Abstract
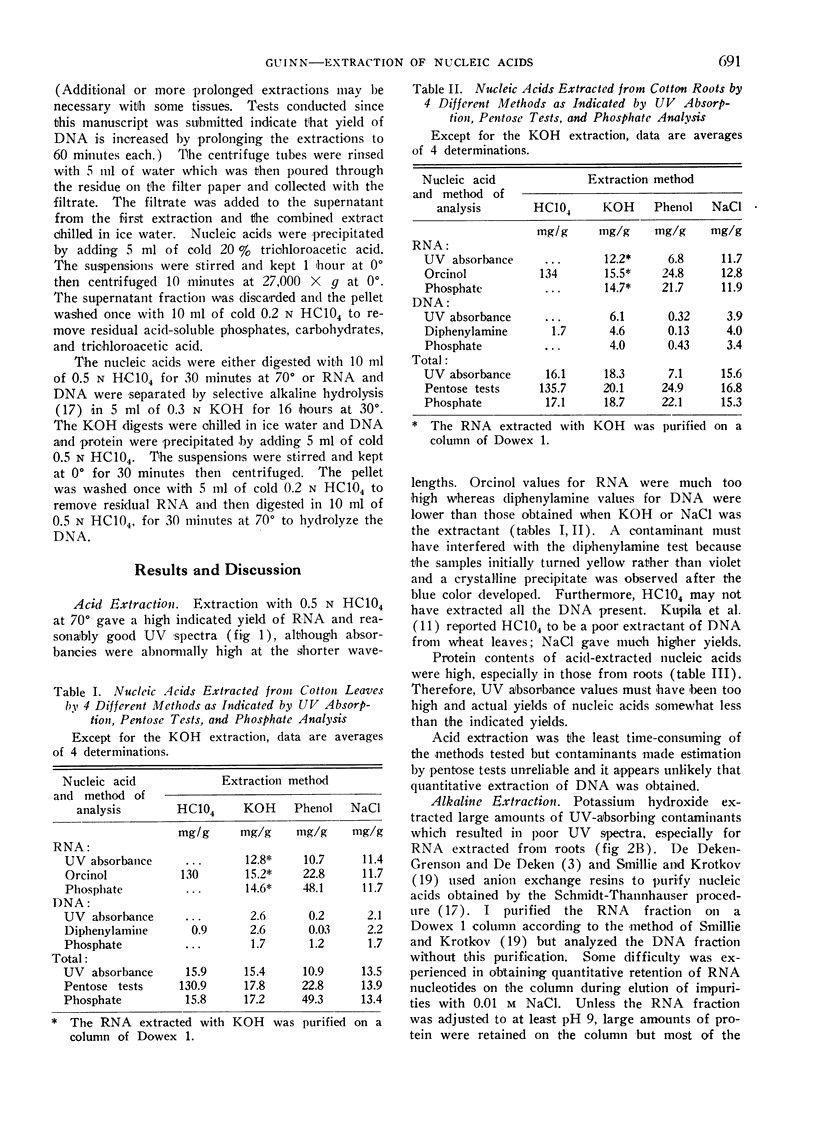
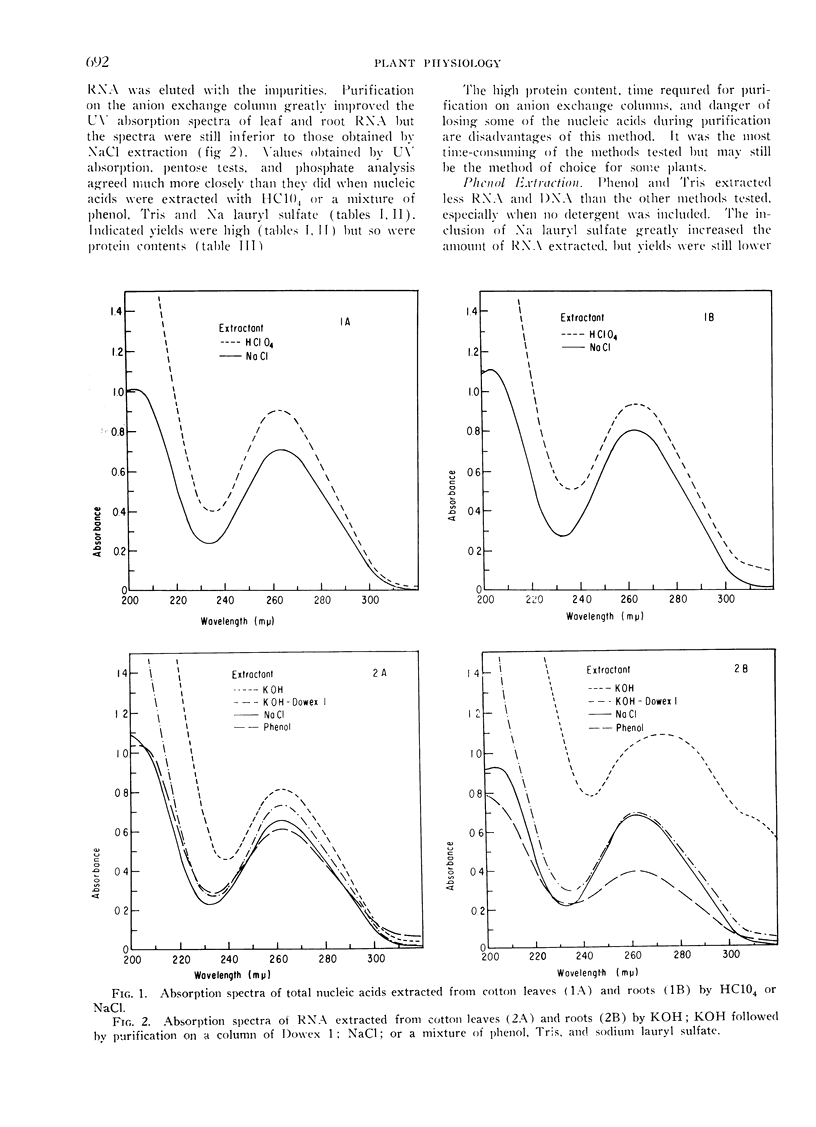
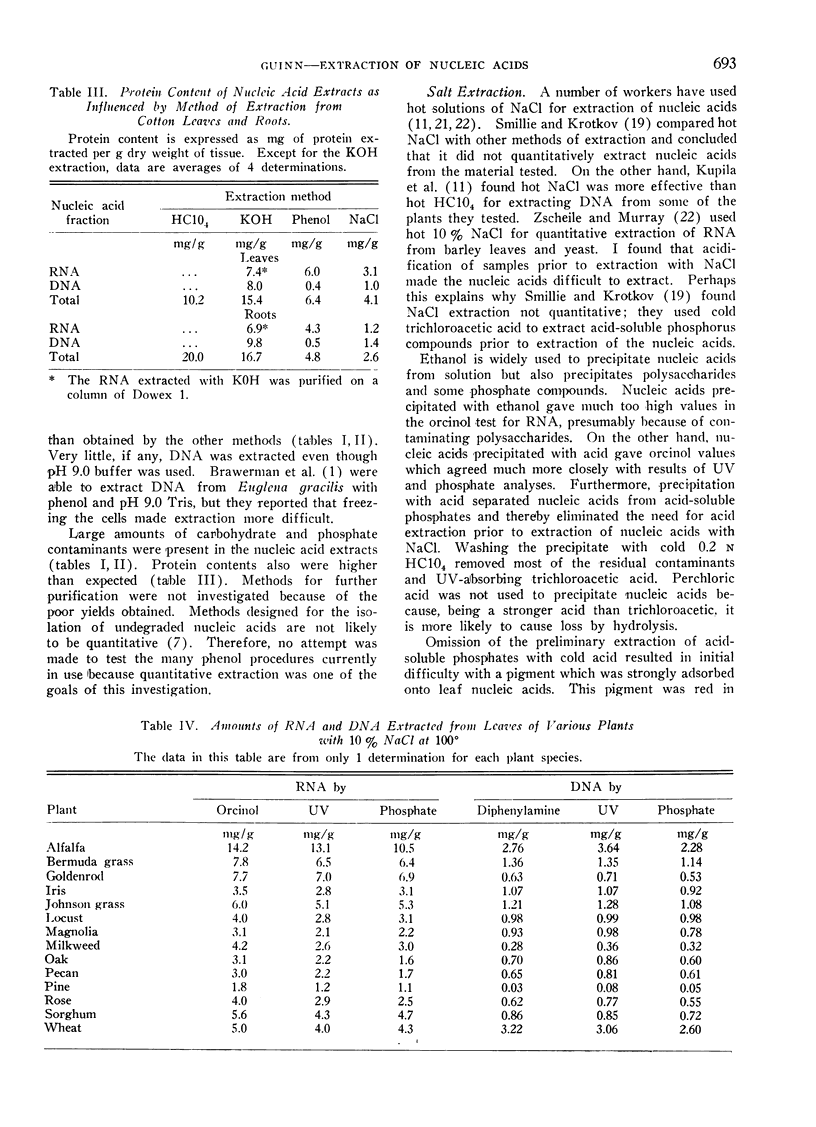
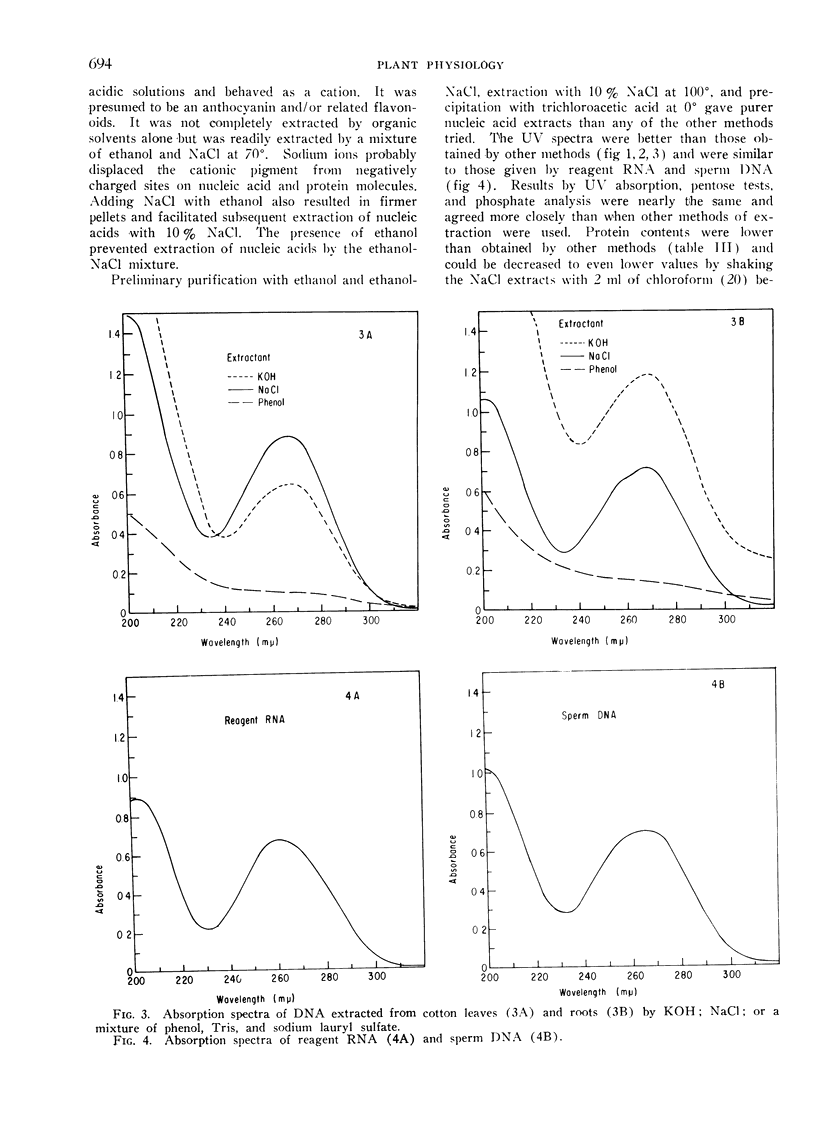
Four methods for extracting nucleic acids from lyophilized cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. cv. Stoneville 62) leaves and roots were compared. They were based on the use of: (I) HC104; (II) KOH; (III) a mixture of 90% phenol, Tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane buffer, and sodium lauryl sulfate; and (IV) NaCl. (I) extracted large amounts of RNA but little DNA and extracted much carbohydrate and protein contaminants. (II) gave a good yield of both RNA and DNA but extracted such large amounts of contaminating material that purification of RNA on an anion exchange column was necessary. (III) extracted only part of the RNA and practically no DNA, but extracted contaminating materials. (IV) resulted in high yields of both RNA and DNA when modified to omit preliminary acid extraction of impurities. The use of cold trichloroacetic acid instead of ethanol, to precipitate NaCl-extracted nucleic acids, separated the nucleic acids from most of the carbohydrate and acid-soluble phosphate contaminants and resulted in good agreement among results by ultraviolet absorbance, pentose tests, and phosphate analysis. This method