Abstract
Extracts of pea seedlings (Pisum sativum, variety Alaska) oxidize indole-3-acetic acid to a bacteriostatic compound which has been identified as 3-hydroxymethyloxindole. At physiological pH this compound is readily dehydrated to 3-methyleneoxindole, another bacteriostatic agent. The extracts of pea seedlings also contain a reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide-linked enzyme which reduces 3-methyleneoxindole to 3-methyloxindole, a non-toxic compound.
These enzymatic reactions also take place in intact seedlings; thus, a pathway of indole-3-acetic acid degradation via oxindoles appears to be pertinent to plant metabolism.
The significance of such metabolism lies in the fact that a key intermediate of this pathway, 3-methyleneoxindole, is a sulfhydryl reagent capable of profound effects on metabolism and growth.
Full text
PDF


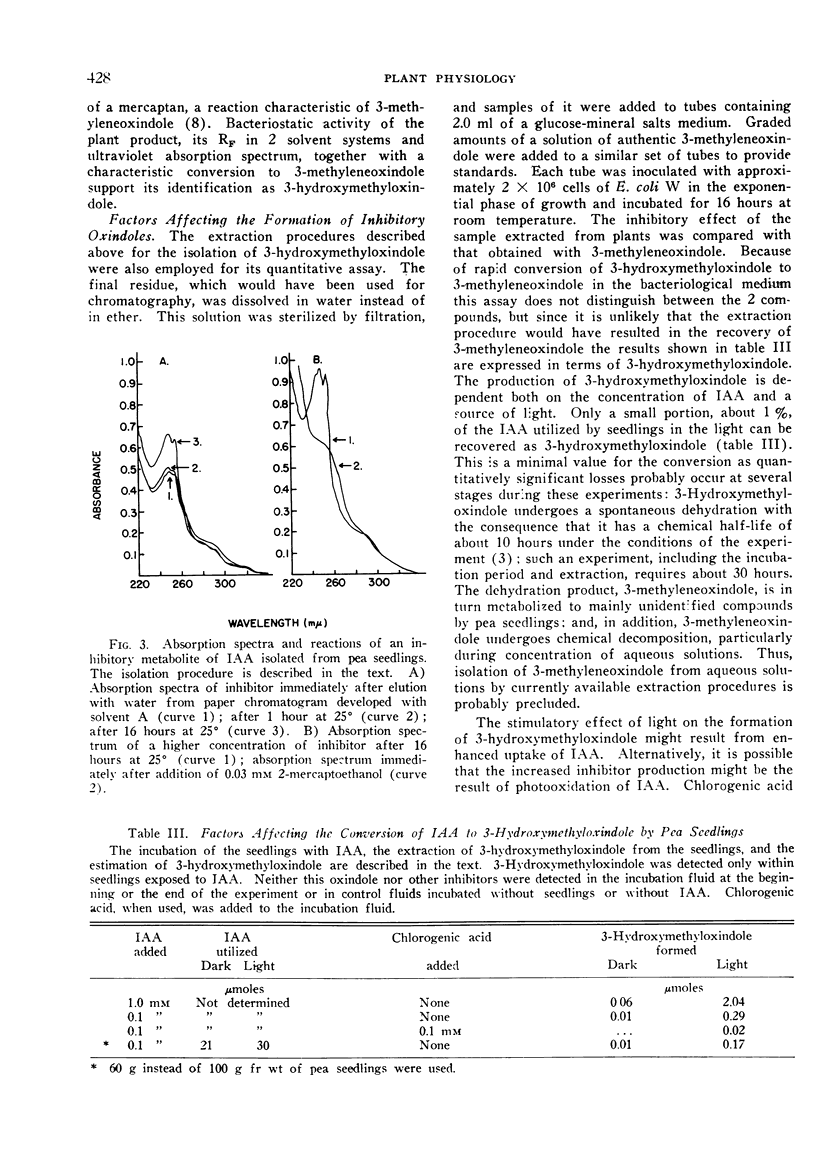
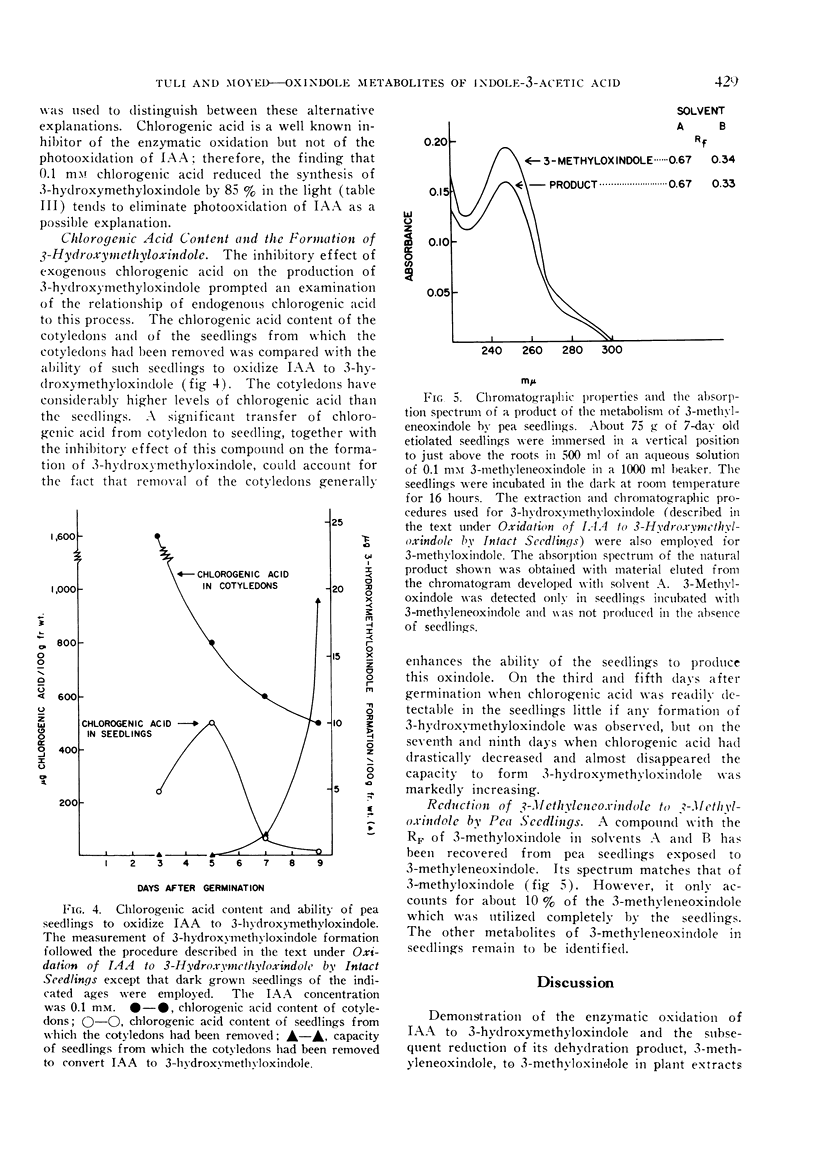

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMOVITCH R. A., AHMED K. S. Oxidative decarboxylation of indole-3-acetic acid by mangani-versene and by wheat leaf enzyme. Nature. 1961 Oct 21;192:259–260. doi: 10.1038/192259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dear J., Aronoff S. Relative Kinetics of Chlorogenic and Caffeic Acids During the Onset of Boron Deficiency in Sunflower. Plant Physiol. 1965 May;40(3):458–459. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.3.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUYAMA T. T., MOYED H. S. INHIBITION OF CELL GROWTH BY PHOTOOXIDATION PRODUCTS OF INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2392–2397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALSTON A. W. Riboflavin, light, and the growth of plants. Science. 1950 Jun 9;111(2893):619–624. doi: 10.1126/science.111.2893.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINMAN R. L., LANG J. PEROXIDASE-CATALYZED OXIDATION OF INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1965 Jan;4:144–158. doi: 10.1021/bi00877a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY P. M., CURRY G. M. Intermediates and competing reactions in the photodestruction of indoleacetic acid. Nature. 1958 Mar 29;181(4613):895–896. doi: 10.1038/181895a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILL C. C., FUKUYAMA T. T., MOYED H. S. INHIBITORY OXIDATION PRODUCTS OF INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID. MECHANISM OF ACTION AND ROUTE OF DETOXIFICATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2612–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuli V., Moyed H. S. Desensitization of regulatory enzymes by a metabolite of plant auxin. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4564–4566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


