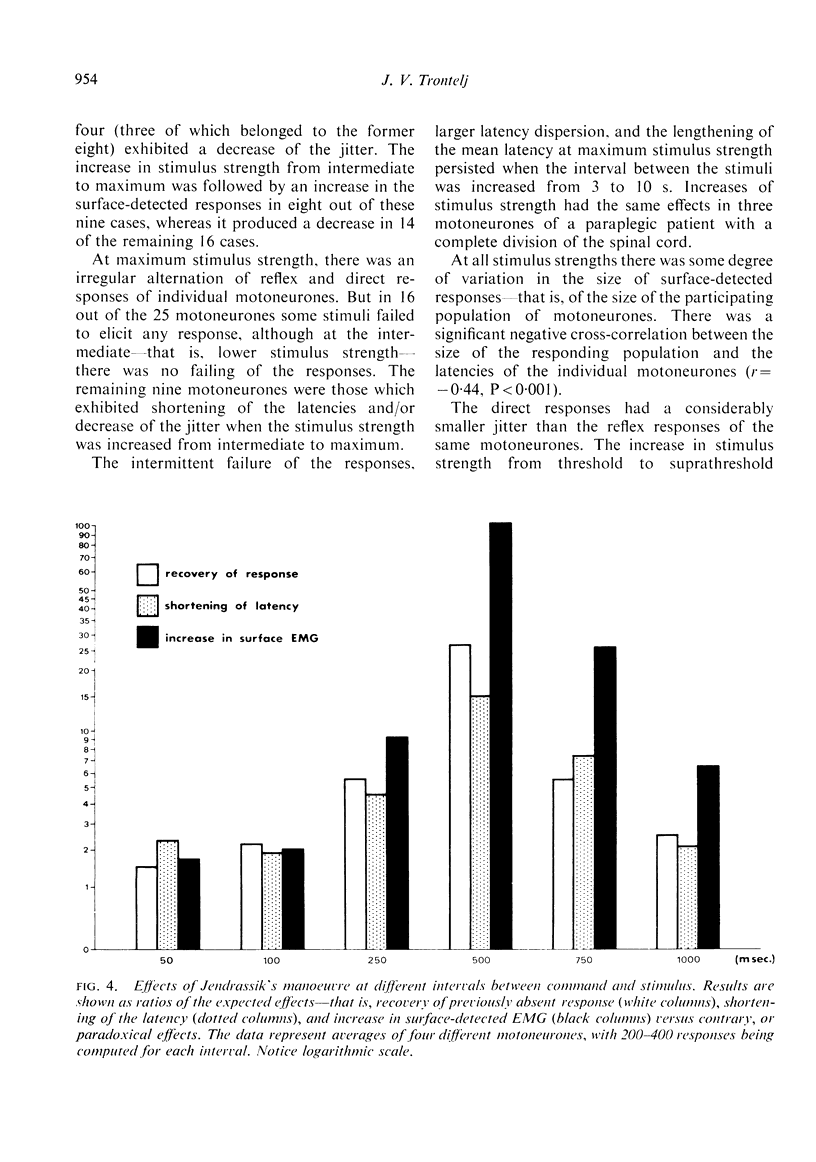
The latency of consecutive H-reflex responses of single human triceps surae motoneurones varies up to 2,500 μs. A large part of this variation was shown to occur at the synaptic transmission. A moderate increase in stimulus strength from the threshold value shortened the mean latency and reduced the latency variation, presumably as a result of spatial summation of excitatory inputs. Further increase to maximum strength lengthened the mean latency, increased the variation, and resulted in a dropping out of some responses which was not produced by collision by antidromic impulses. These effects are believed to be due to an active inhibition. Changes of the latency were also obtained by Jendrassik's manoeuvre and facilitatory and inhibitory conditioning stimuli.