also resulted in lower protein contents and better ultraviolet absorption spectra than the other methods tested. Nucleic acids were extracted from leaves of 14 other species of plants, in addition to cotton, by this modified NaCl procedure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAWERMAN G., HUFNAGEL D. A., CHARGAFF E. On the nucleic acids of green and colorless Euglena gracilis: isolation and composition of deoxyribonucleic acid and of transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Sep 17;61:340–345. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DEKEN-GRENSON M., DE DEKEN R. H. Elimination of substances interfering with nucleic acids estimation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jan;31(1):195–207. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ergle D. R., Katterman F. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid of cotton. Plant Physiol. 1961 Nov;36(6):811–815. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.6.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. A new method for the isolation of ribonucleic acids from mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1956 Nov;64(3):405–408. doi: 10.1042/bj0640405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. Ribonucleic acids. II. Improved preparation of rat-liver ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 2;55:545–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90988-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupila S., Bryan A. M., Stern H. Extractability of DNA & its determination in tissues of higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1961 Mar;36(2):212–215. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.2.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman R. H., Poulsen L. L. Spectrophotometric Estimation of Nucleic Acid of Plant Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1963 Jan;38(1):31–35. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGUR M., ROSEN G. The nucleic acids of plant tissues; the extraction and estimation of desoxypentose nucleic acid and pentose nucleic acid. Arch Biochem. 1950 Feb;25(2):262–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS A. J., SHERRATT H. S. The isolation of nucleic acid fractions from plant leaves and their purine and pyrimidine composition. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):1–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zscheile F. P., Murray H. C. A Chromatographic-Spectrophotometric Method for Determining Nucleotide Composition of RNA in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1963 Mar;38(2):133–138. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