Full text
PDF
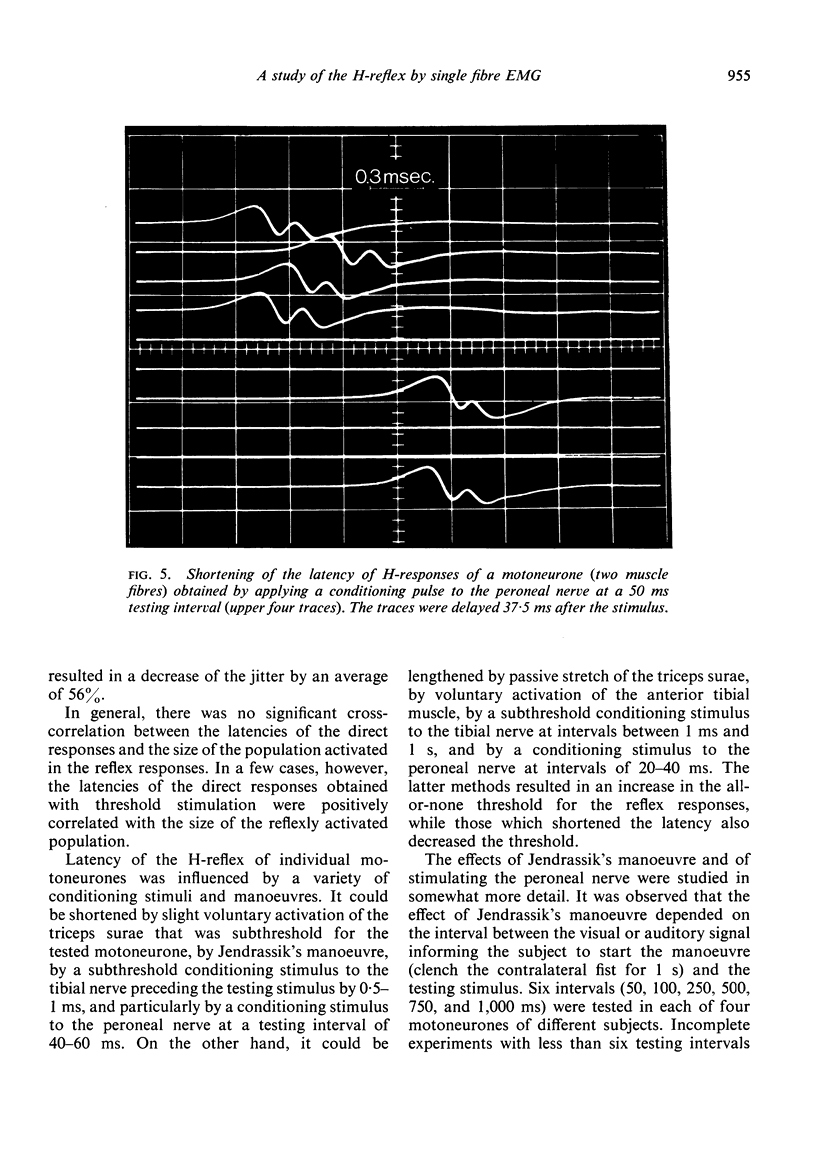
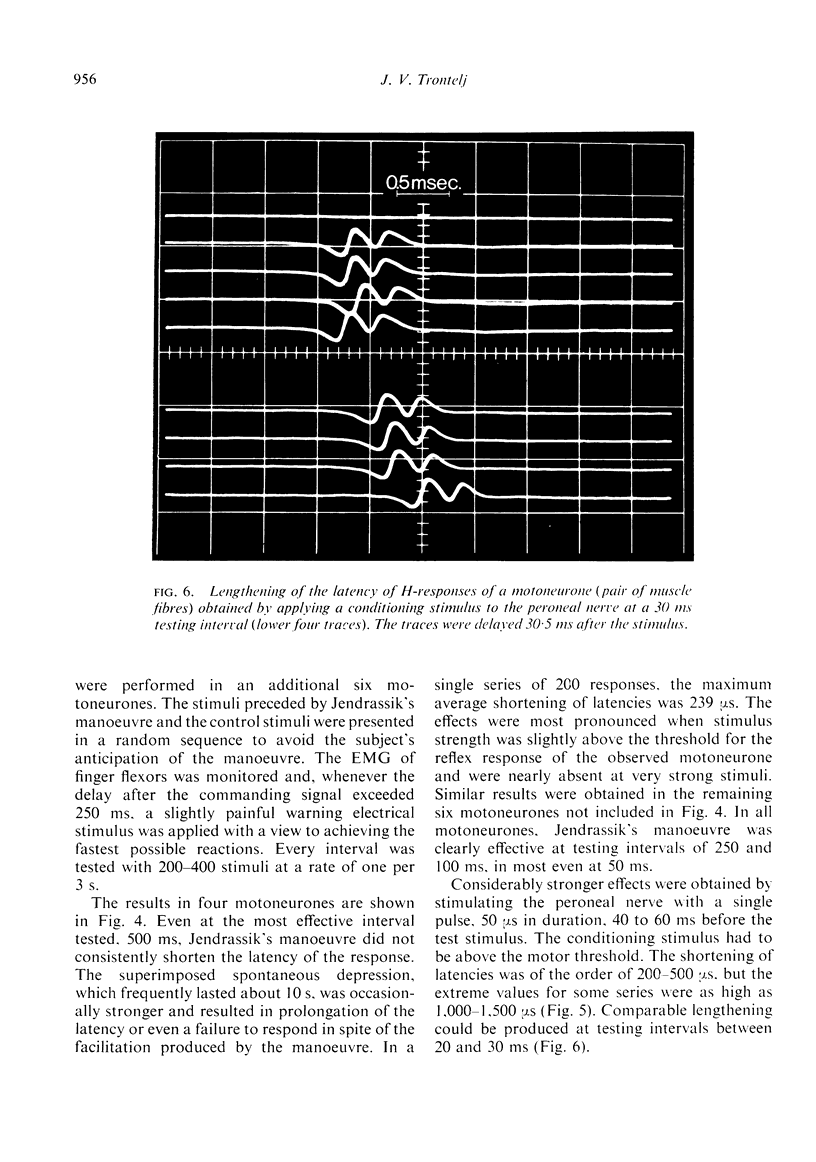



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASH R. W., KAY R. N. Stimulation and inhibition of reticulum contractions, rumination and parotid secretion from the forestomach of conscious sheep. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:43–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The generation of impulses in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Dec 3;139(2):232–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. Excitatory synaptic action in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):374–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., STARK L. Local responses in single medullated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1952 Oct;118(2):207–215. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamantopoulos E., Gassel M. M. Electrically induced monosynaptic reflexes in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1965 Dec;28(6):496–502. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.28.6.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones in relation to the two components of the group I muscle afferent volley. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):527–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C. The central action of antidromic impulses in motor nerve fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1955;260(5):385–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00363548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKSTEDT J. HUMAN SINGLE MUSCLE FIBER ACTION POTENTIALS. EXTRACELLULAR RECORDING DURING VOLUNTARY AND CHEMICAL ACTIVATION. WITH SOME COMMENTS ON END-PLATE PHYSIOLOGY AND ON THE FIBER ARRANGEMENT OF THE MOTOR UNIT. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1964:SUPPL 226–226:1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt J., Häggqvist P., Stålberg E. The construction of needle multi-electrodes for single fiber electromyography. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Nov;27(5):540–543. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt J., Stålberg E. The effect of non-paralytic doses of D-tubocurarine on individual motor end-plates in man, studied with a new electrophysiological method. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Dec;27(6):557–562. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. Monosynaptic reflex response of individual motoneurons as a function of frequency. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Jan 20;40(3):435–450. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., PORTER W. E., PARK A. M., TEASDALL R. D. Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. IV. The two-neurone reflex and identification of certain action potentials from spinal roots and cord. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1951 Jun;88(6):499–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK A. M., TEASDALL R. D., MAGLADERY J. W. Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. VII. Certain effects of brief stretch. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1951 Jun;88(6):549–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Ekstedt J., Broman A. The electromyographic jitter in normal human muscles. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1971 Nov;31(5):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(71)90164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Trontelj J. V. Demonstration of axon reflexes in human motor nerve fibres. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Oct;33(5):571–579. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.5.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj J. V. H-reflex of single motoneurons in man. Nature. 1968 Dec 7;220(5171):1043–1044. doi: 10.1038/2201043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj J. Latency variation of single human motoneurones in the H-reflex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Sep;27(7):723–723. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)91406-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholt W. C. Threshold and conduction velocity in human median nerve sensory fibers. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Sep;27(7):718–718. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)91391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]